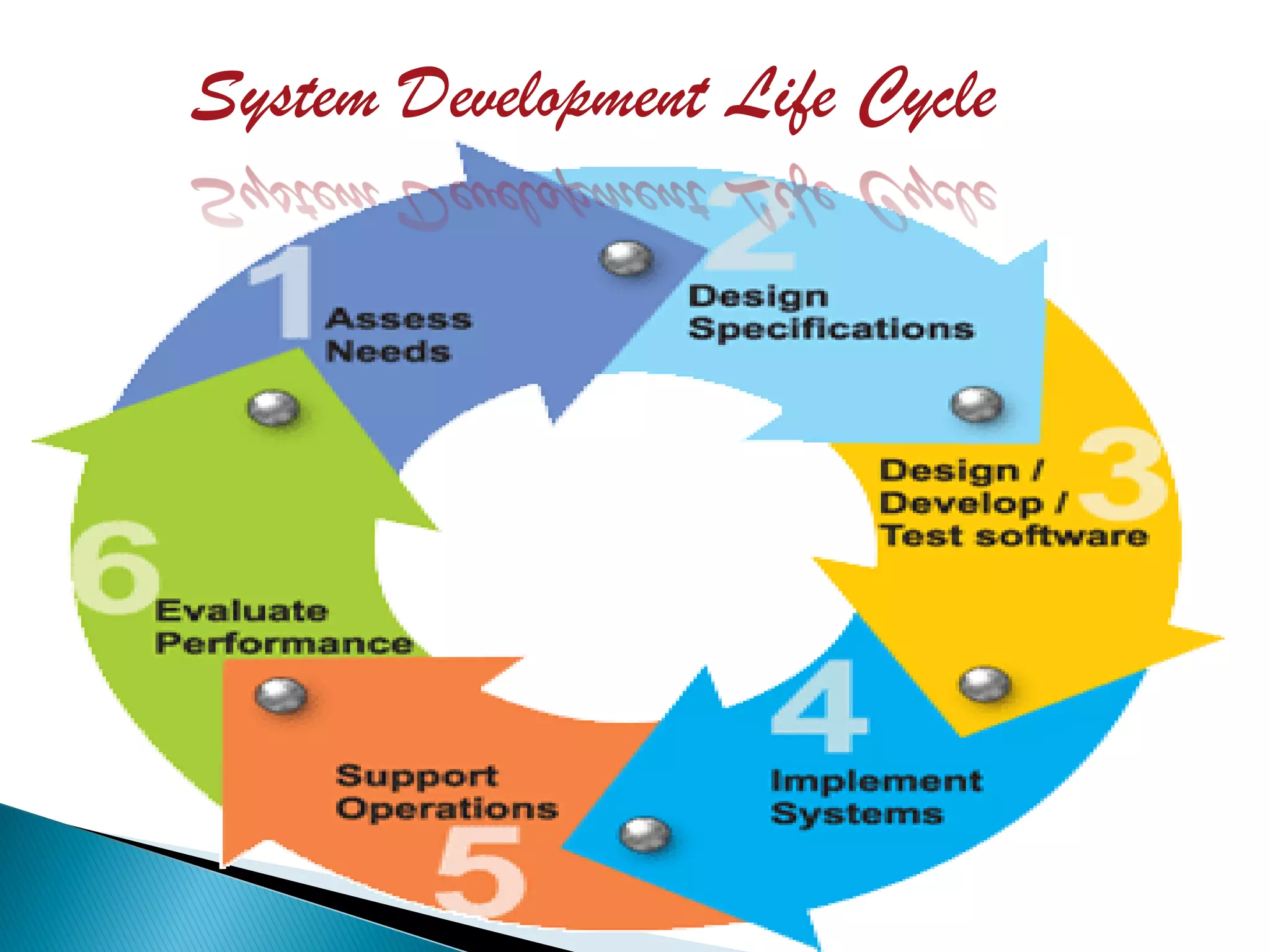
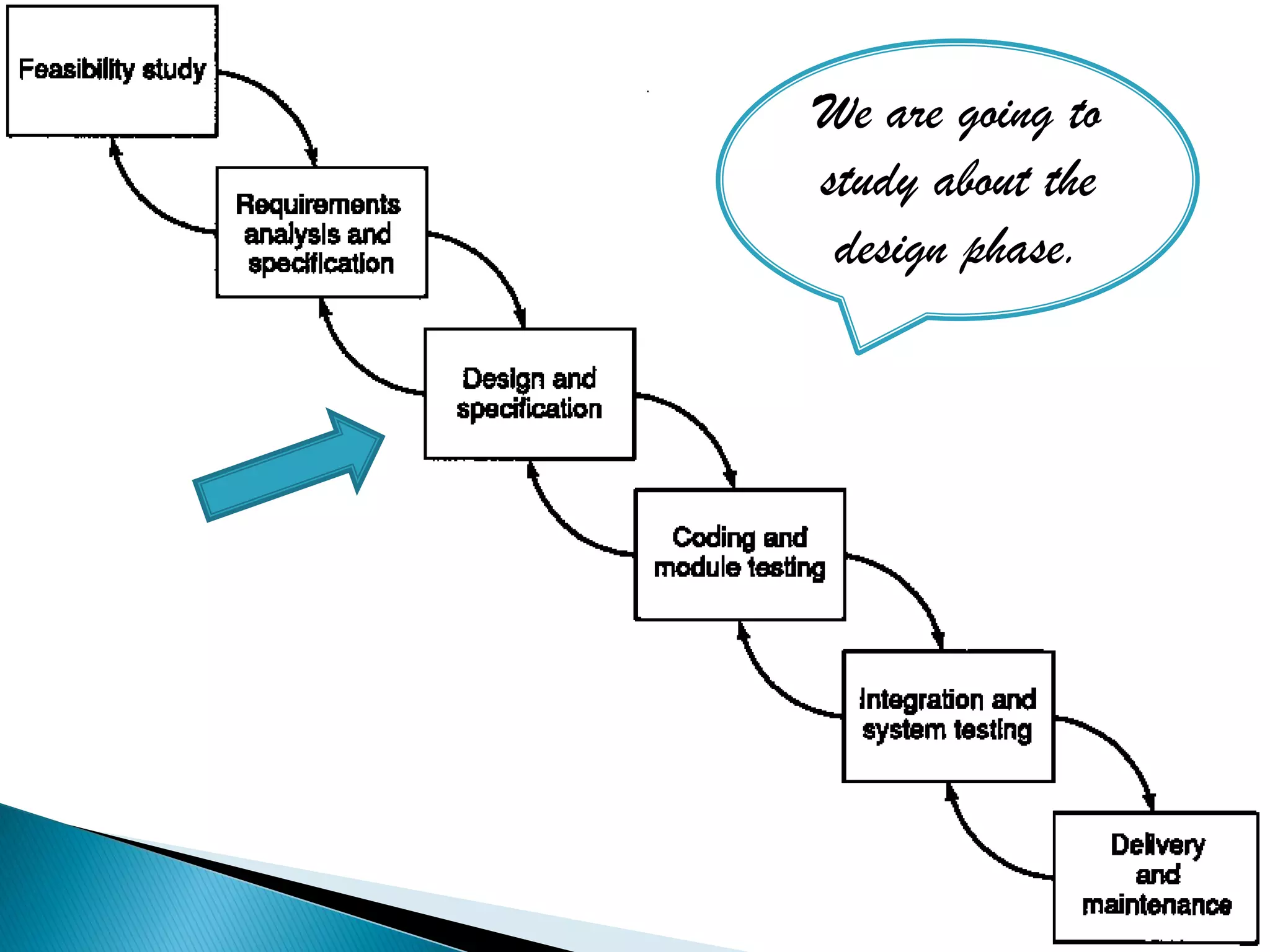
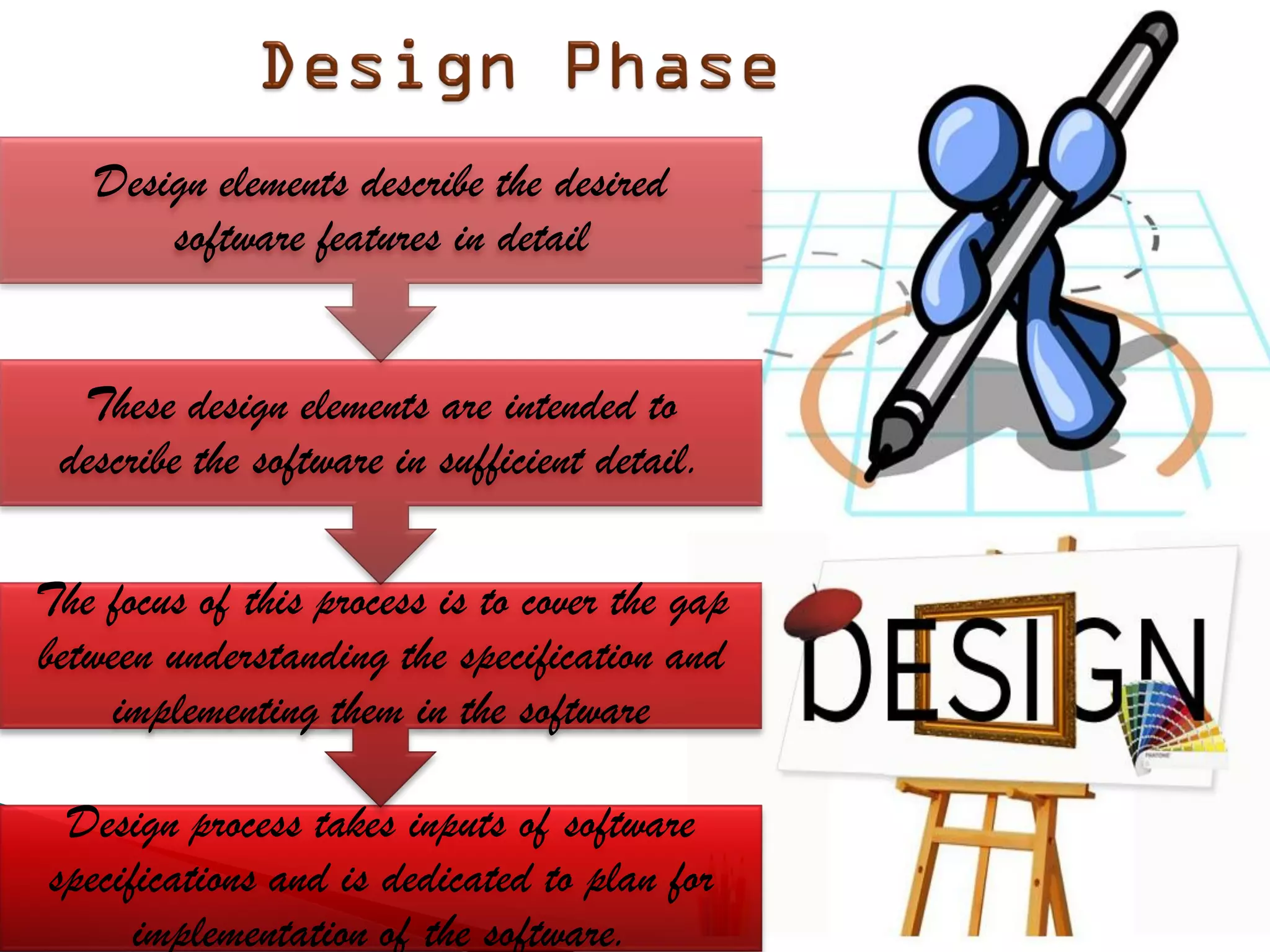
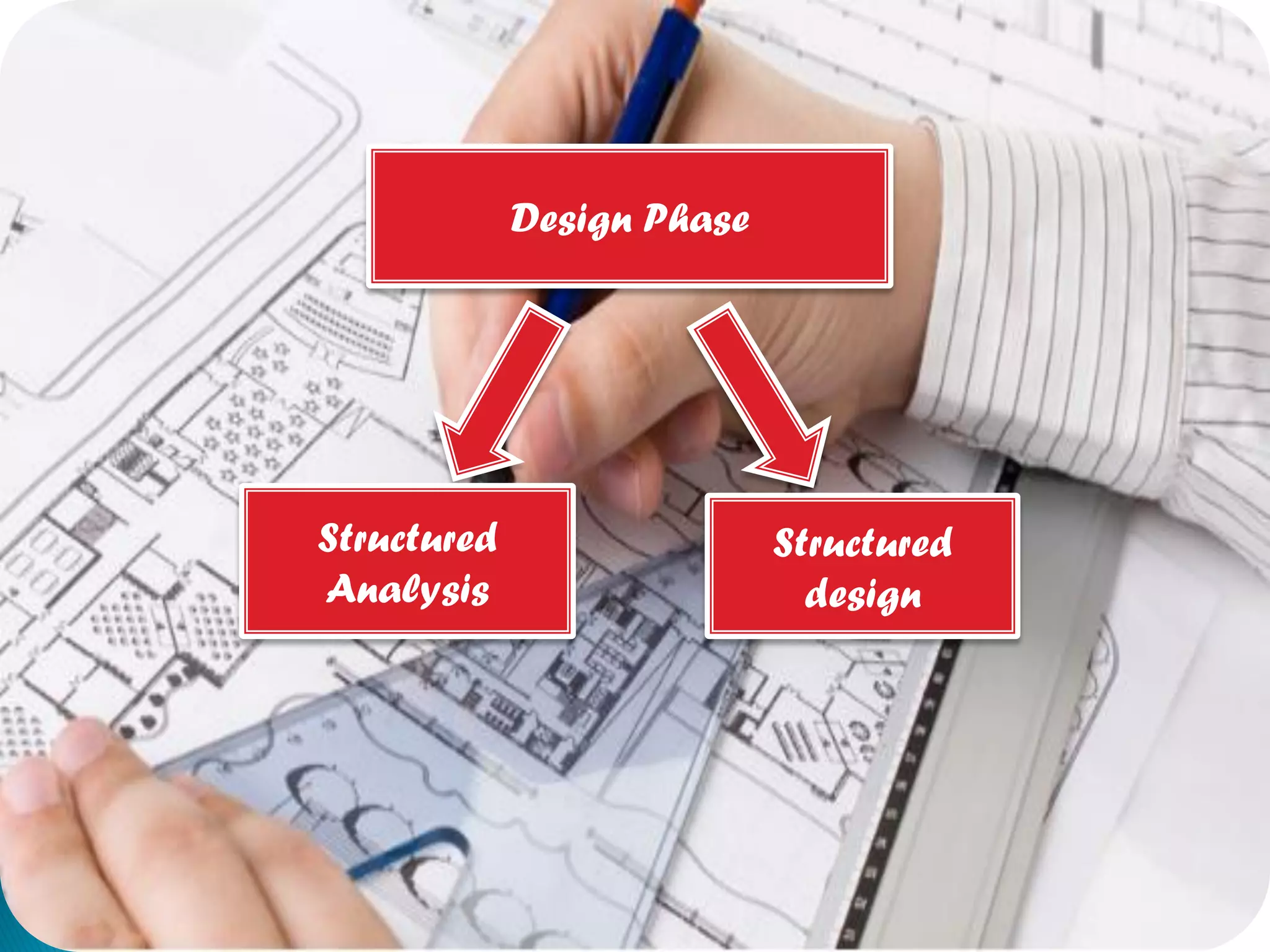
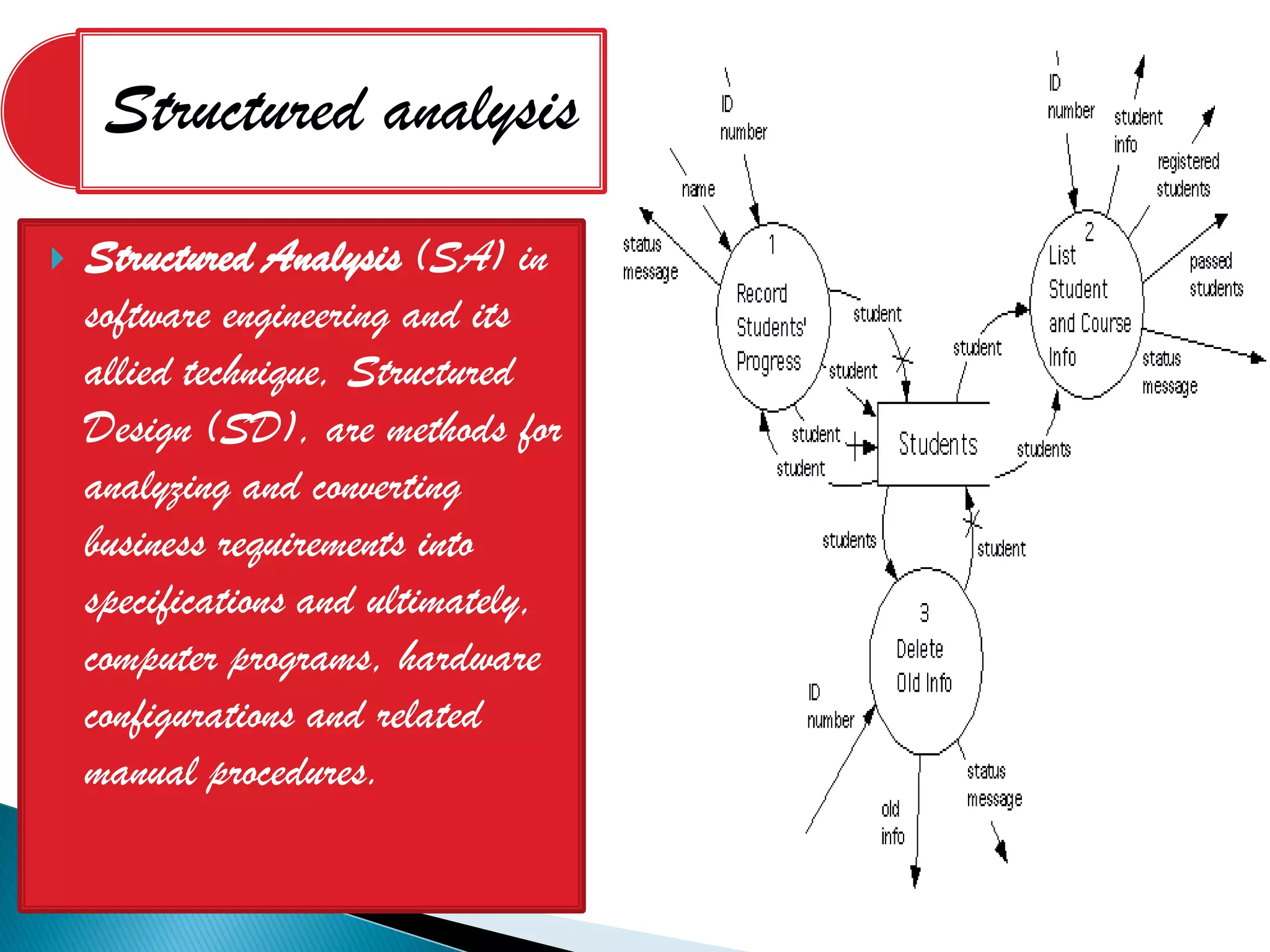
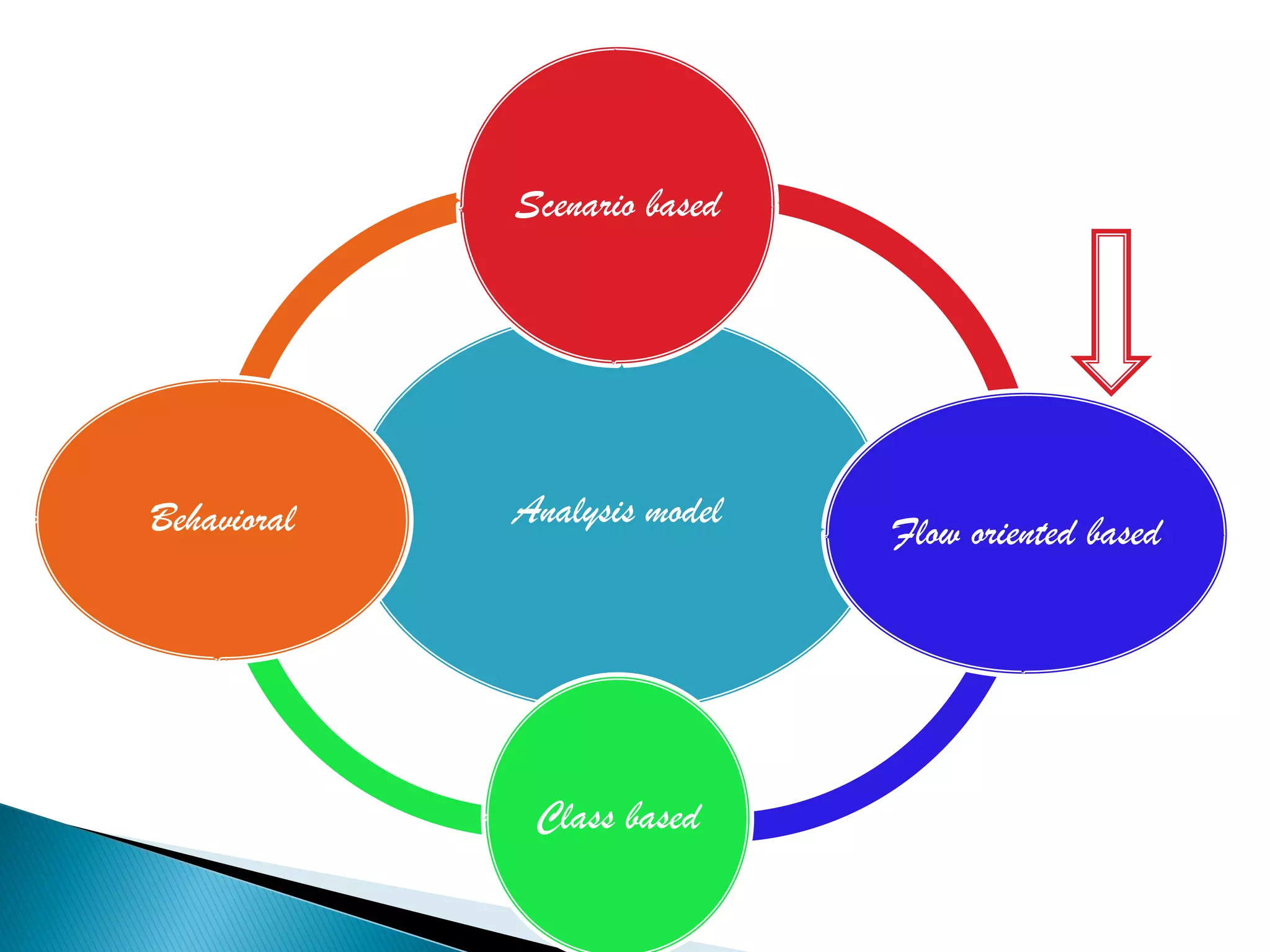
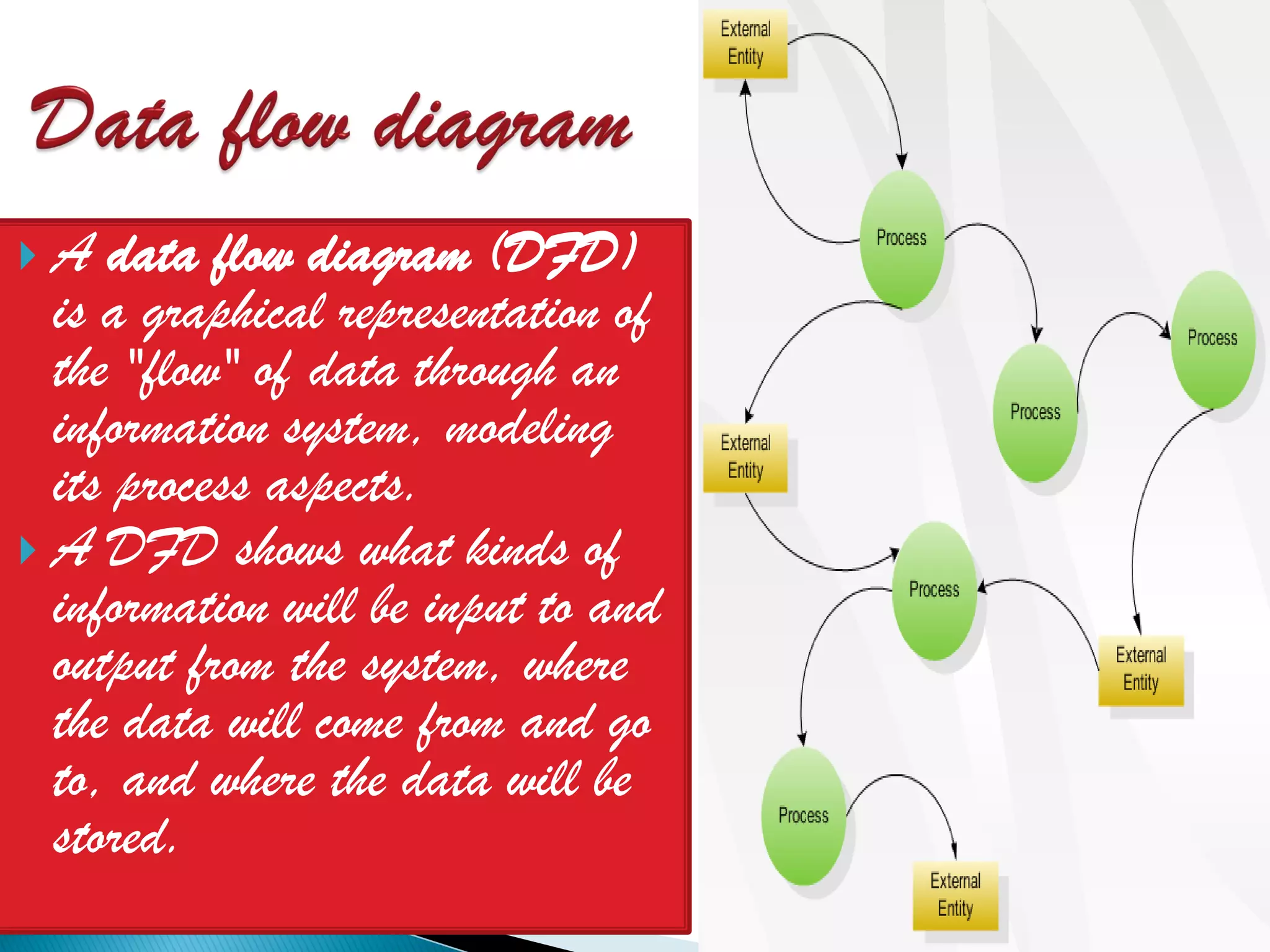
