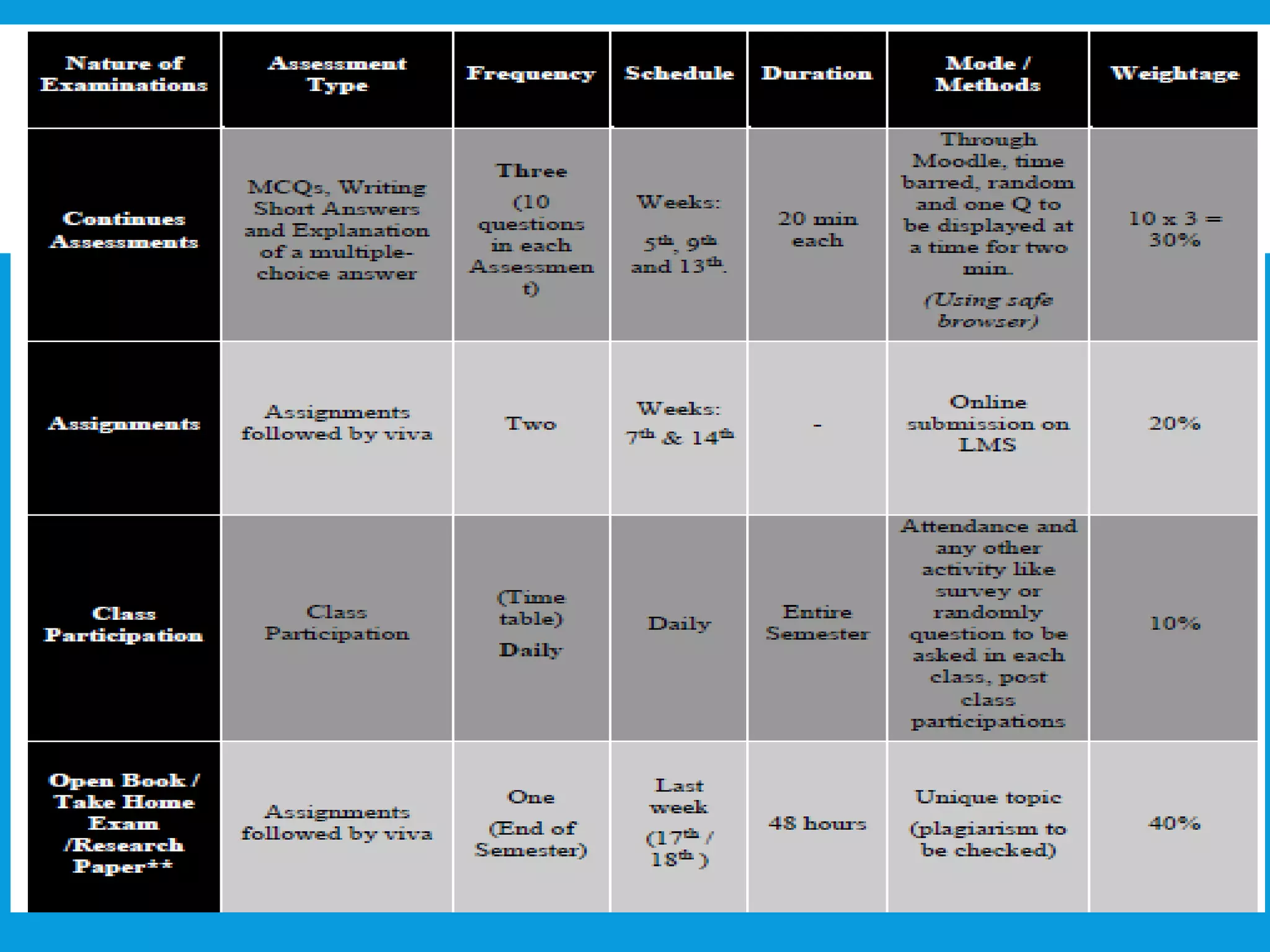
