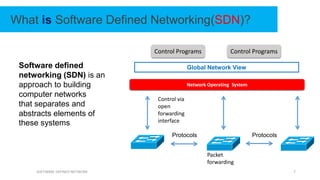
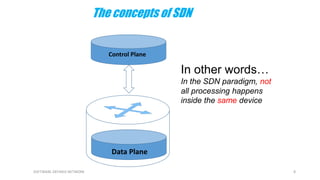
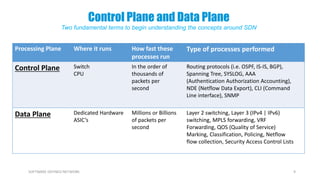
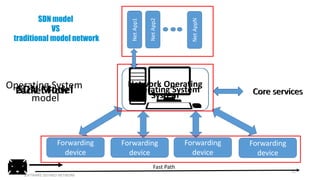
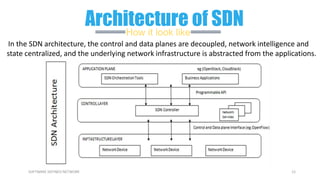
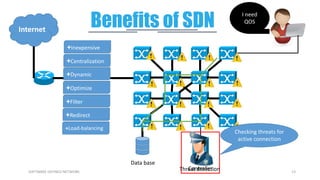
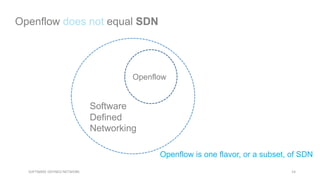
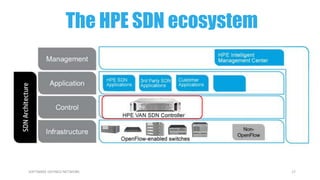
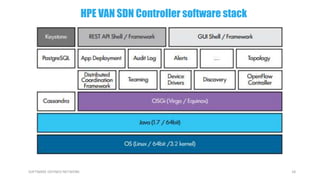
This document provides an overview of software-defined networking (SDN) and the HPE VAN SDN Controller. It defines SDN and describes its key concepts including the separation of the control plane and data plane. The benefits of SDN like centralization, dynamism, and optimization are outlined. The architecture of the HPE SDN Controller is presented along with the core applications it provides for network discovery, path selection, topology management and more. In conclusion, SDN is positioned to transform static networks into scalable, programmable platforms.