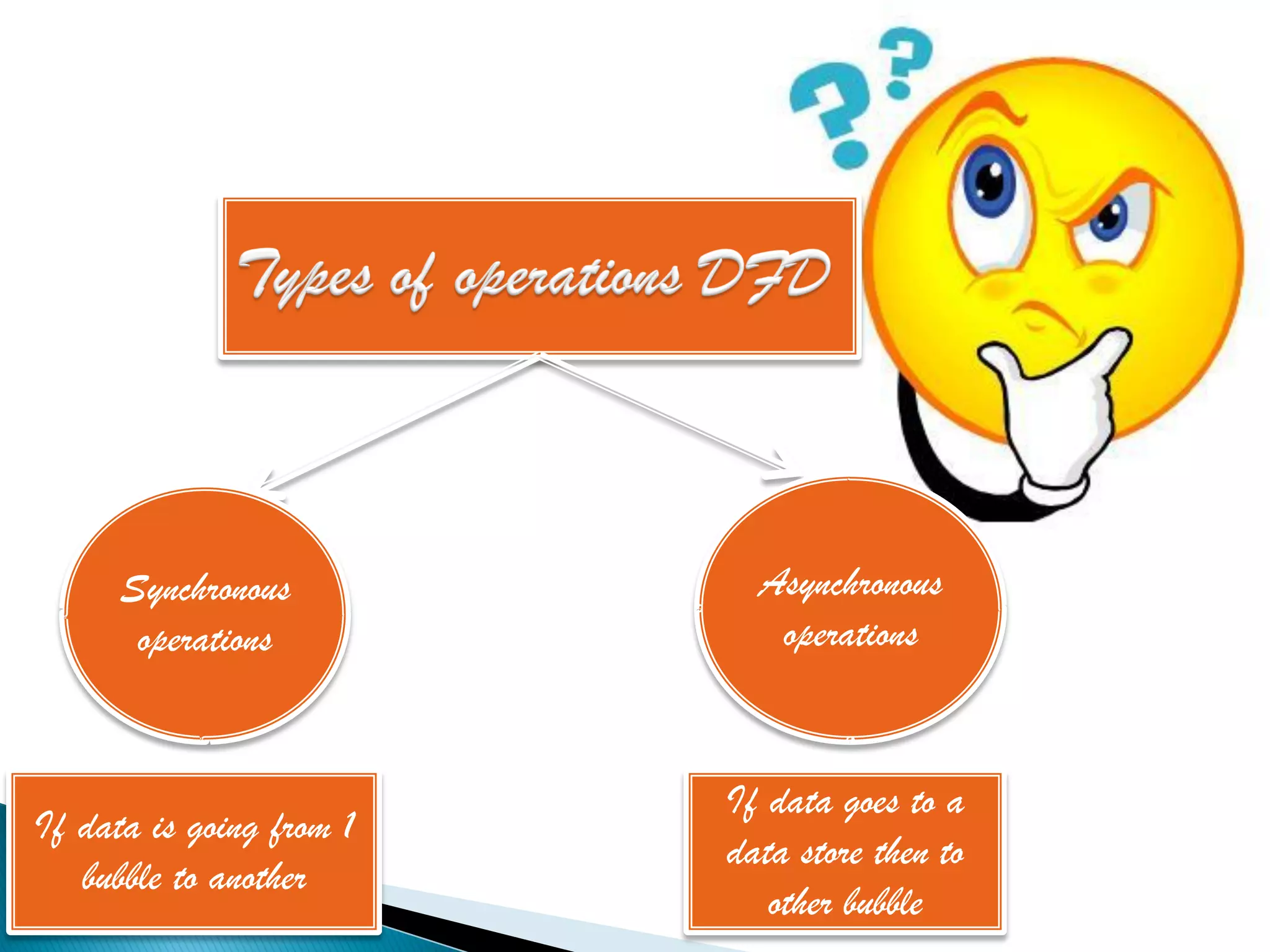
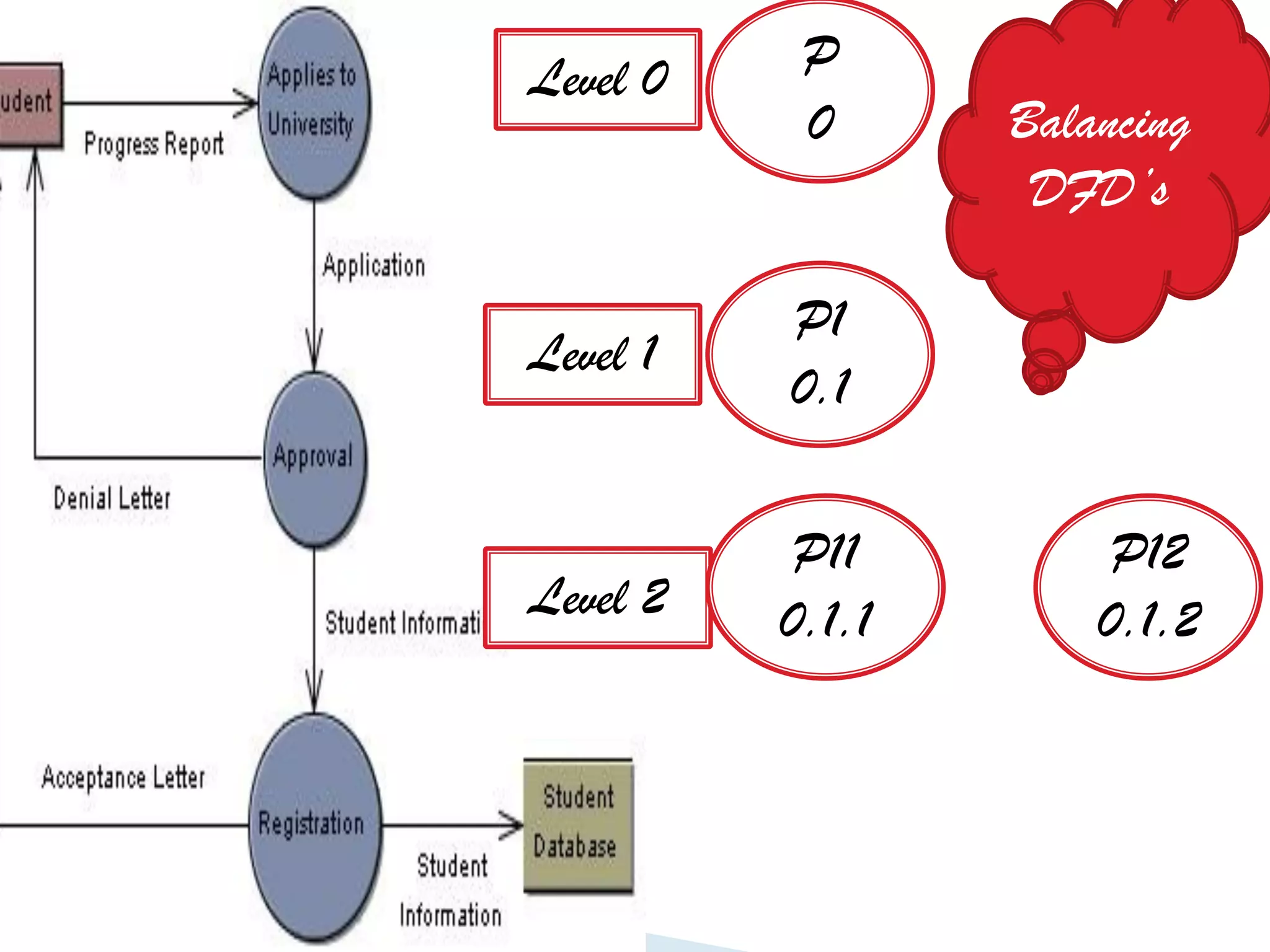
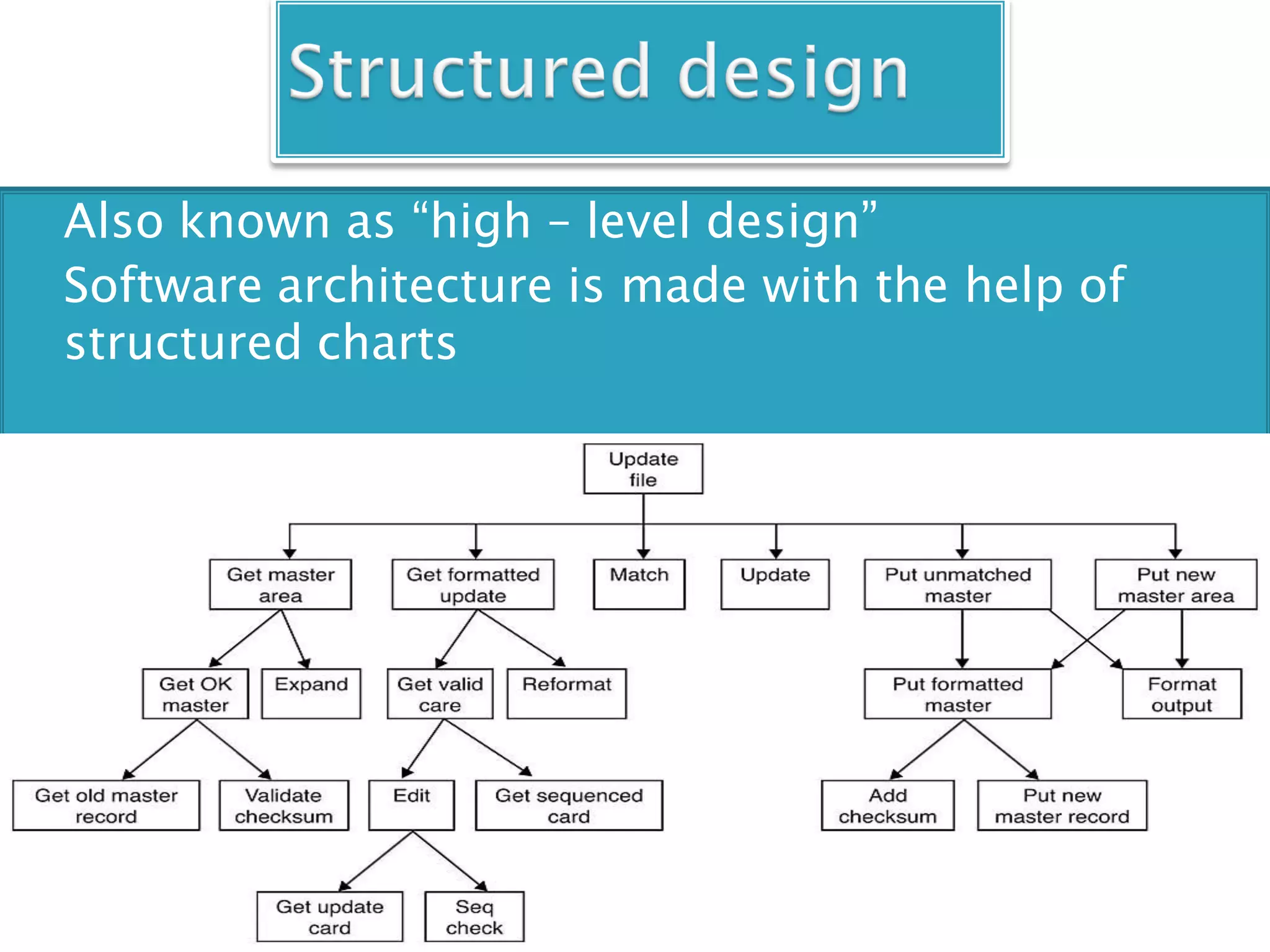
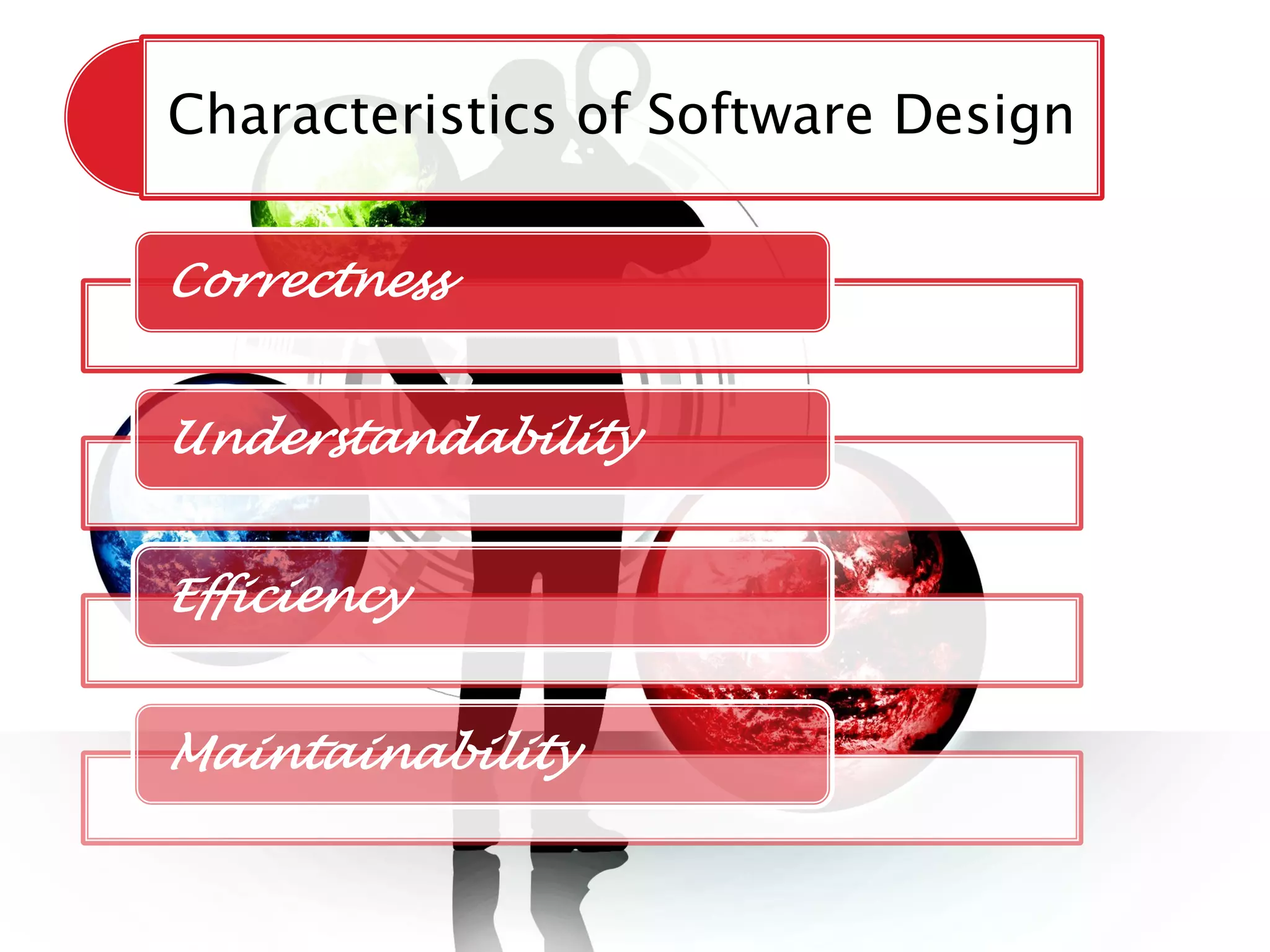
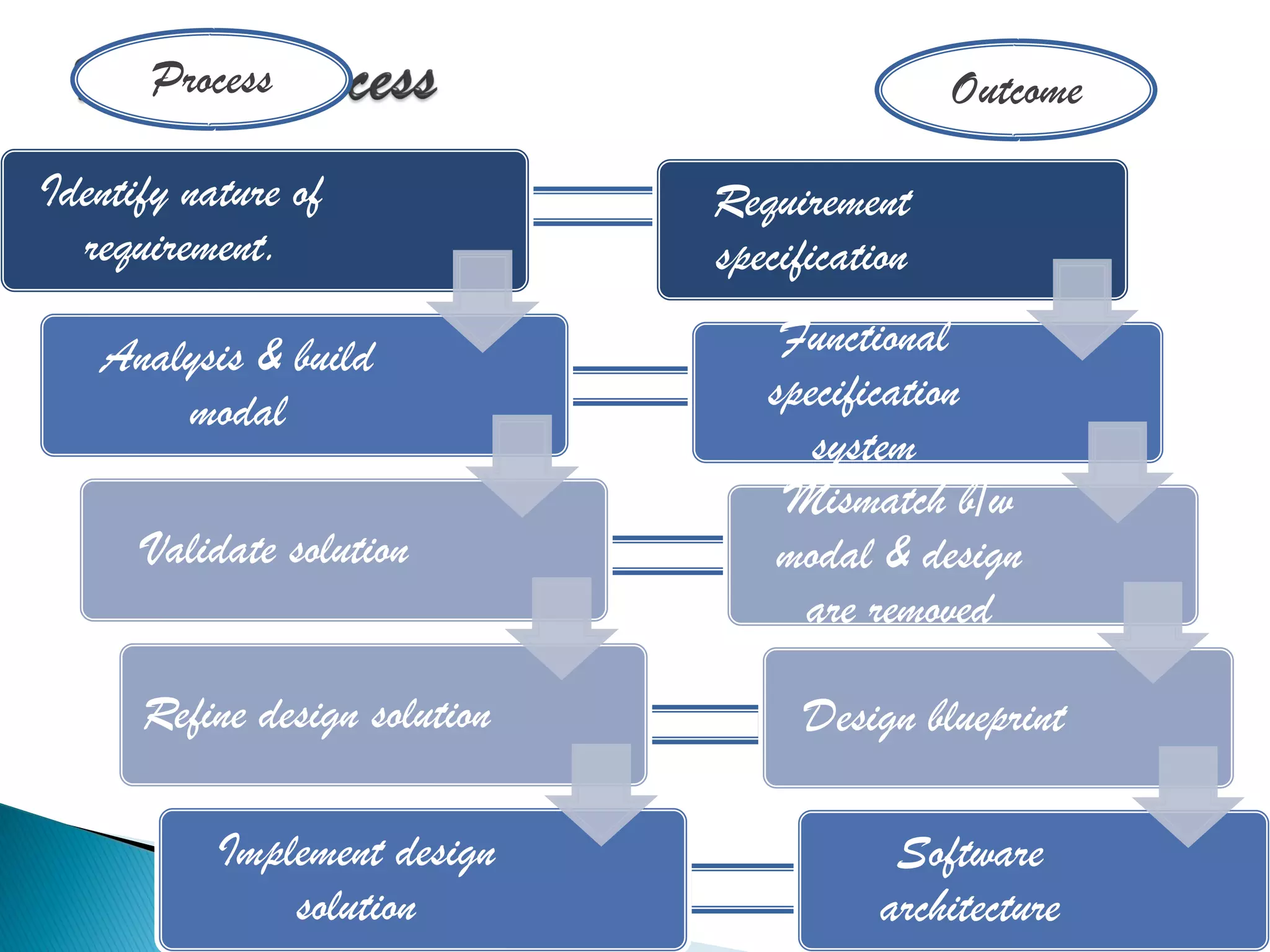
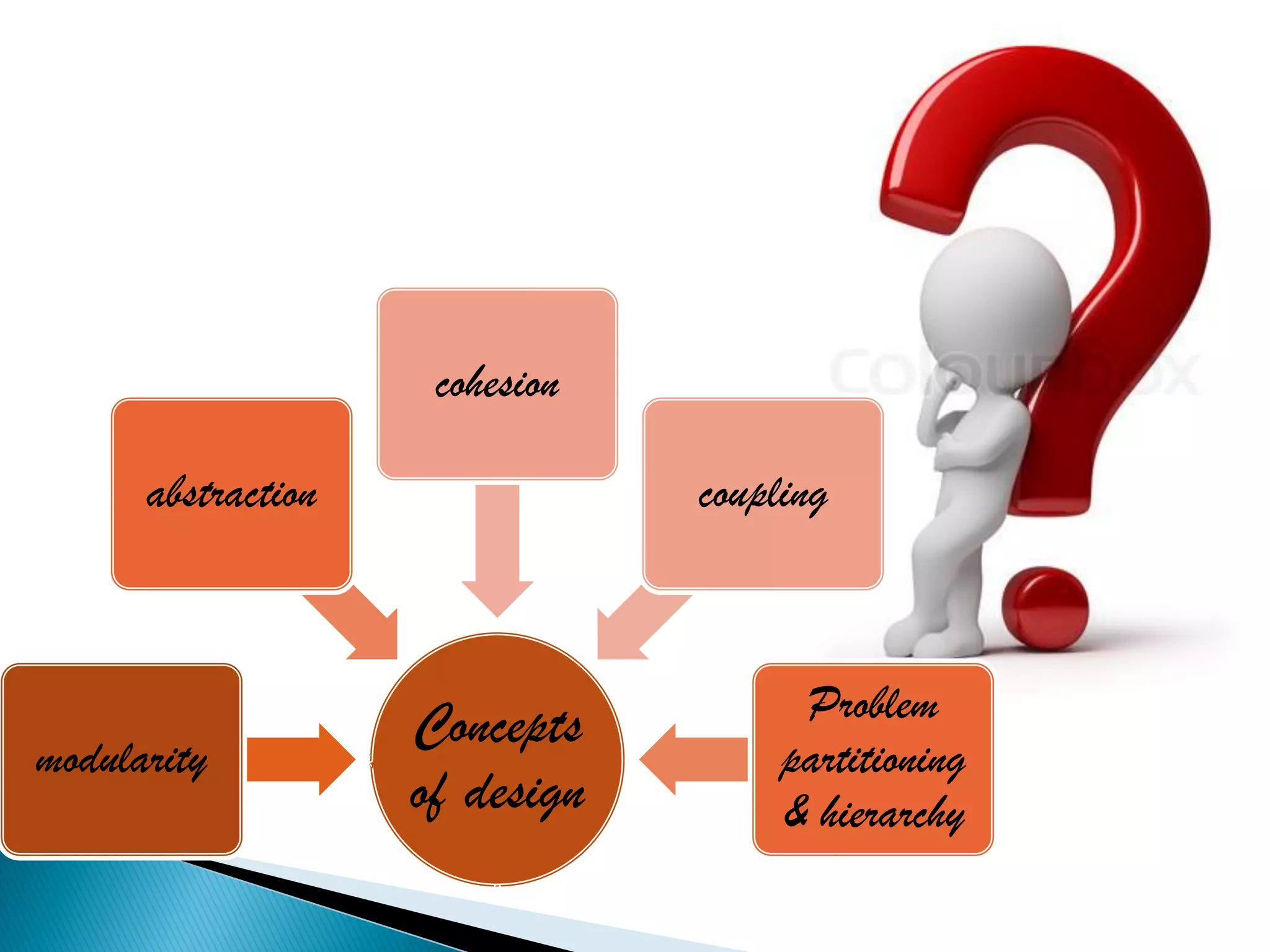