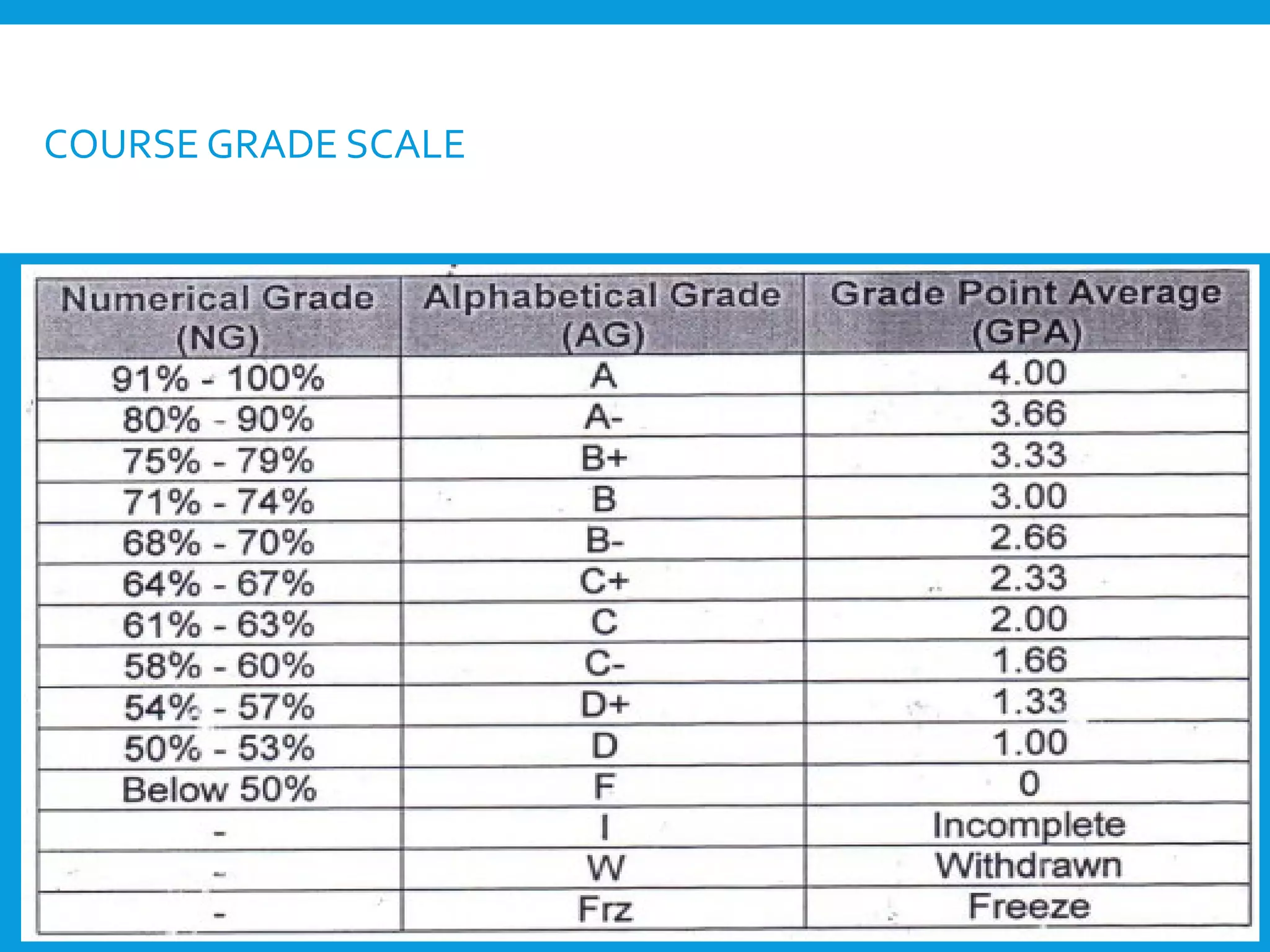
