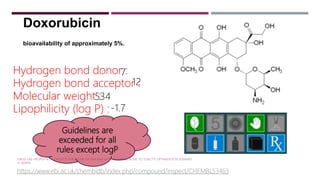
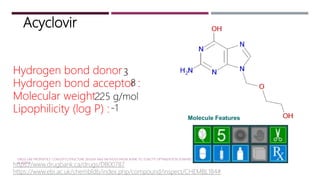
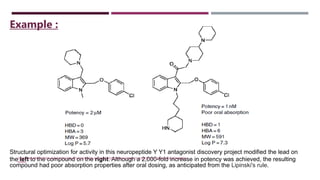
The Lipinski Rule of Five provides guidelines for drug-like properties that influence a compound's absorption and bioavailability after oral dosing. The rules specify that an orally active drug have less than 5 hydrogen bond donors, less than 10 hydrogen bond acceptors, a molecular weight less than 500, and an octanol-water partition coefficient log P of less than 5. Violating more than one of these guidelines reduces the likelihood of adequate absorption. While optimizing activity may increase violations by adding hydrogen bonds or lipophilicity, this can compromise a compound's drug-like properties.