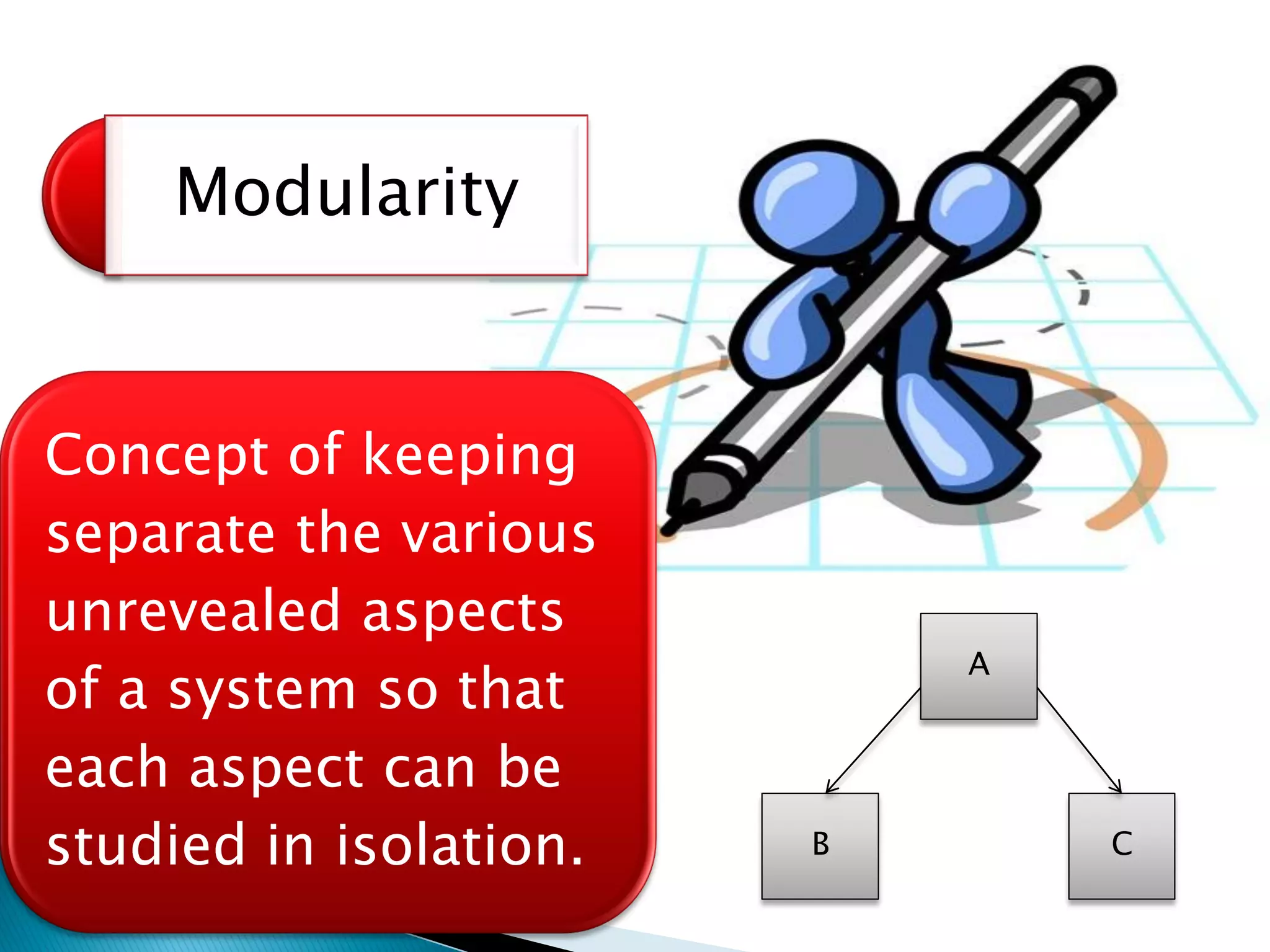
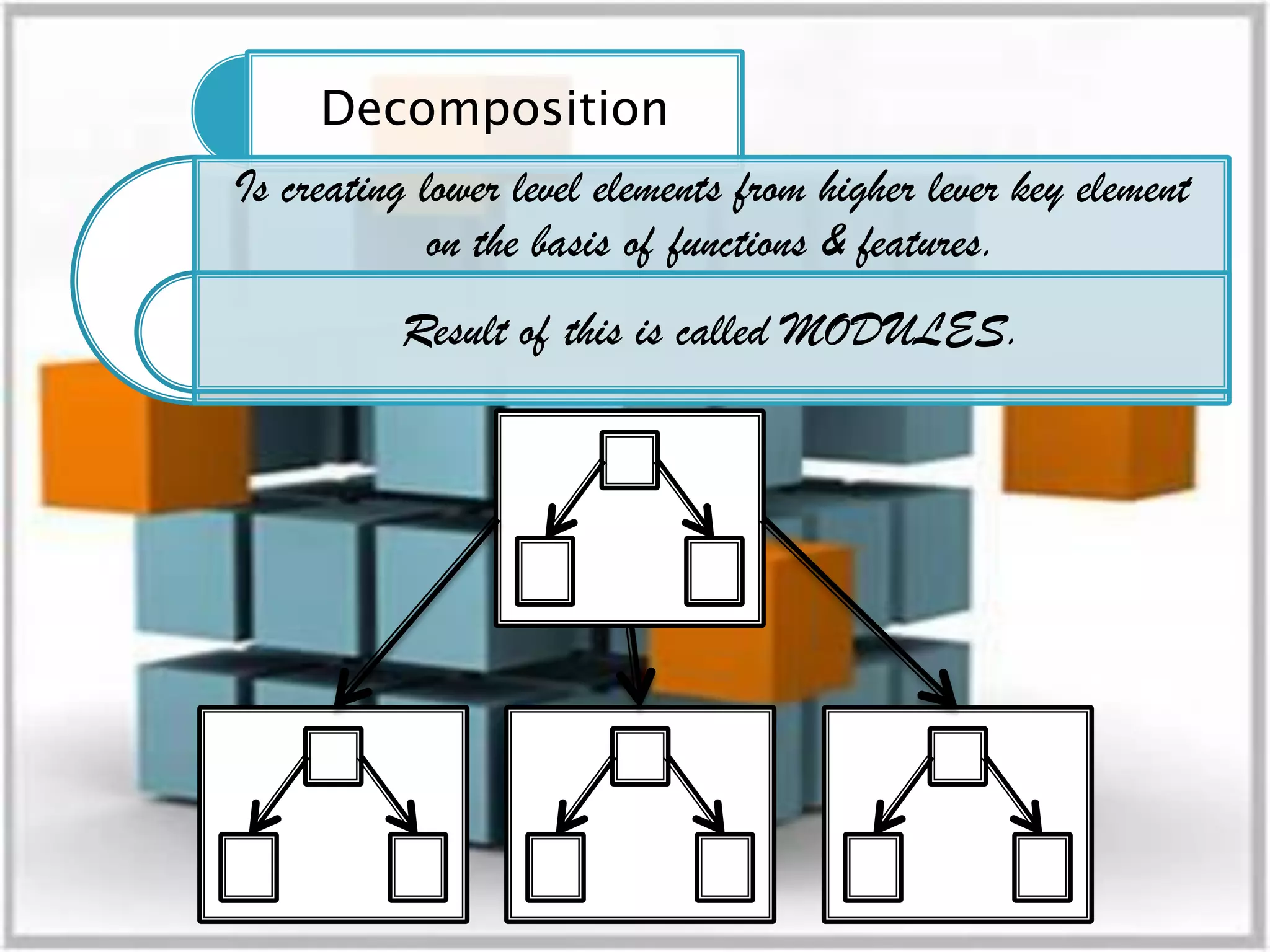
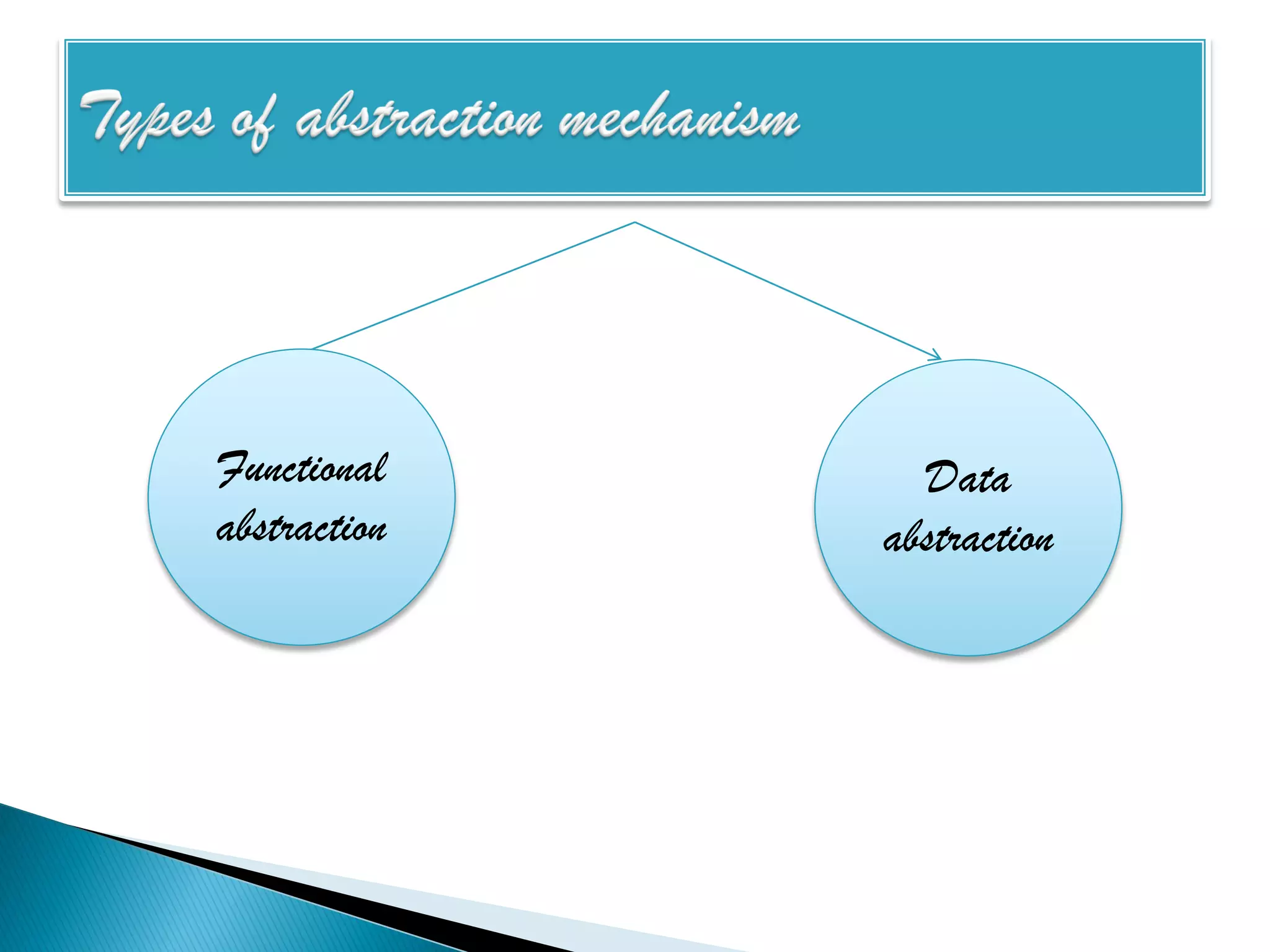
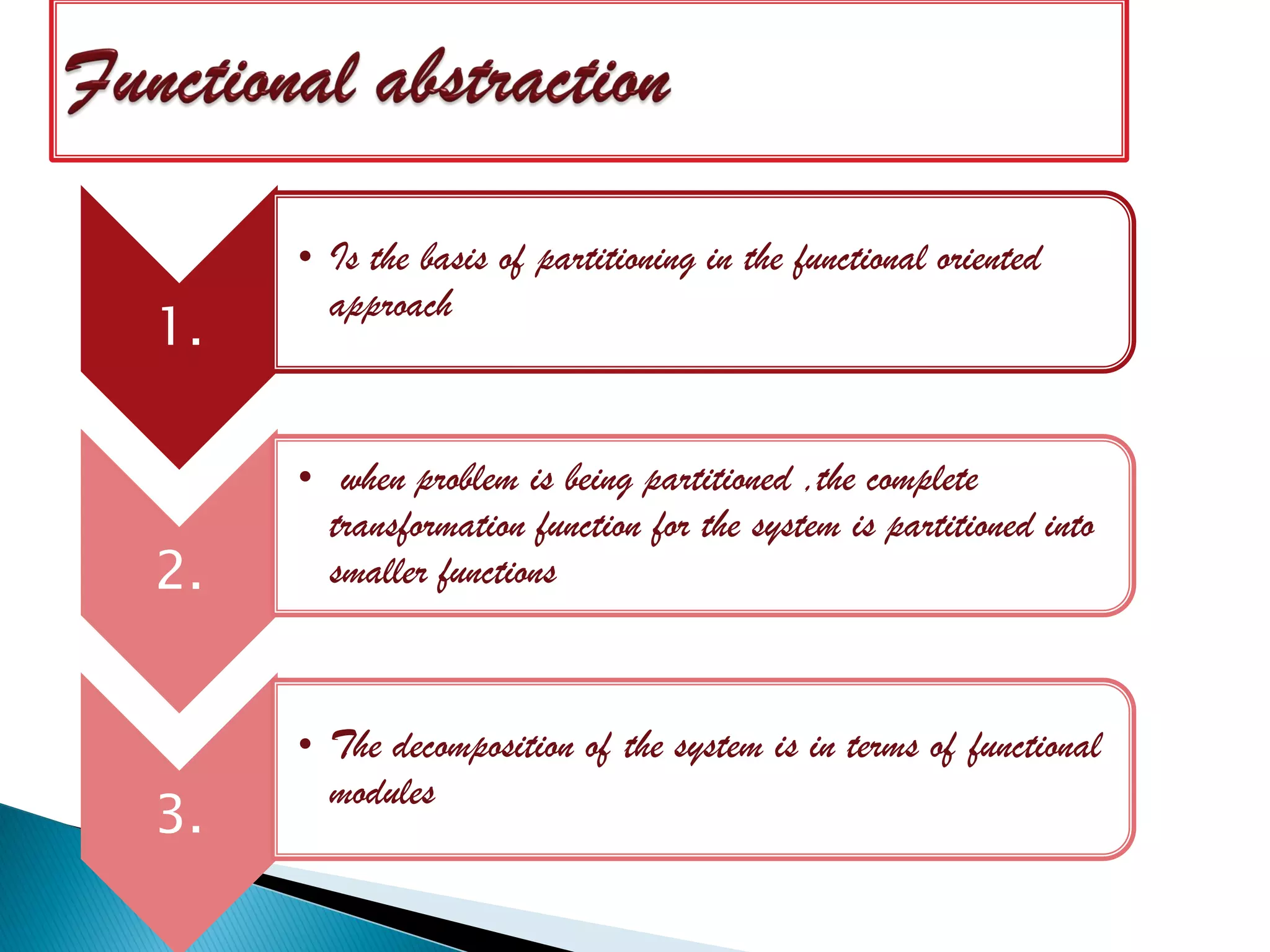
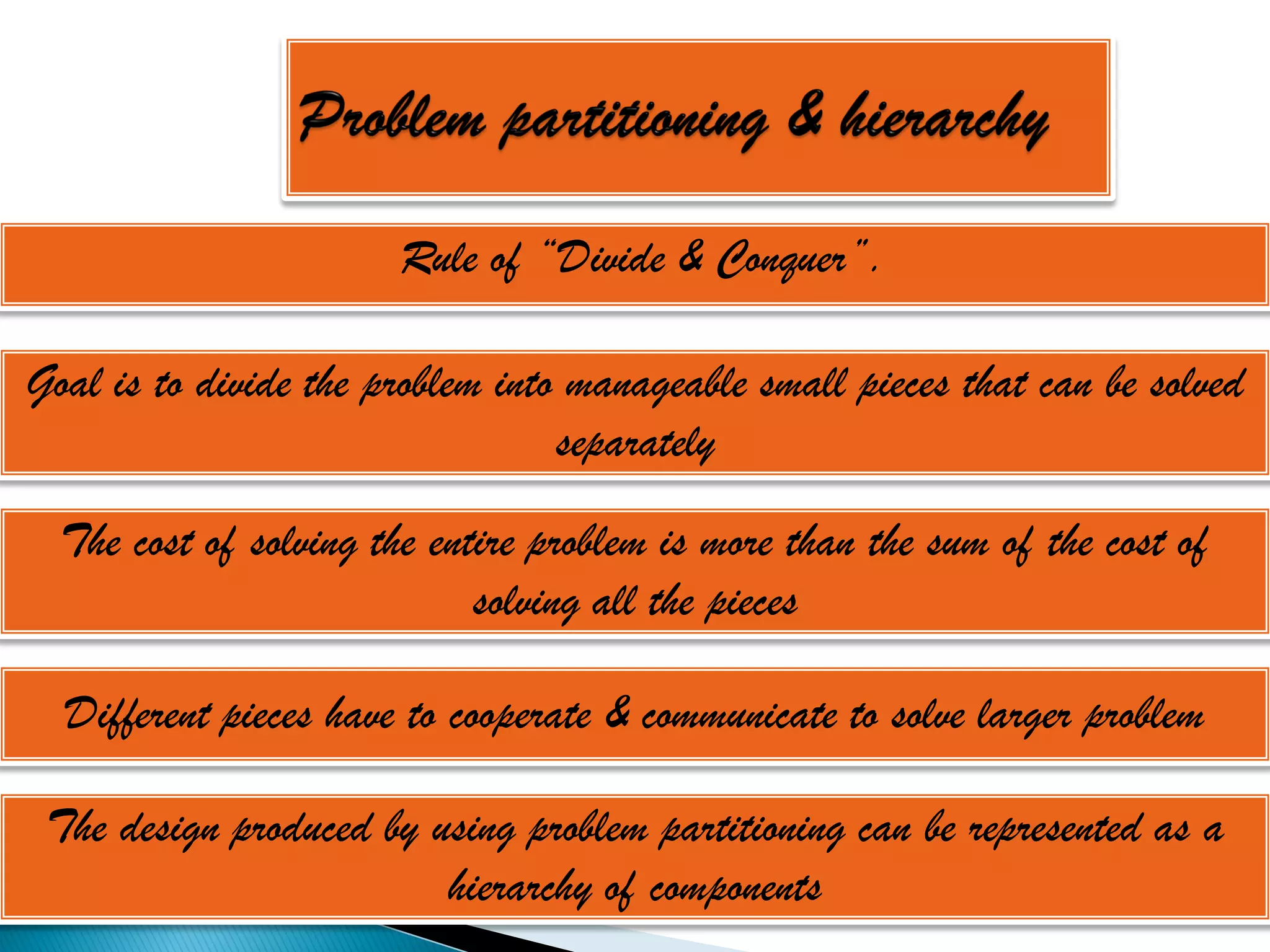
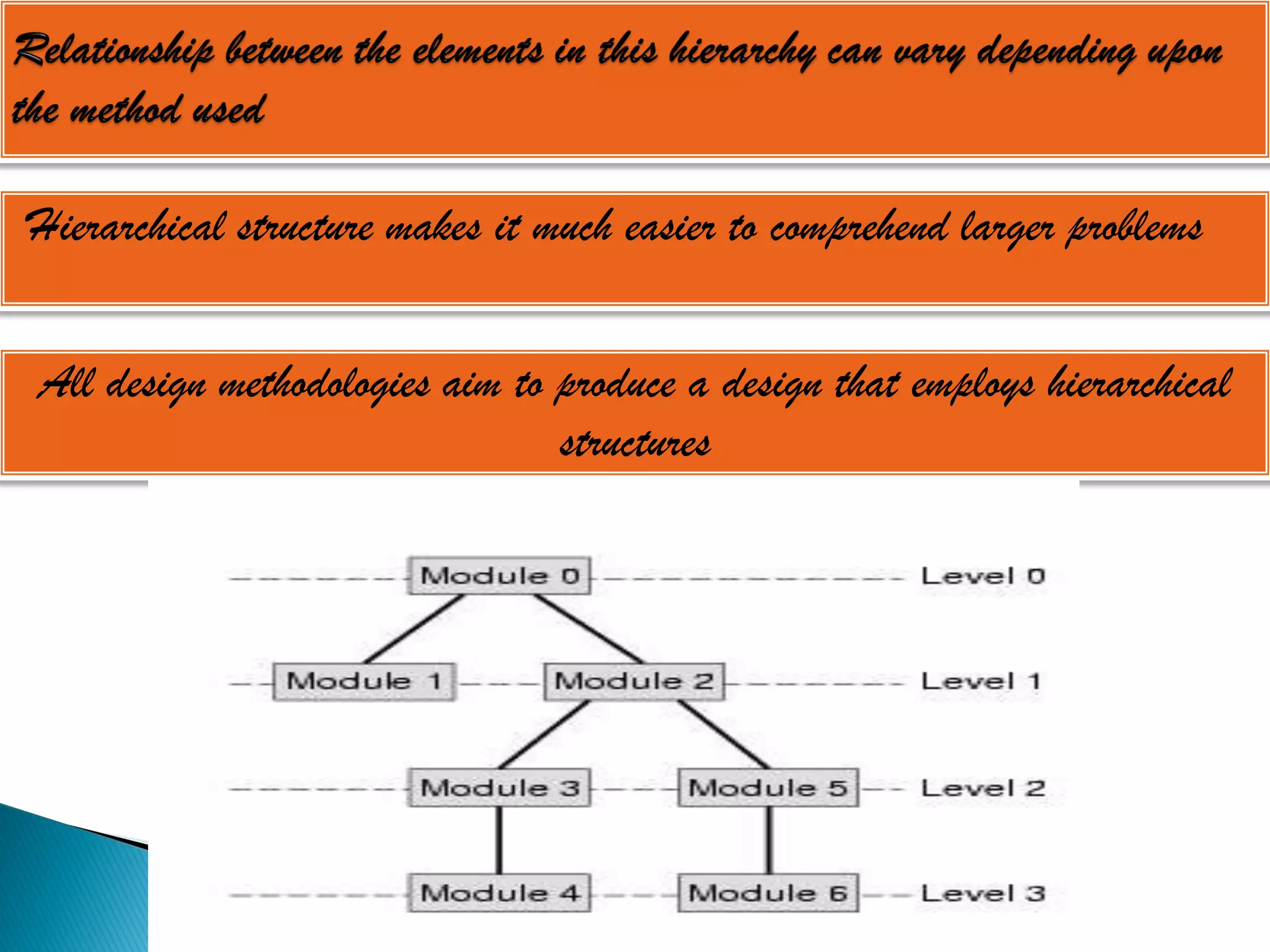
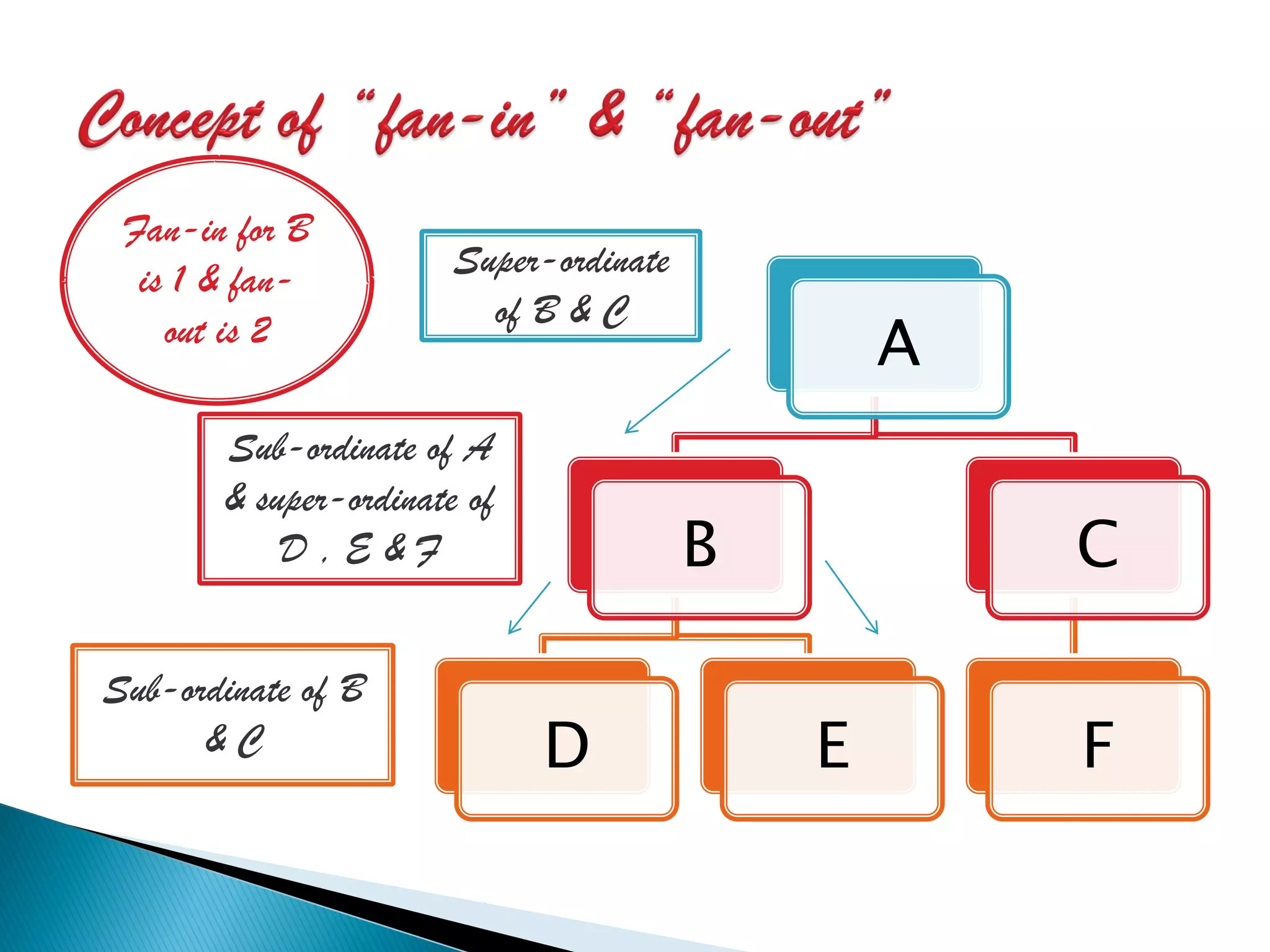