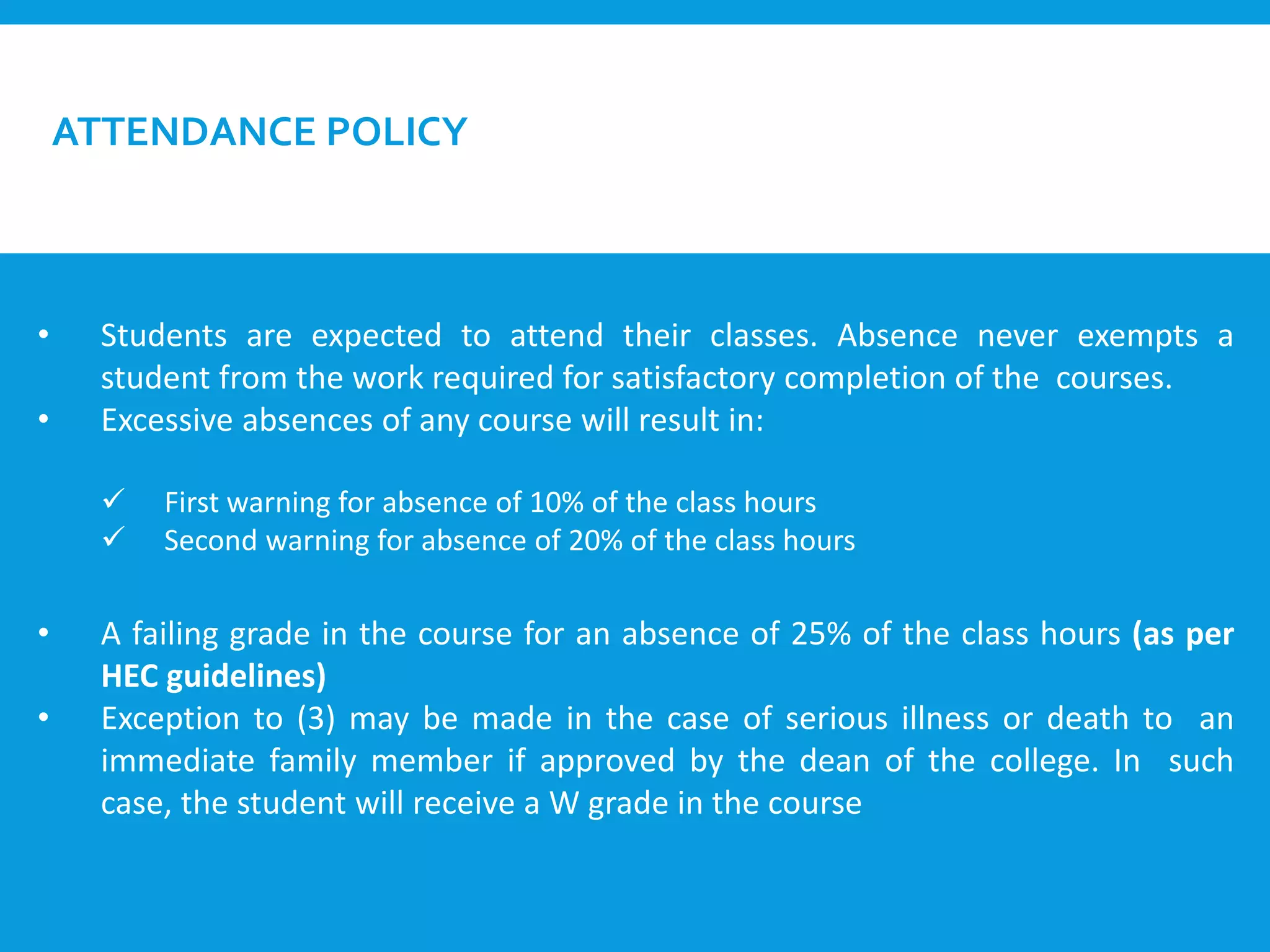
