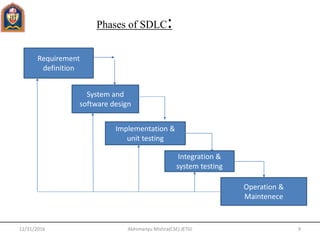
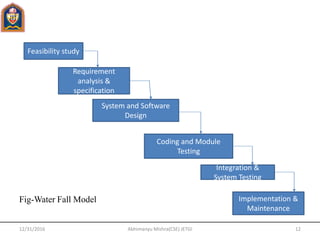
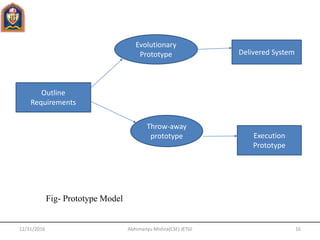
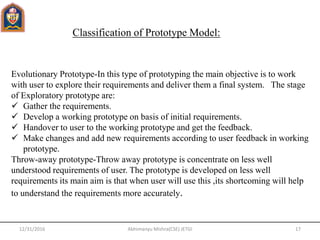
This document provides an overview of software engineering concepts including the definition of software engineering, software components, characteristics of software, the software crisis, software quality attributes, and software development life cycle (SDLC) models. It discusses several SDLC models - waterfall model, prototype model, spiral model, evolutionary development model - outlining their phases and advantages/disadvantages.