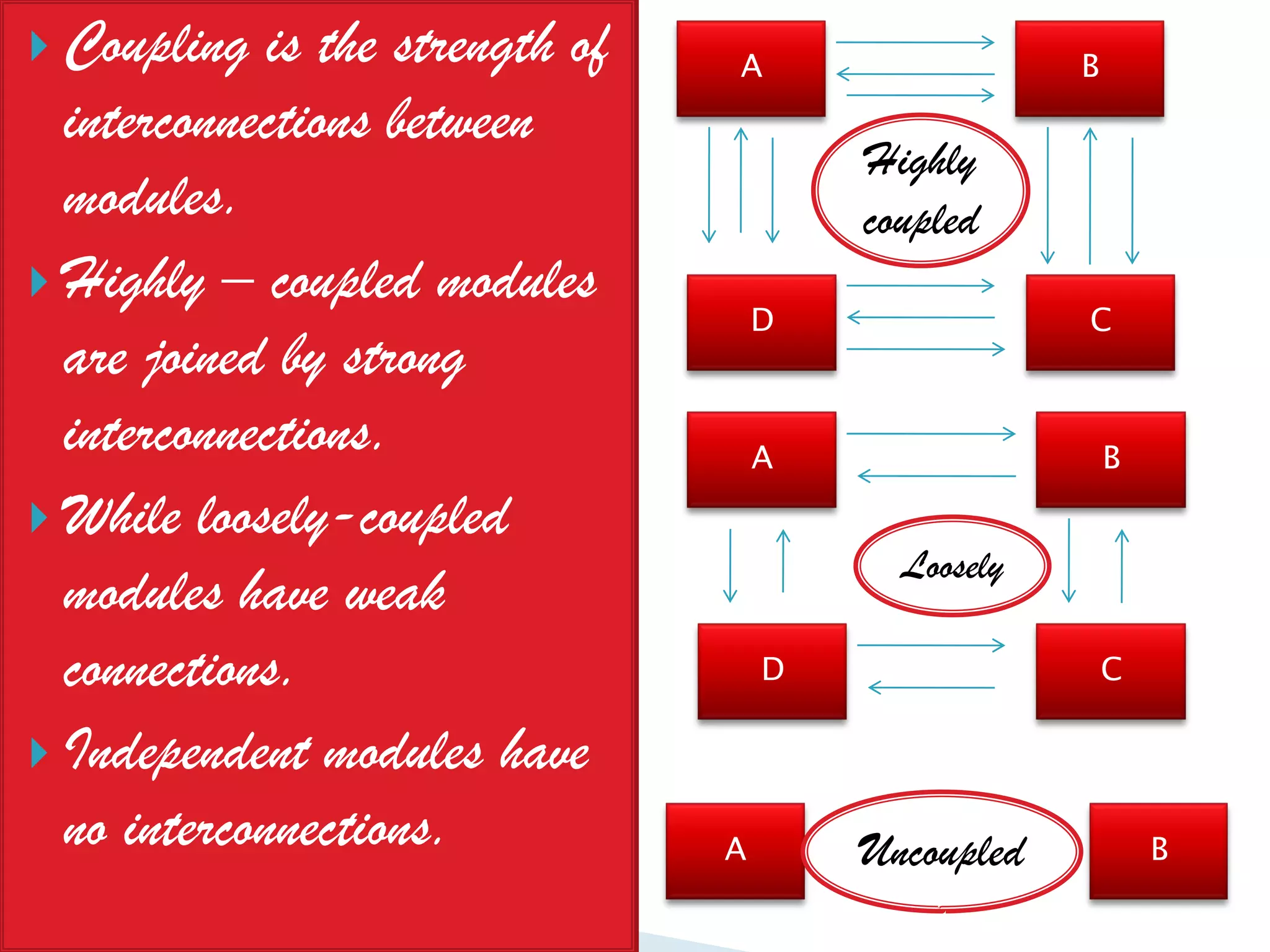
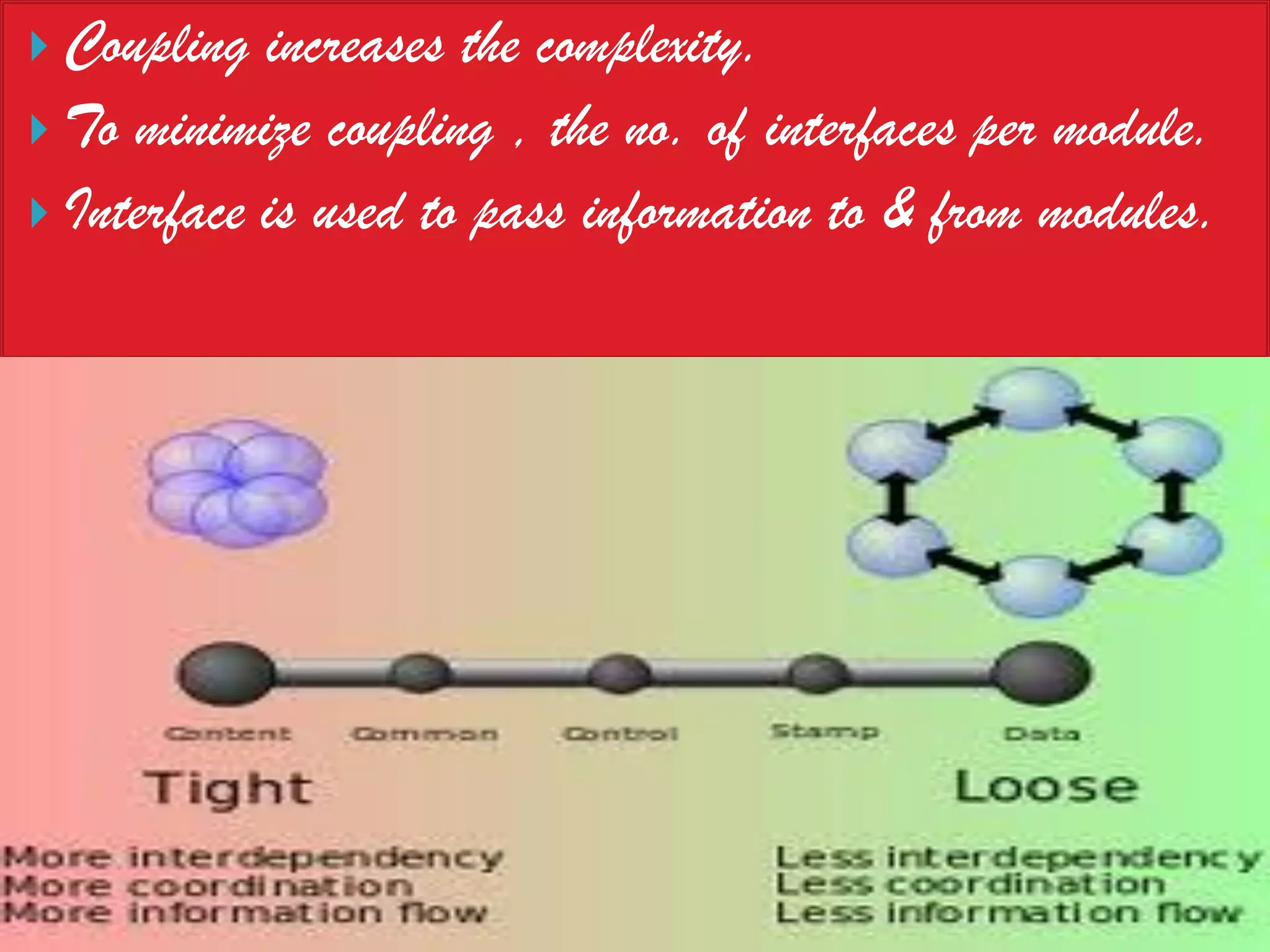
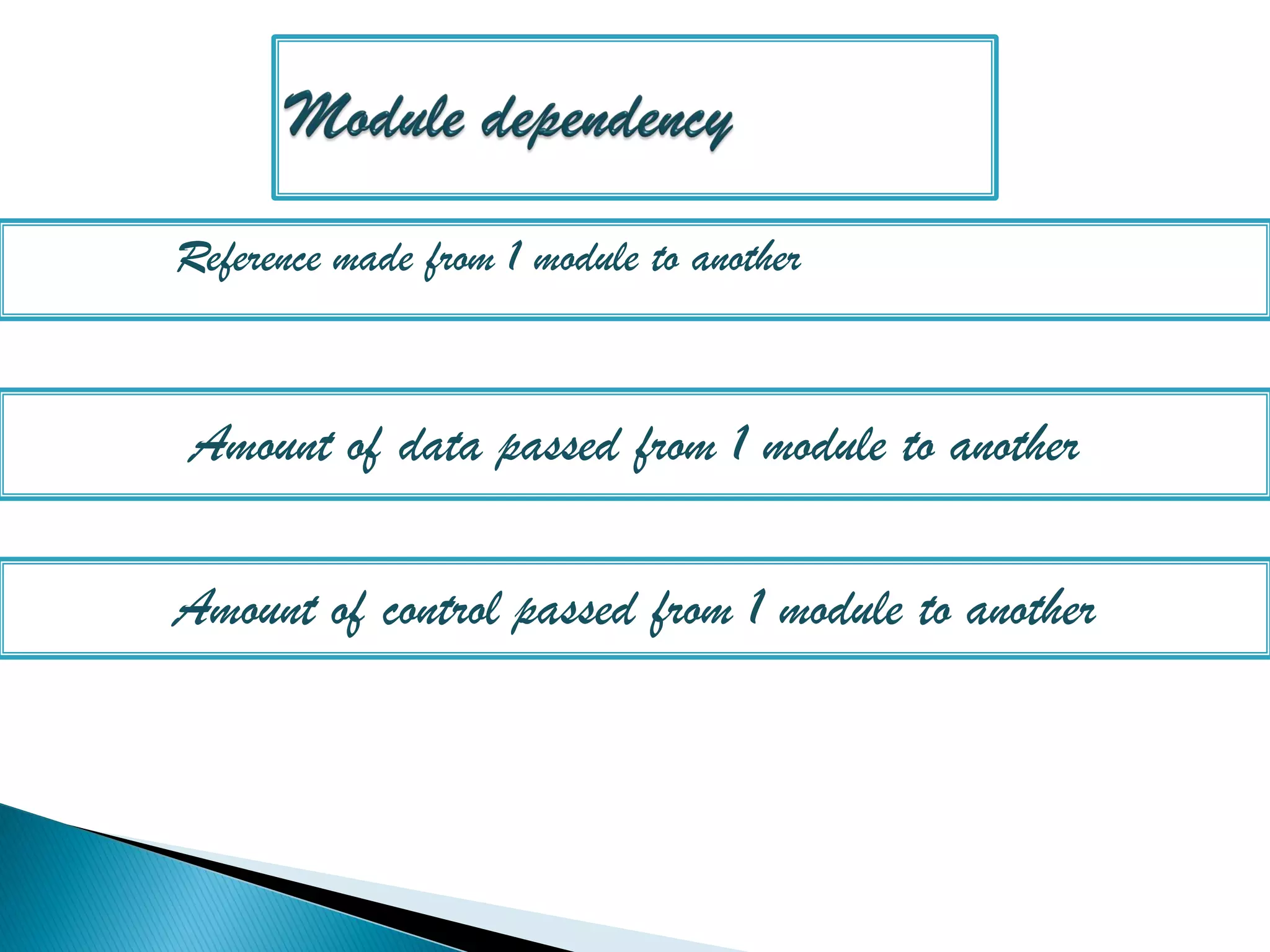
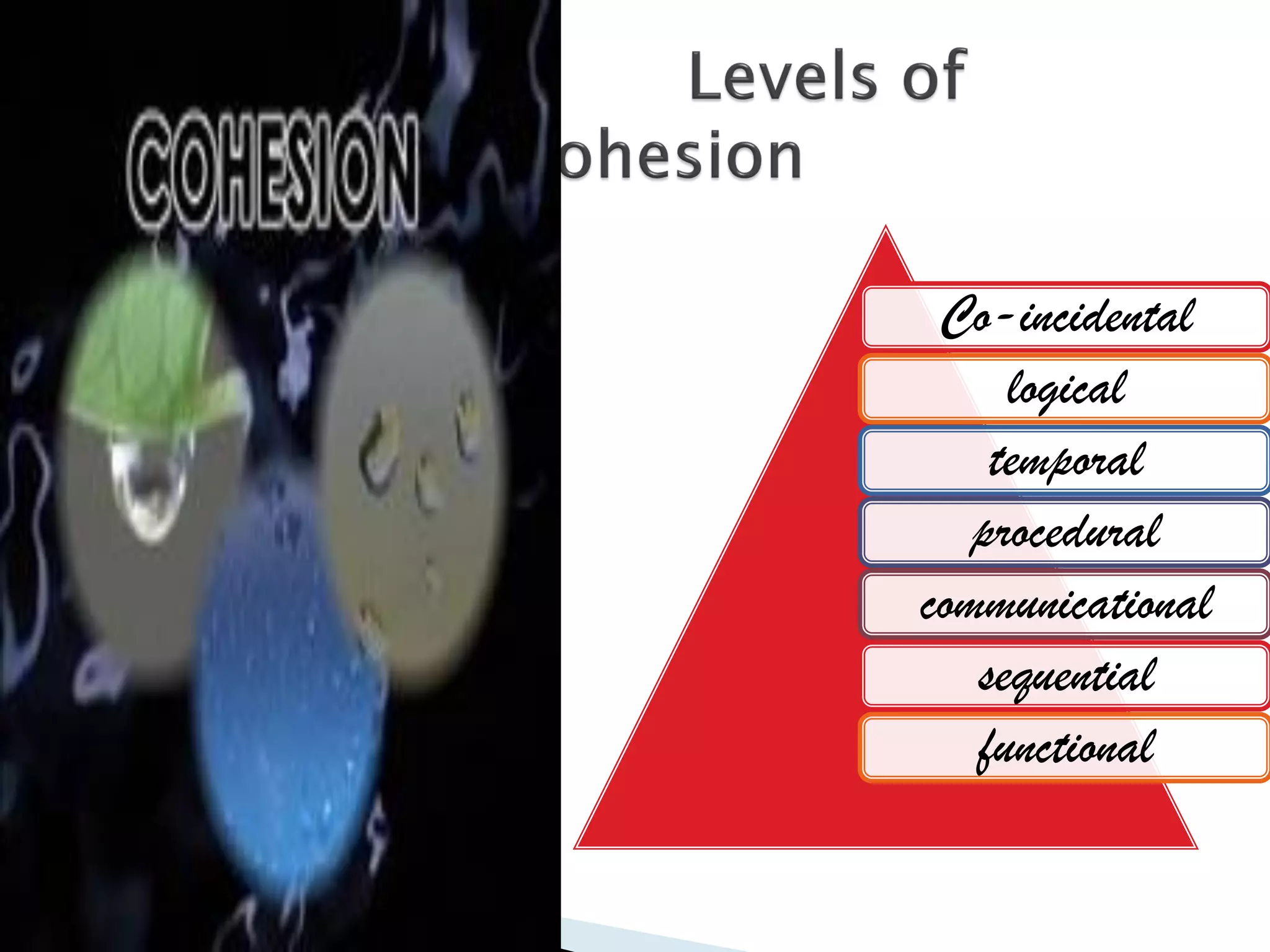
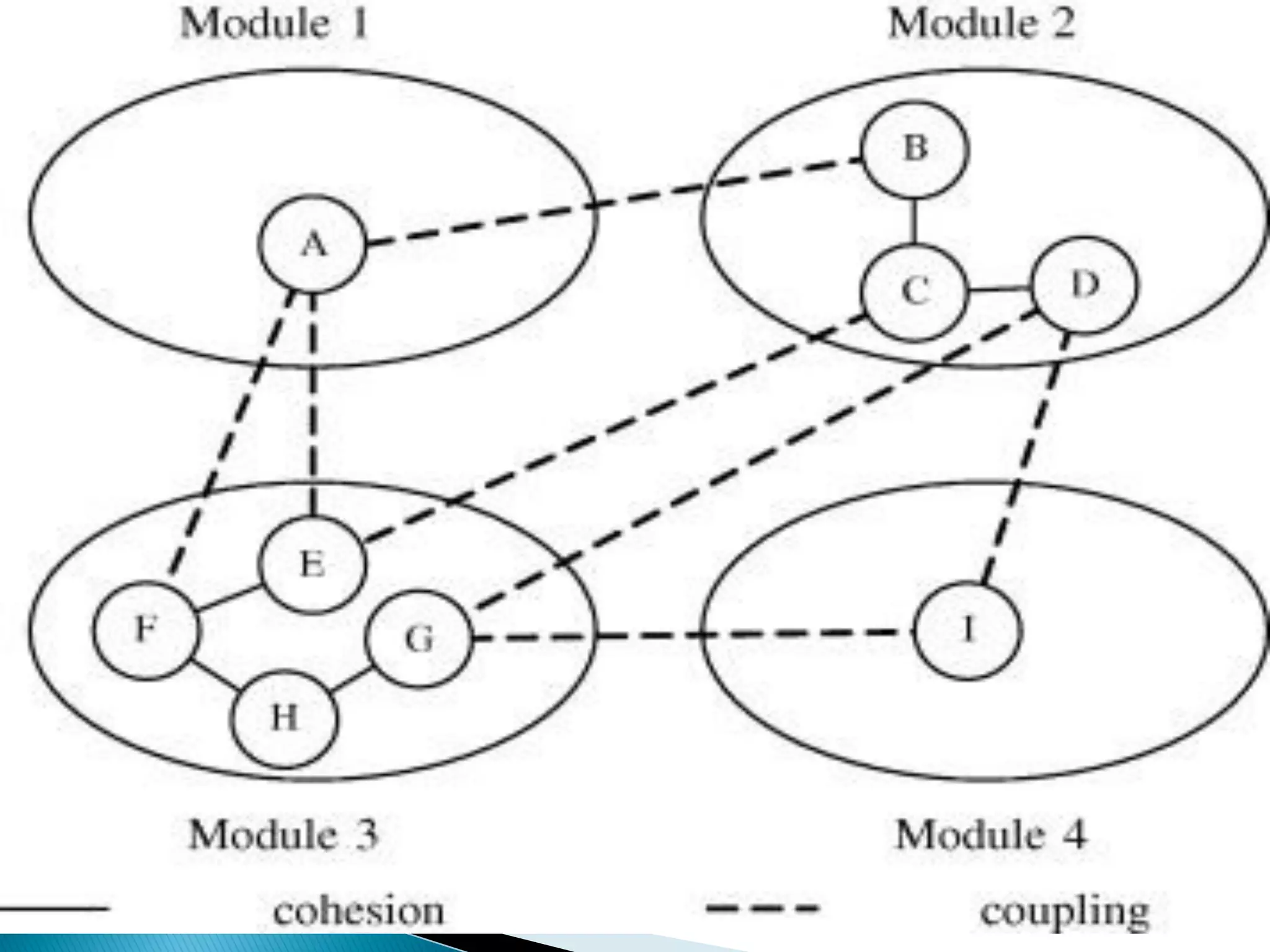
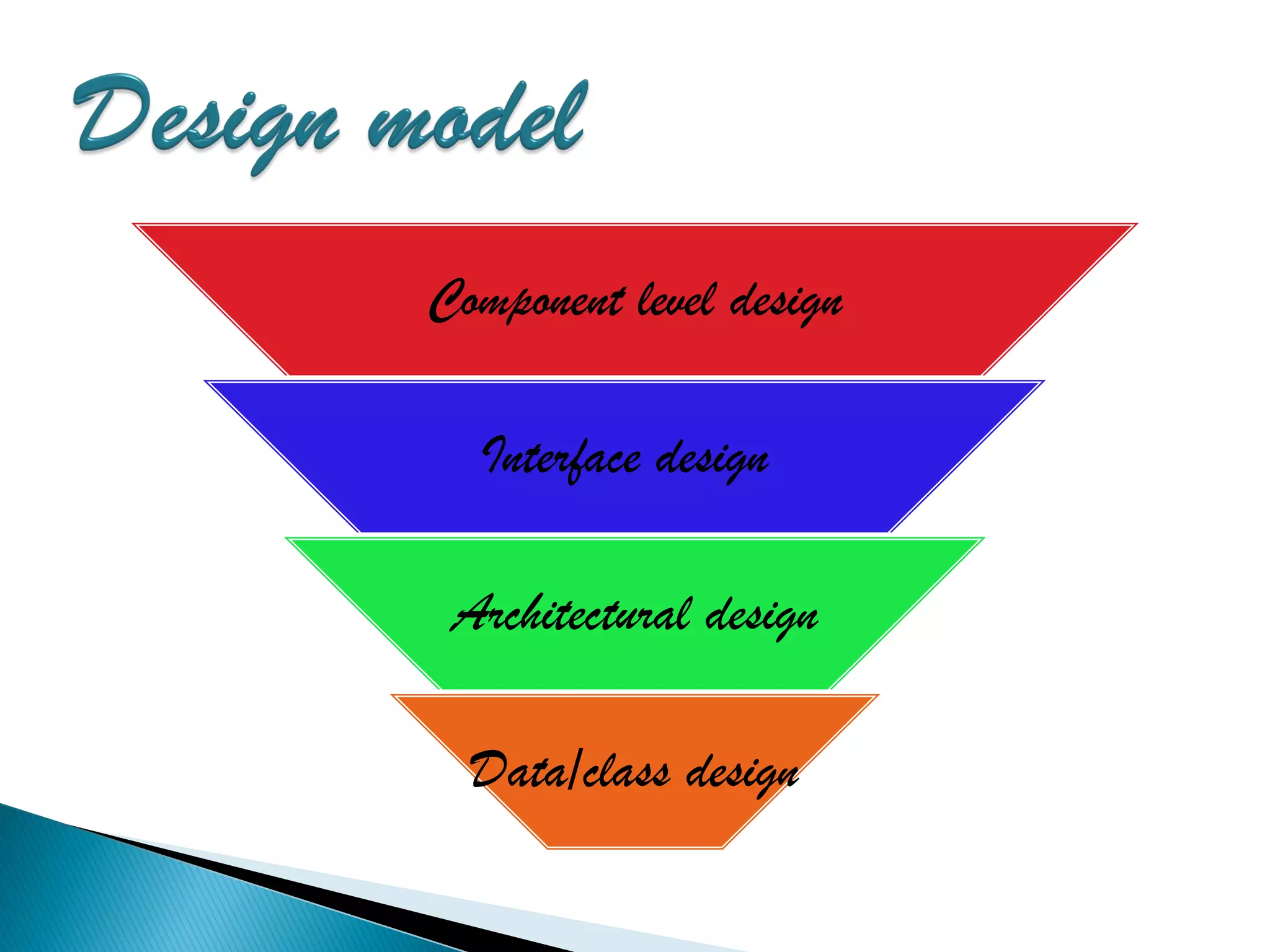