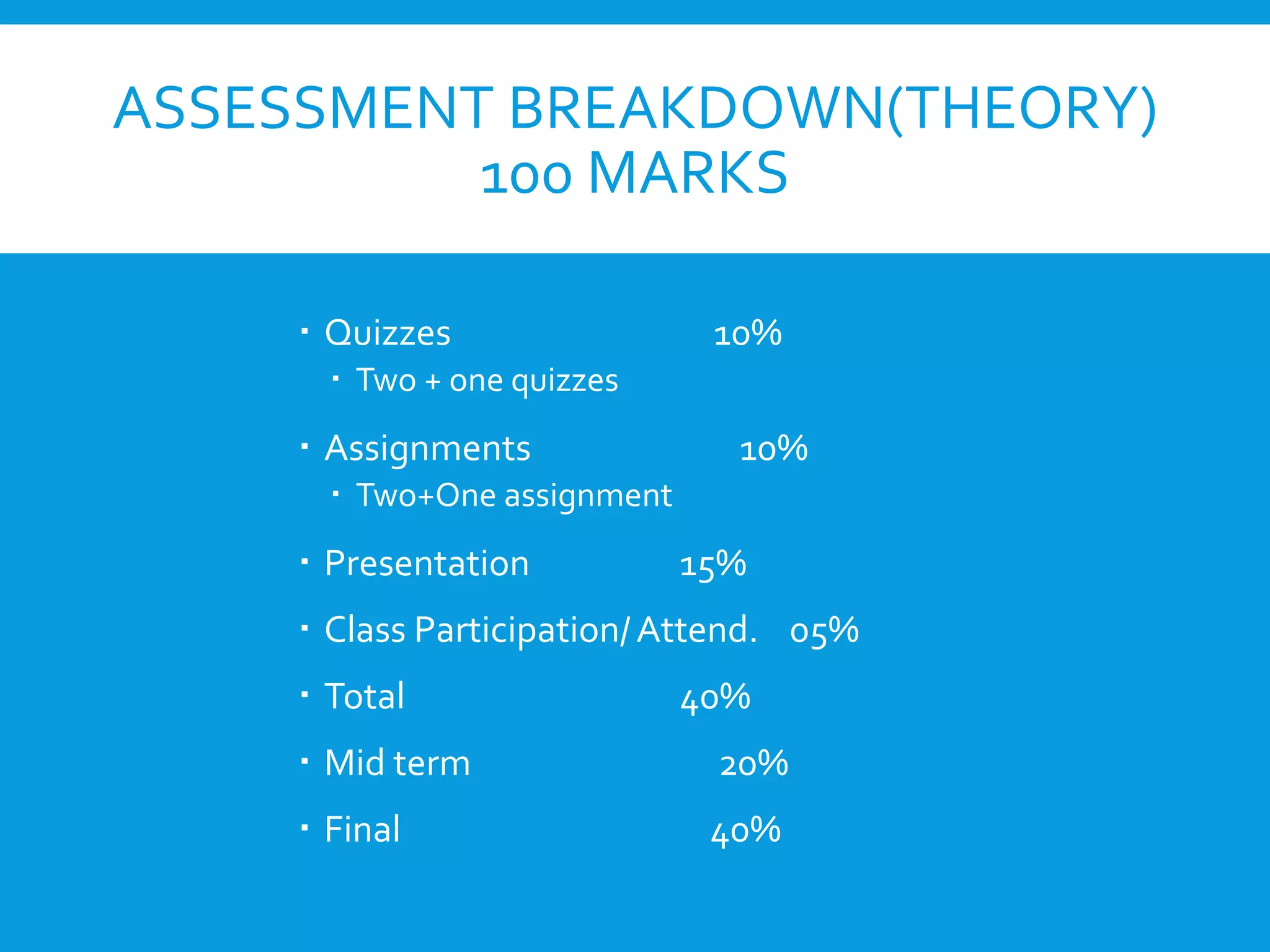
