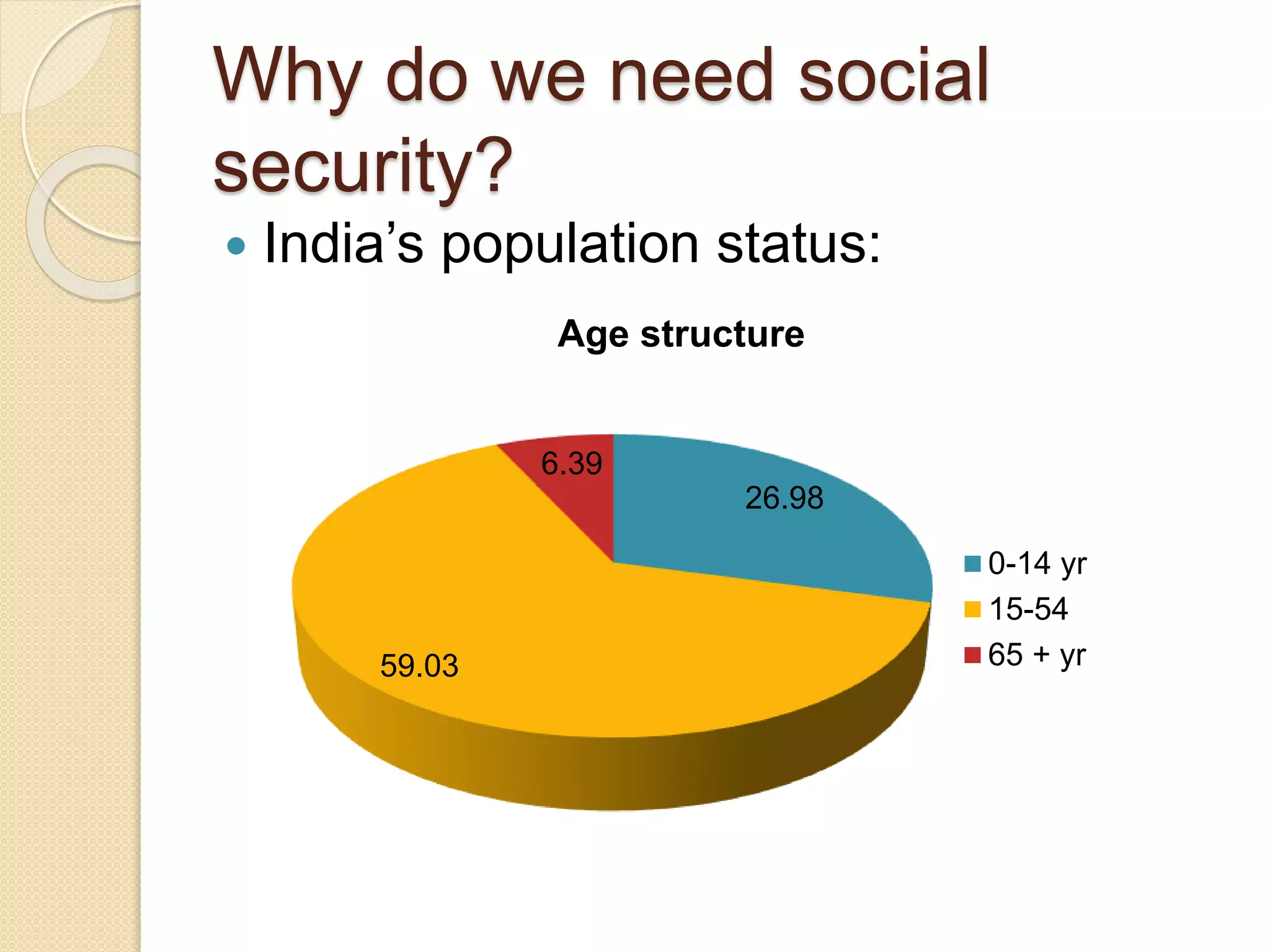
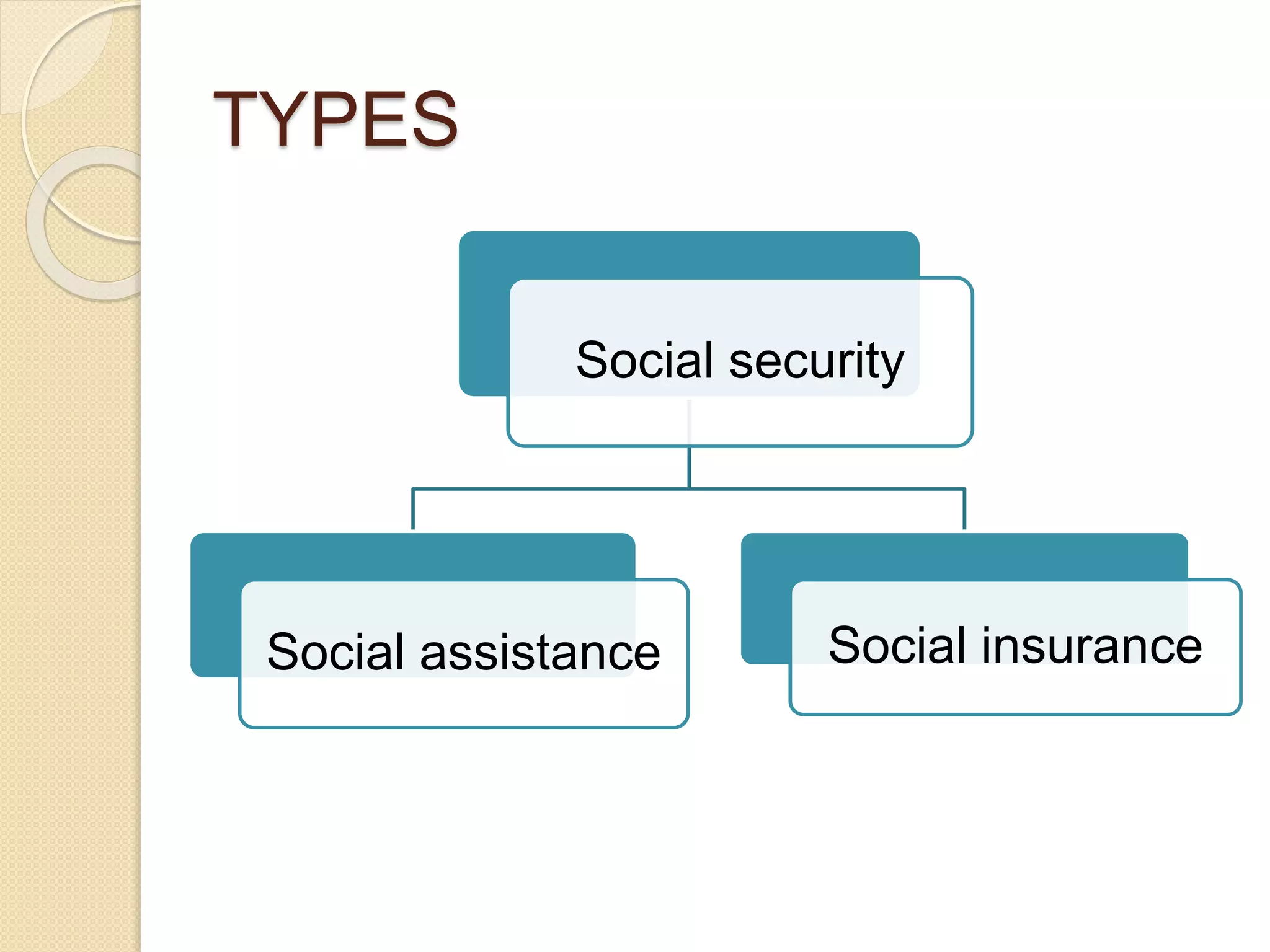
Social security is defined as security provided by society through appropriate organizations against certain risks like sickness, invalidity, old age, and death. It is recognized as a human right by the UN. Germany pioneered social security programs in the late 1800s and many other countries developed similar programs in the early 1900s. India has implemented various acts to provide social security for organized and unorganized sector workers covering areas like employment injury, maternity, old age, contracts, and more. Examples of comprehensive foreign social security systems include Finland, which covers all residents through tax-funded and employment-based programs.