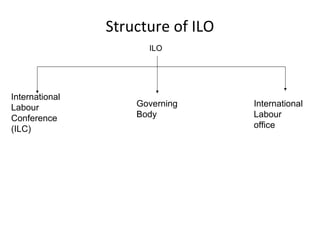
The International Labour Organisation (ILO) was established in 1919 as part of the League of Nations to promote social justice and decent work. It is the only United Nations agency that survived World War II. The ILO aims to advance opportunities for women and men to obtain decent and productive work in conditions of freedom, equity, security and human dignity. It has 183 member states and brings together governments, employers and workers representatives to set labour standards, develop policies and devise programmes promoting decent work.