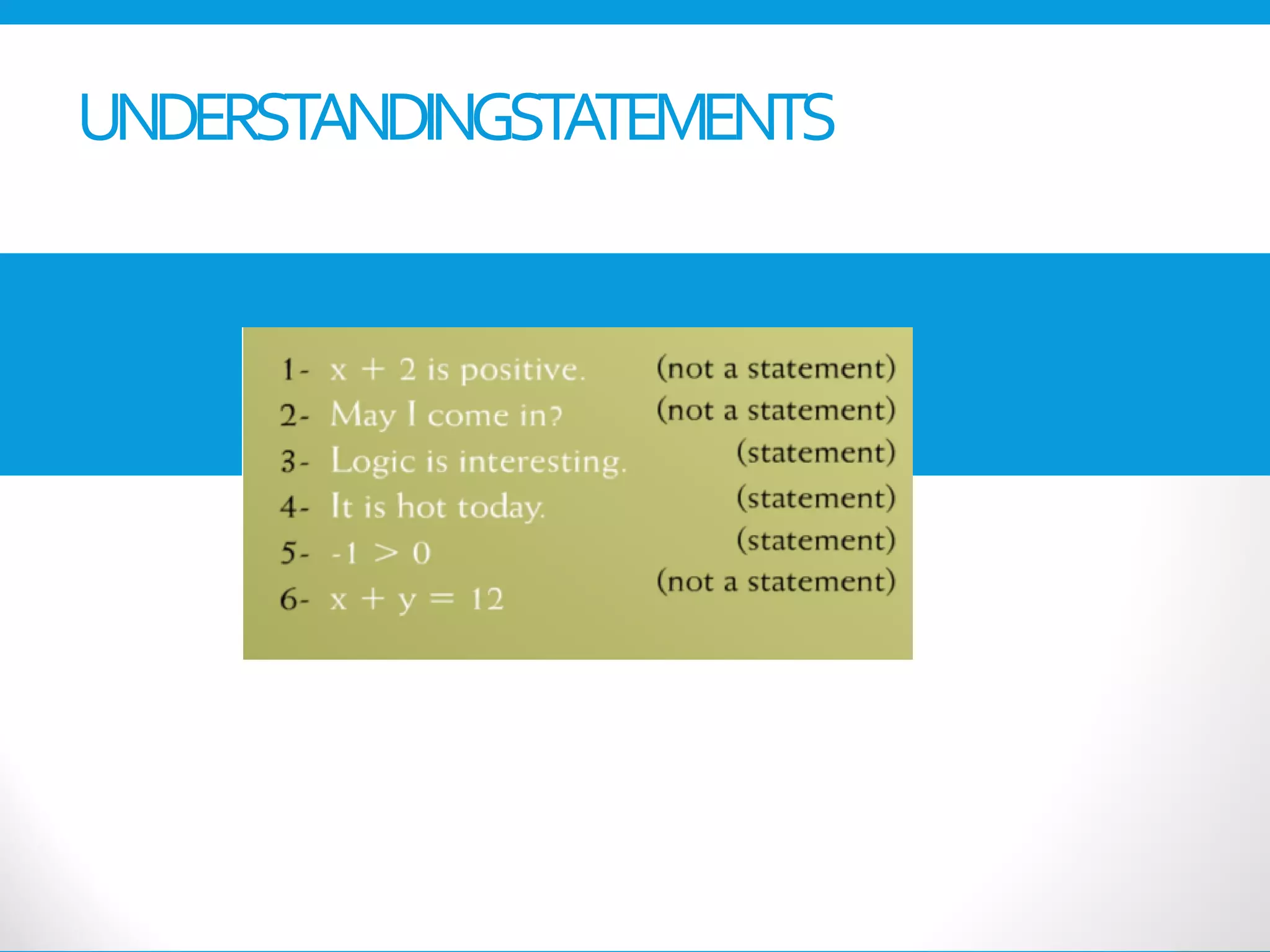
