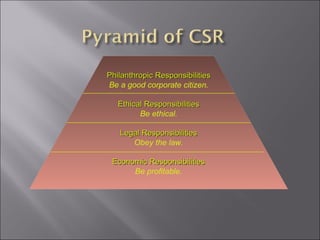
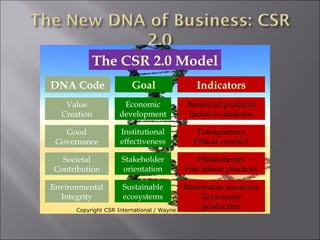
The document discusses social security and welfare schemes in India. It provides details about various social security laws like Employees' State Insurance Act, Employees' Provident Funds & Miscellaneous Provisions Act, and Payment of Gratuity Act. It also summarizes BHEL's social security and labor welfare schemes like Group Insurance Scheme and Provident Fund. BHEL effectively implements these schemes to provide compensation and benefits to employees.