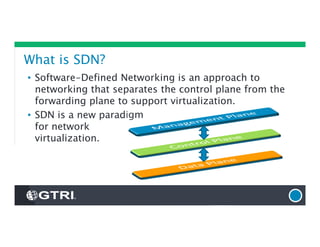
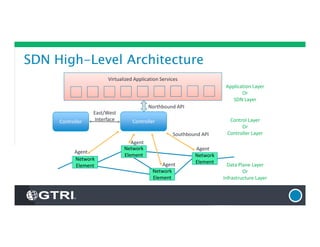
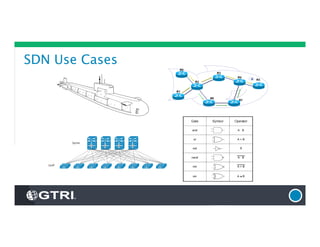
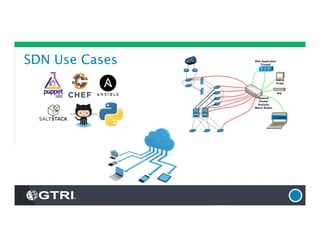
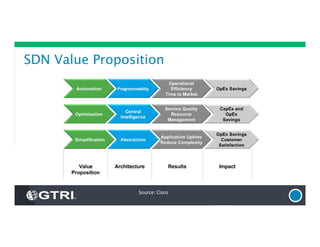
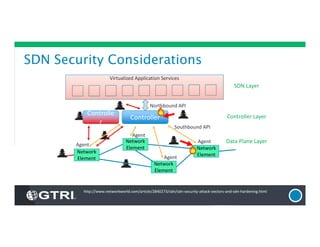
The document provides an overview of Software-Defined Networking (SDN), discussing its benefits, architecture, challenges, and use cases. It highlights the transformative impact of SDN on IT infrastructure, enabling better network management and application deployment through virtualization. Additionally, it outlines the industry's outlook, GTRI's solutions, and offers a free technology review service to assess organizations' readiness for SDN.