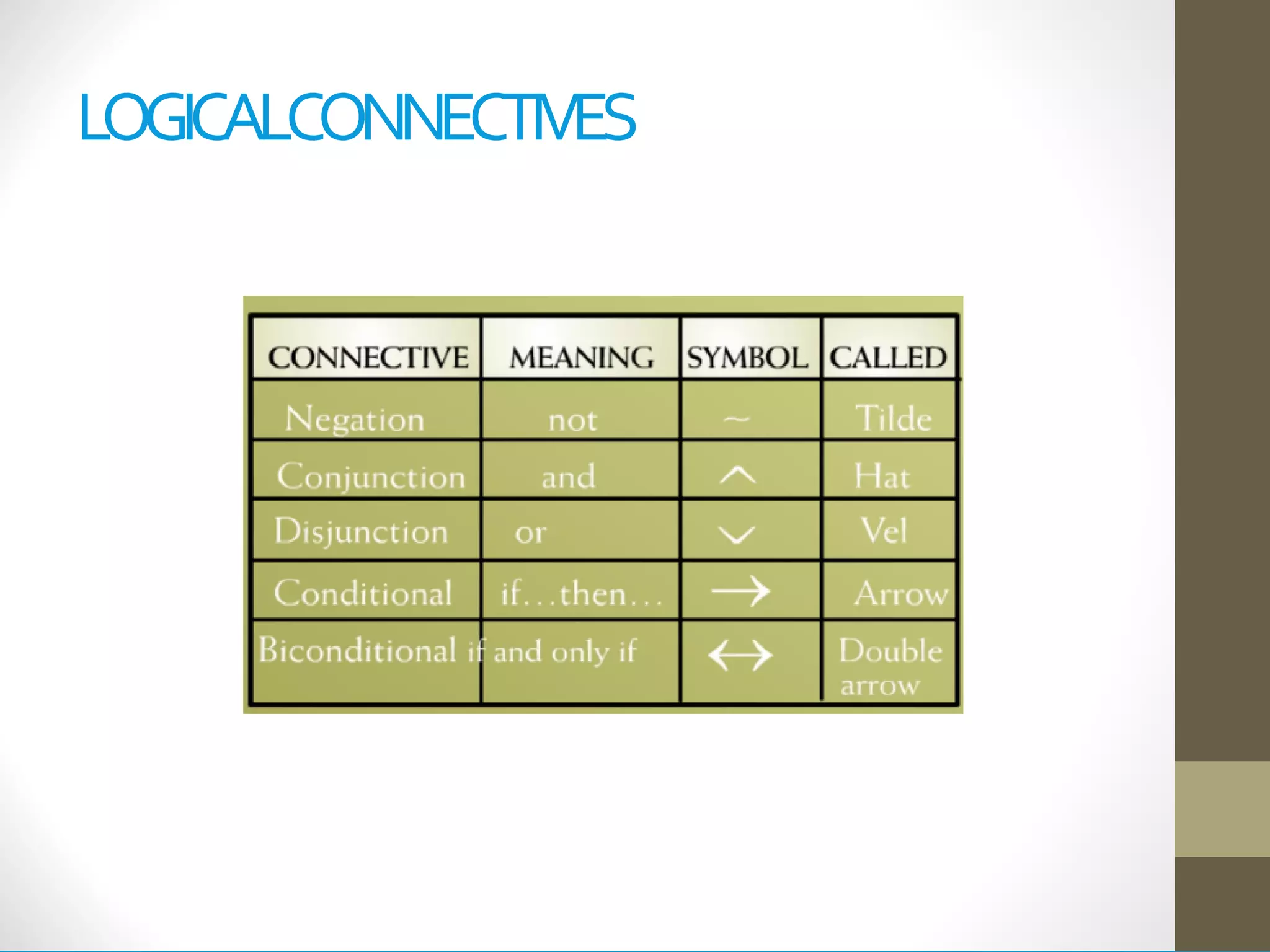
