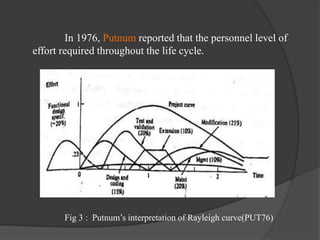
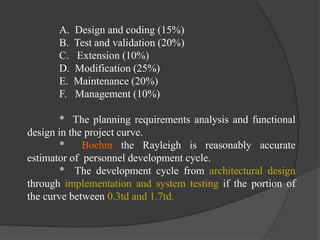
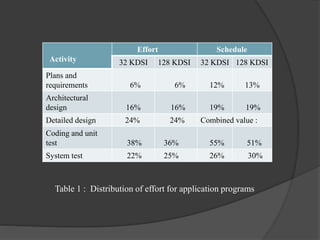
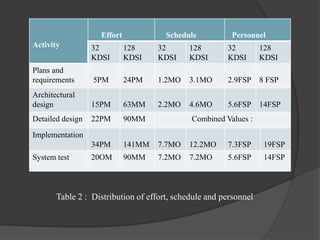
The document discusses staffing level estimation over the course of a software development project. It describes how the number of personnel needed varies at different stages: a small group is needed for planning and analysis, a larger group for architectural design, and the largest number for implementation and system testing. It also references models like the Rayleigh curve and Putnam's interpretation that estimate personnel levels over time. Tables show estimates for the distribution of effort, schedule, and personnel across activities for different project sizes. The key idea is that staffing requirements fluctuate throughout the software life cycle, with peaks during implementation and testing phases.