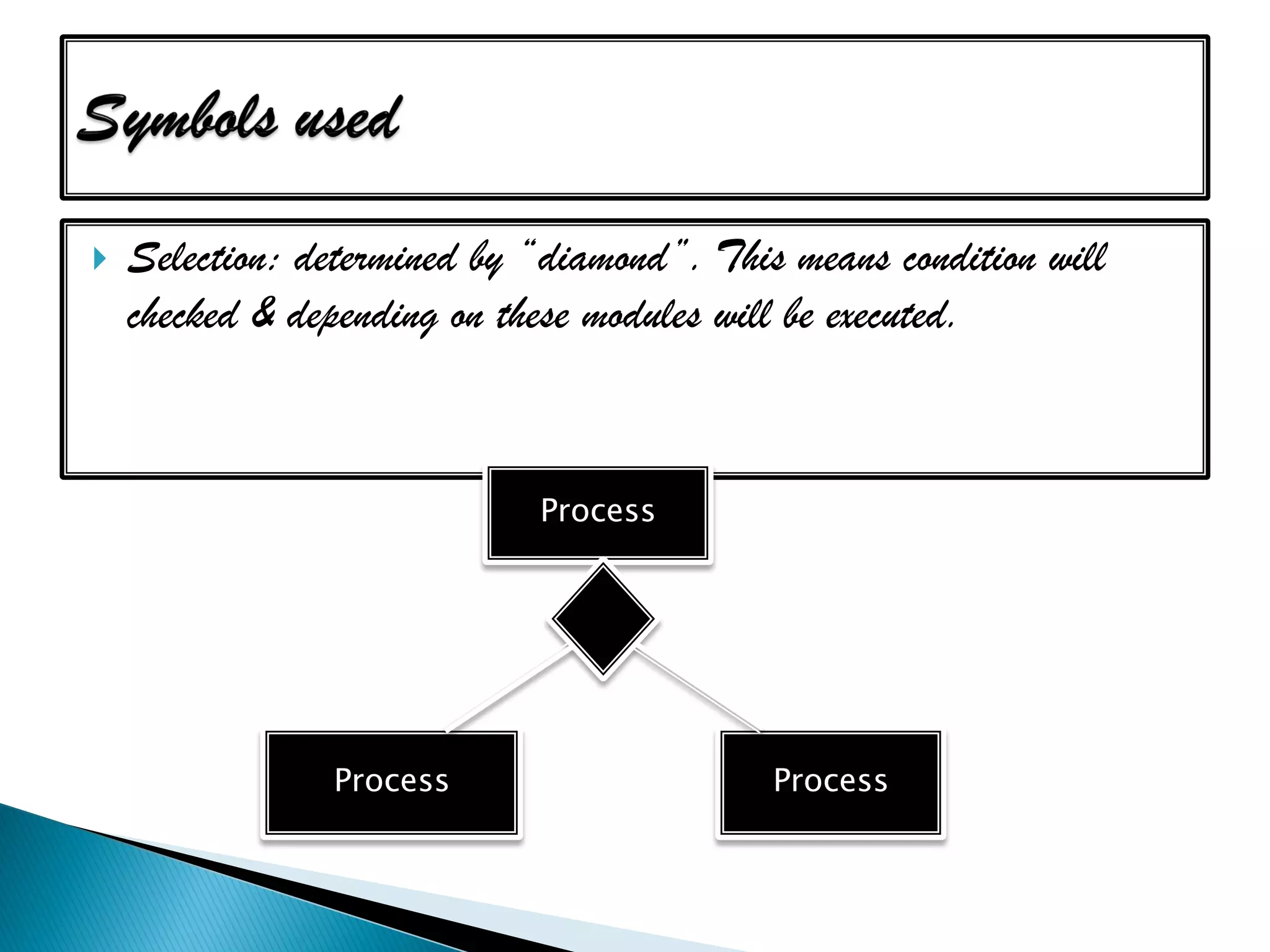
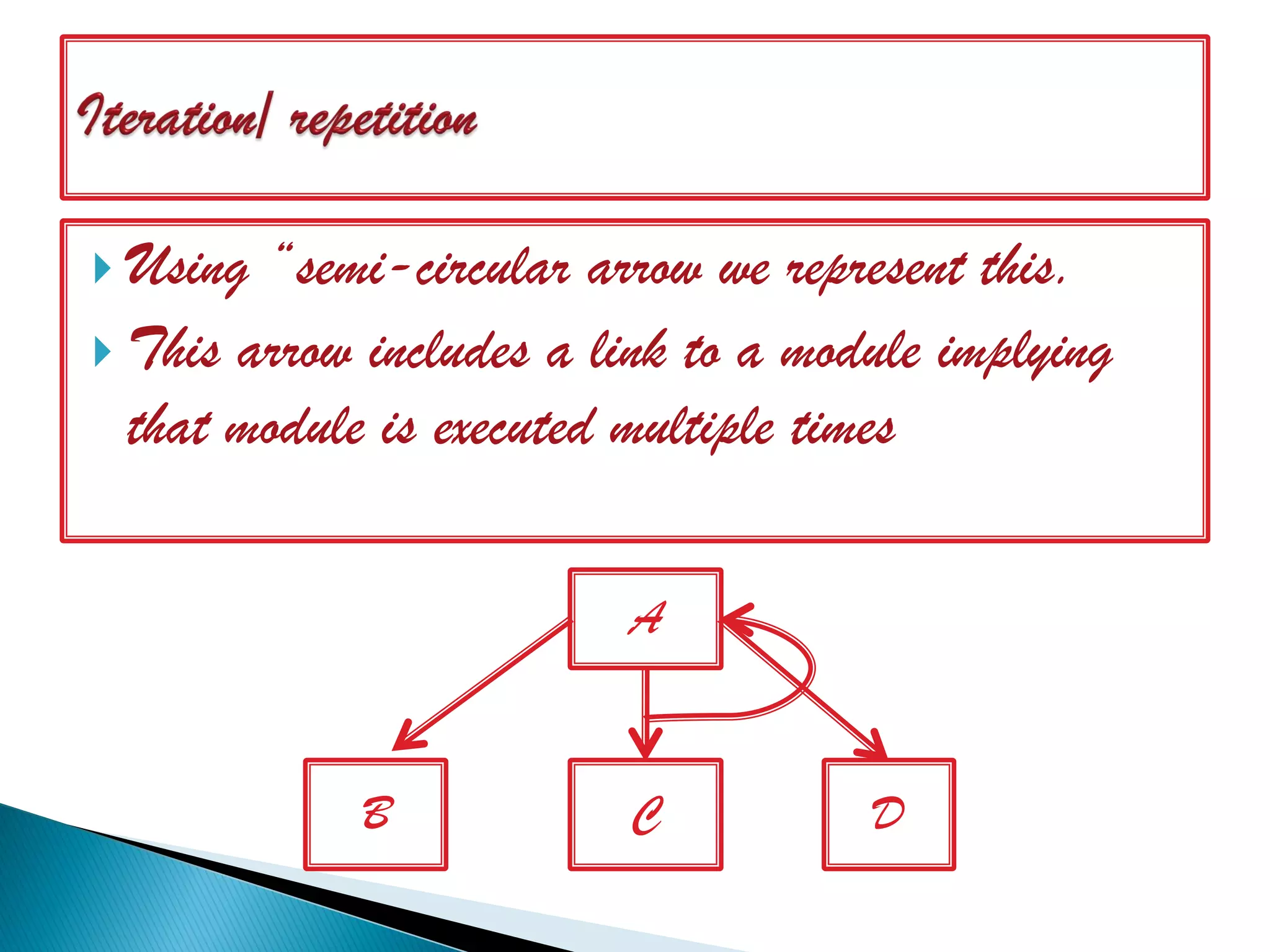
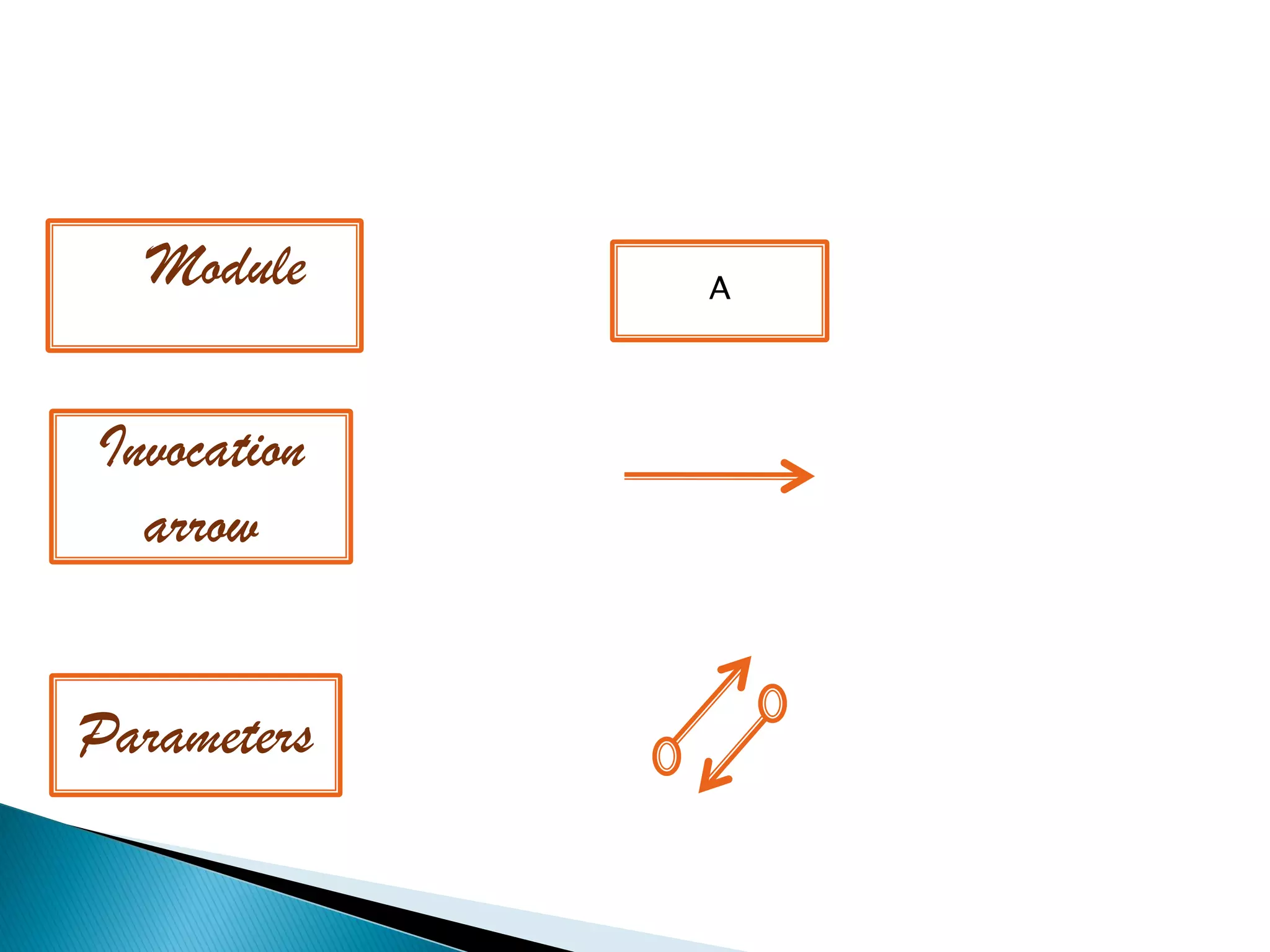
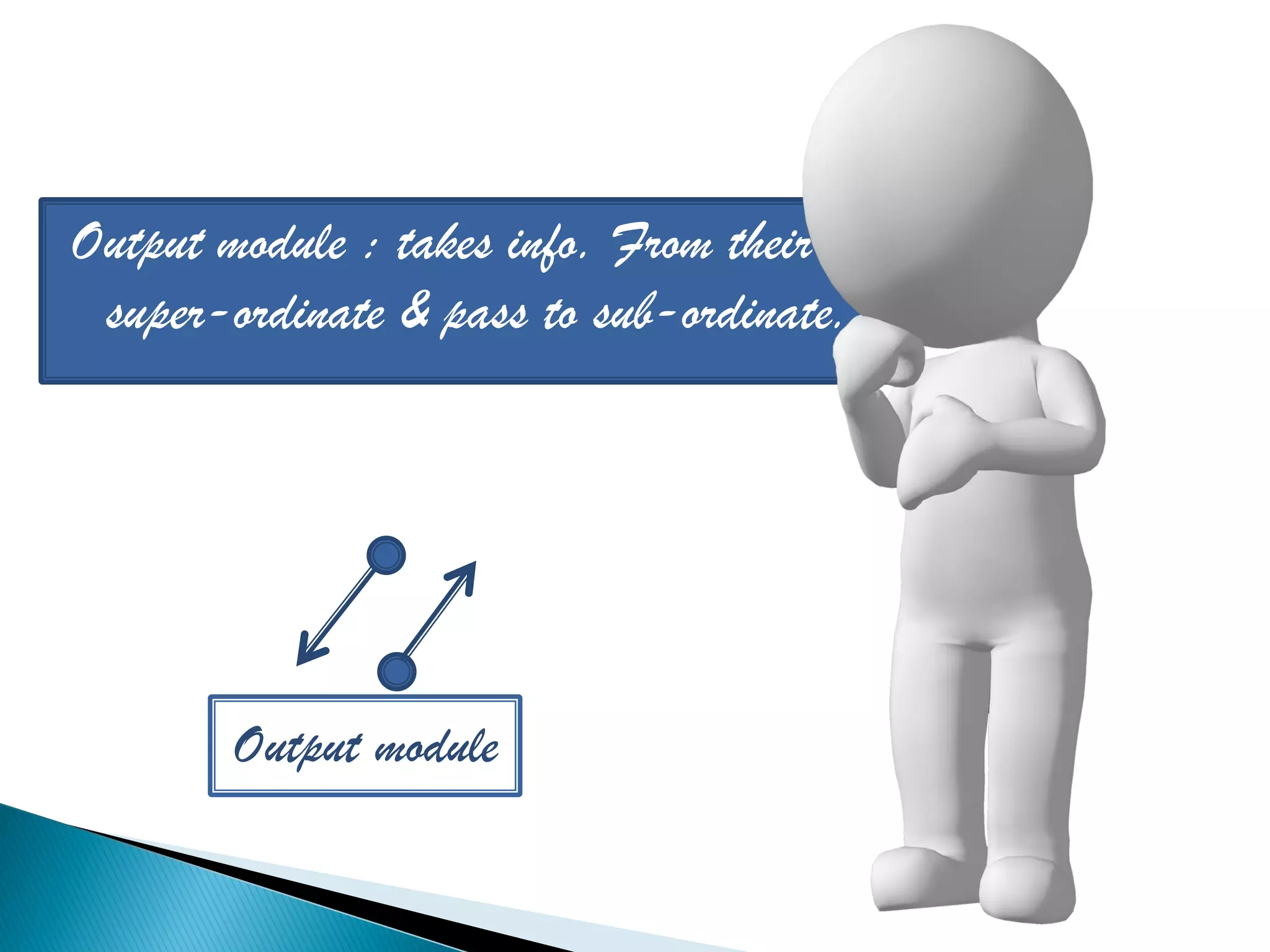
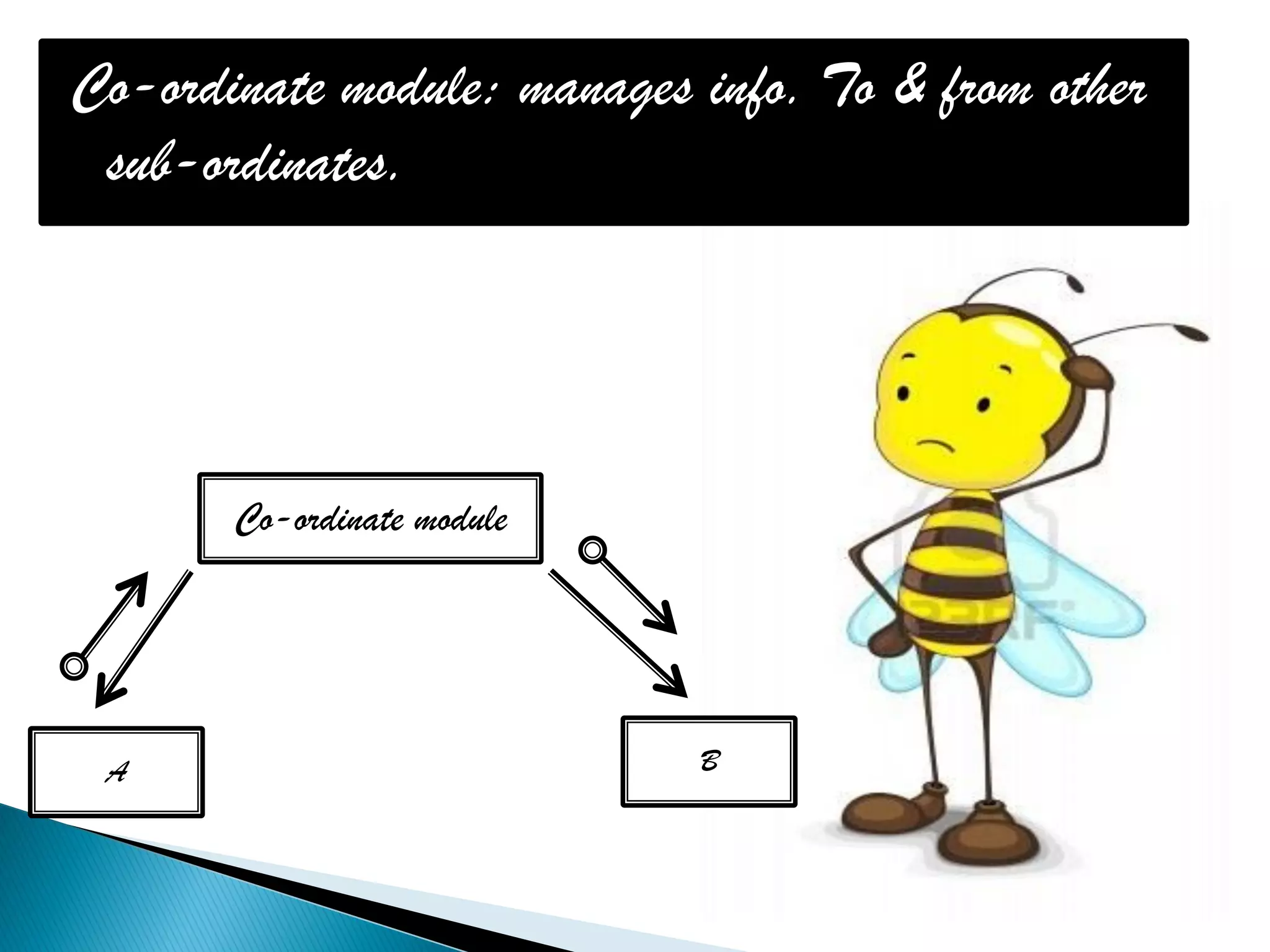
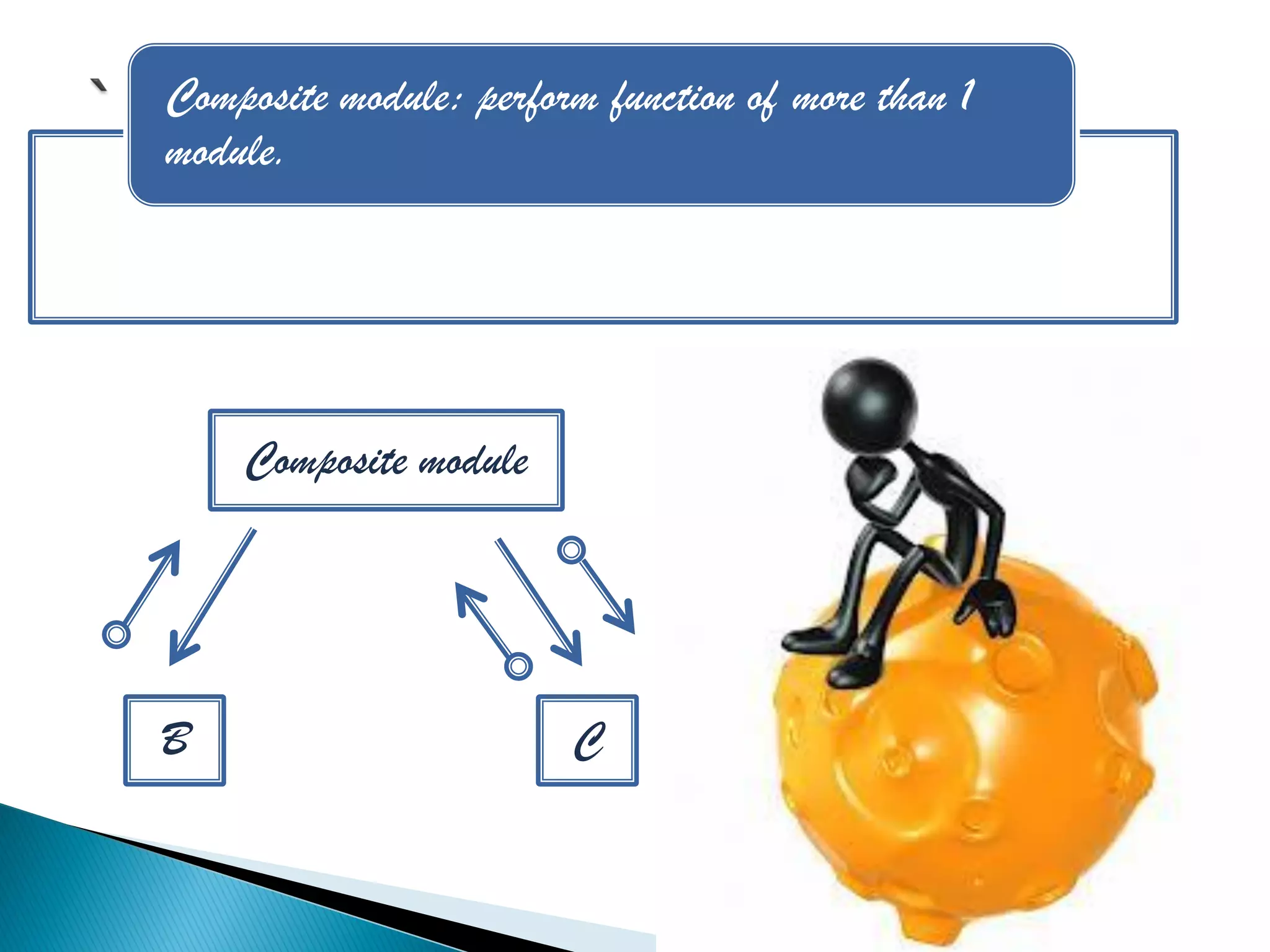
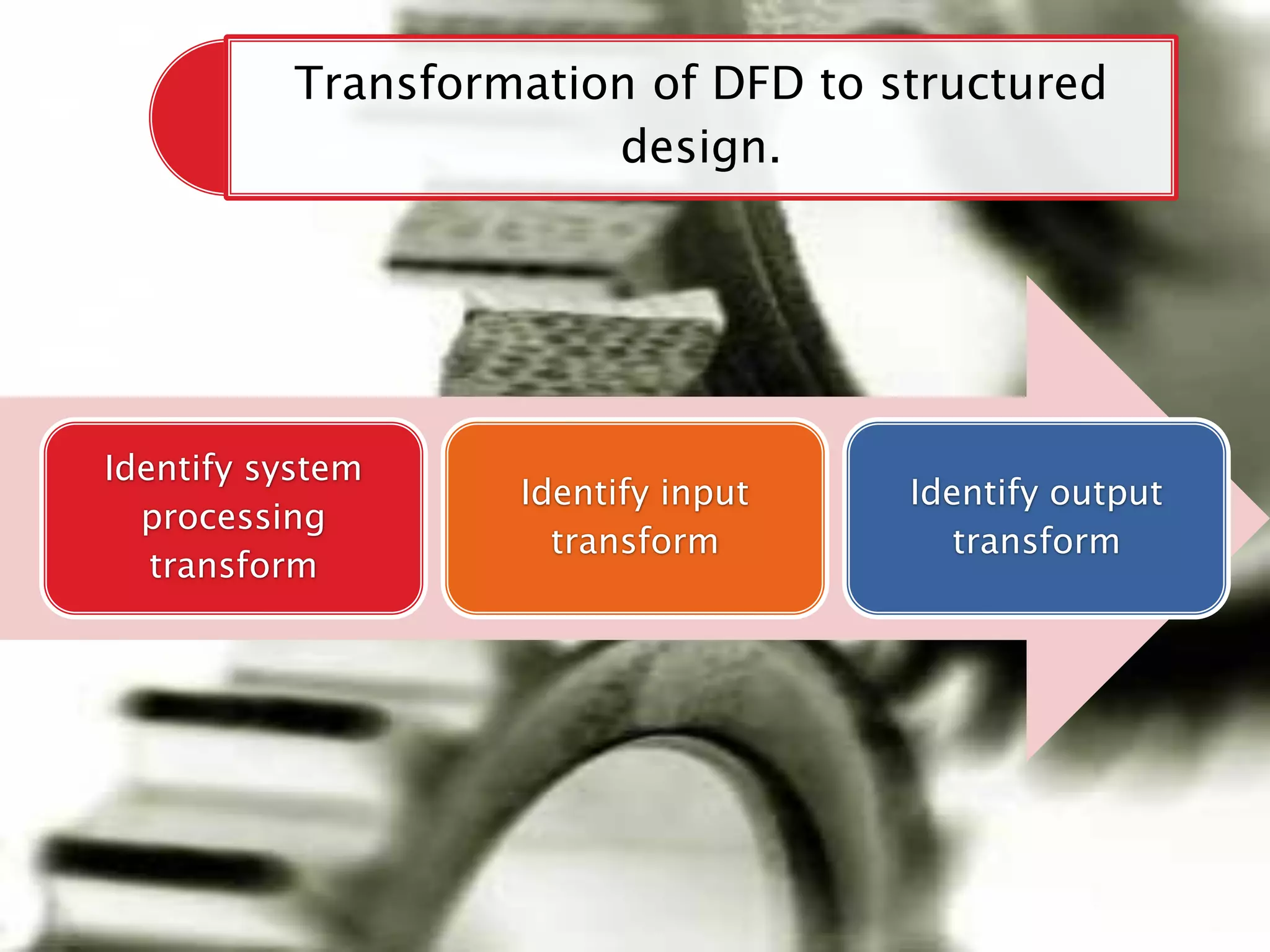