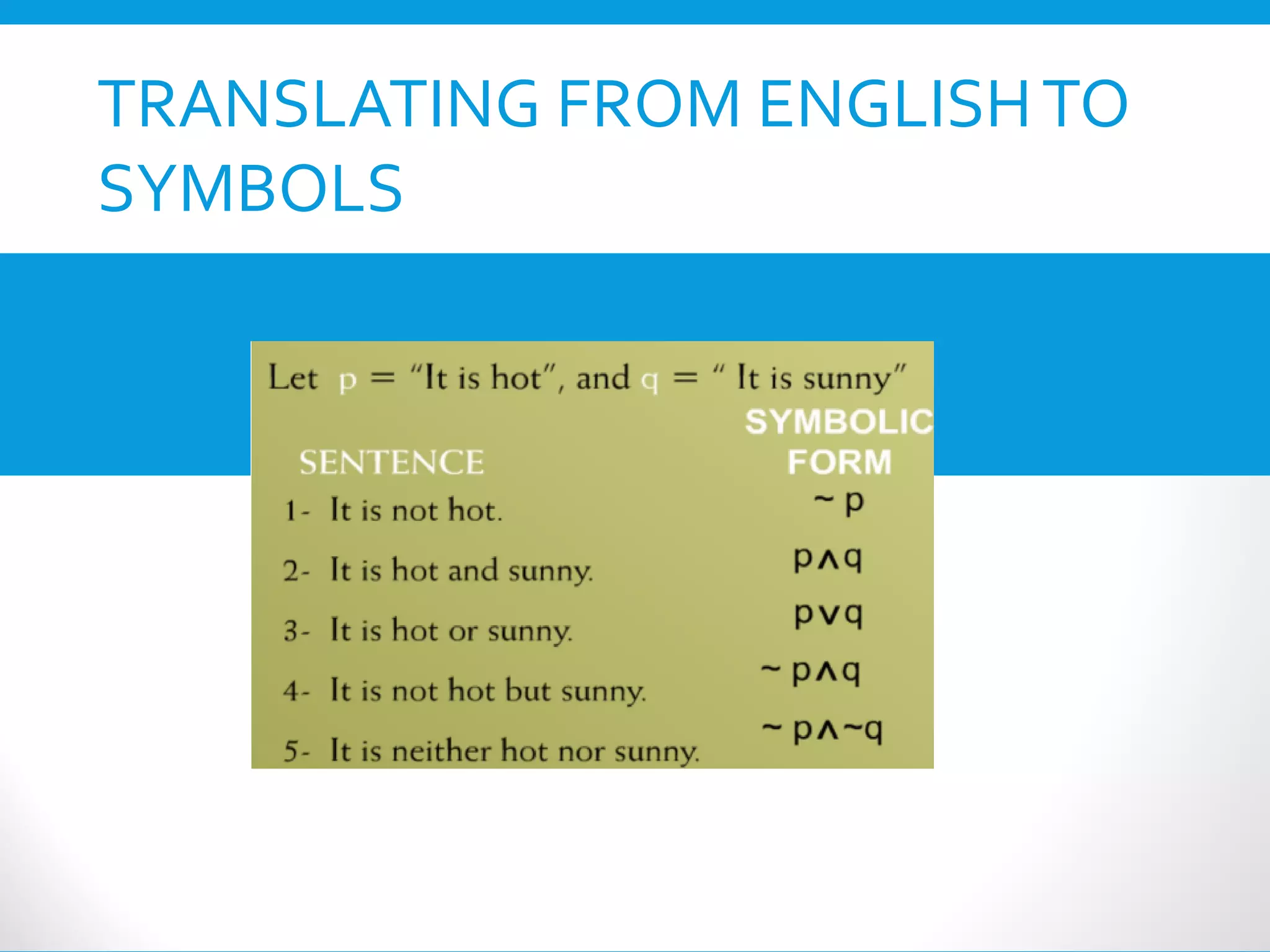