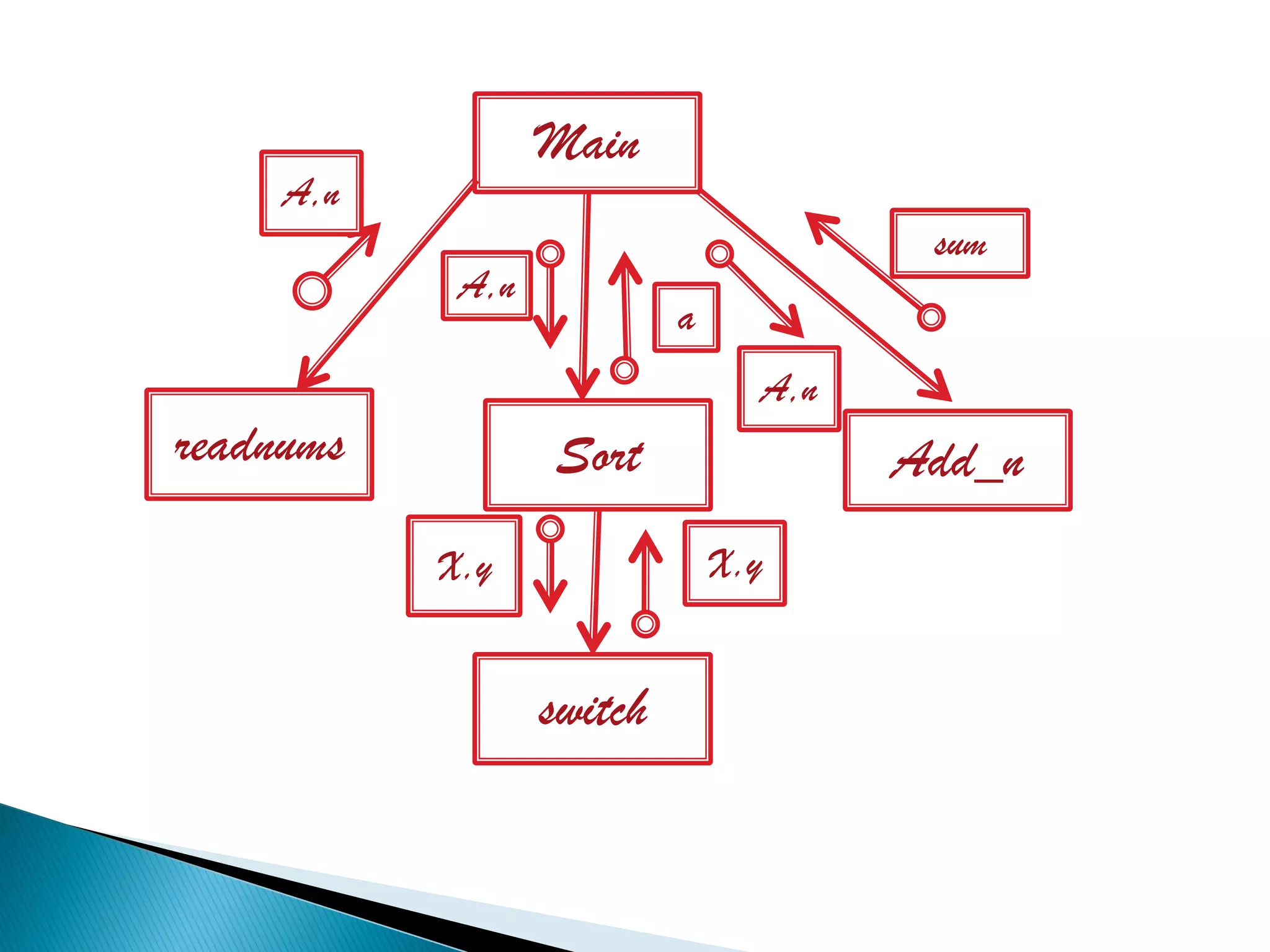
The document discusses the design phase of the system development life cycle. It explains that the design phase involves planning how the software specifications will be implemented. Key aspects of design discussed include structured analysis and design, data flow diagrams, synchronous and asynchronous operations, and design characteristics like correctness, understandability, efficiency and maintainability. The document also covers important design concepts like modularity, abstraction, coupling and cohesion which help to partition problems and create independent, understandable and maintainable modules. It provides examples to illustrate concepts like hierarchical decomposition, fan-in and fan-out, and different types of coupling and cohesion.