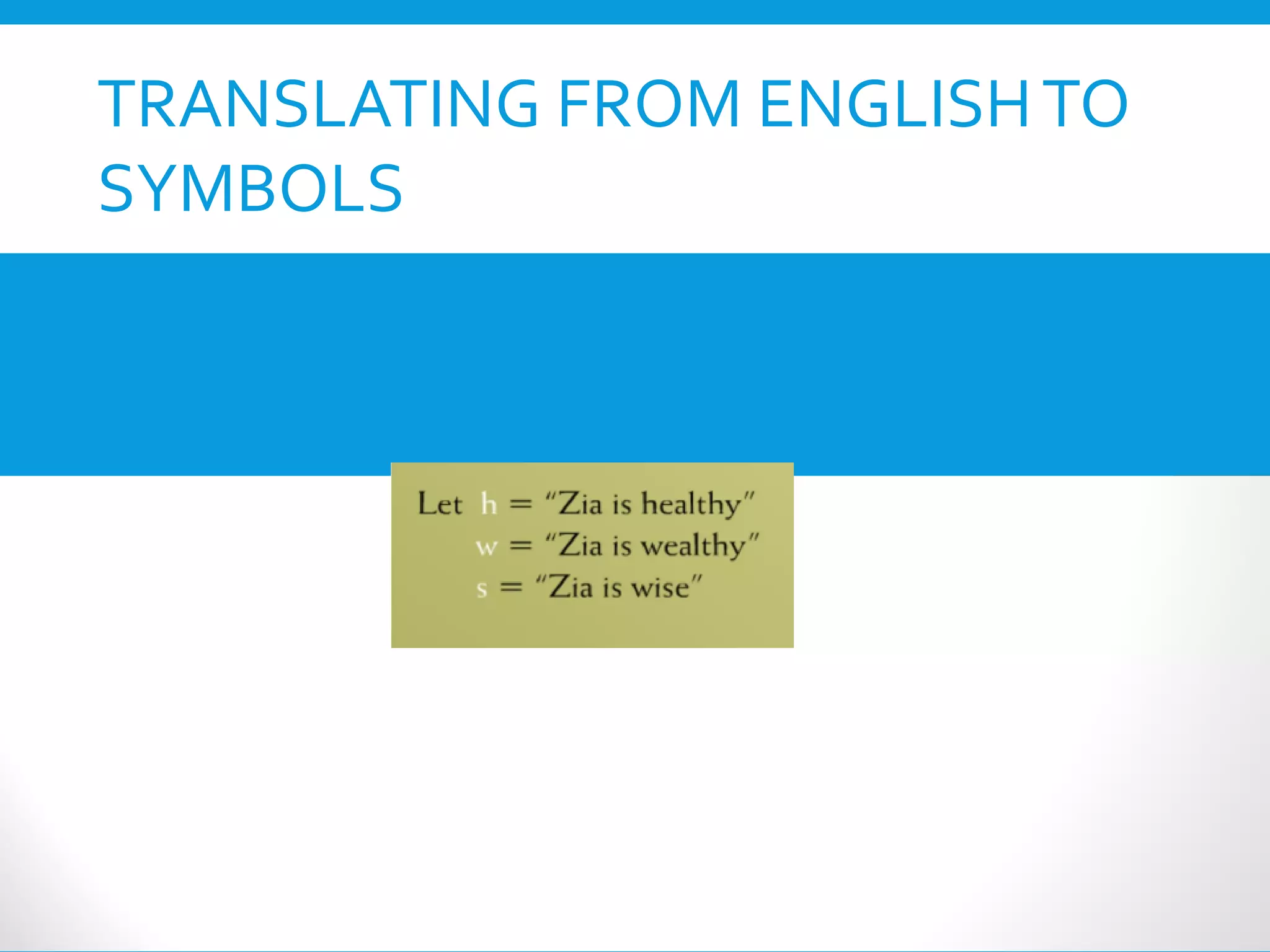
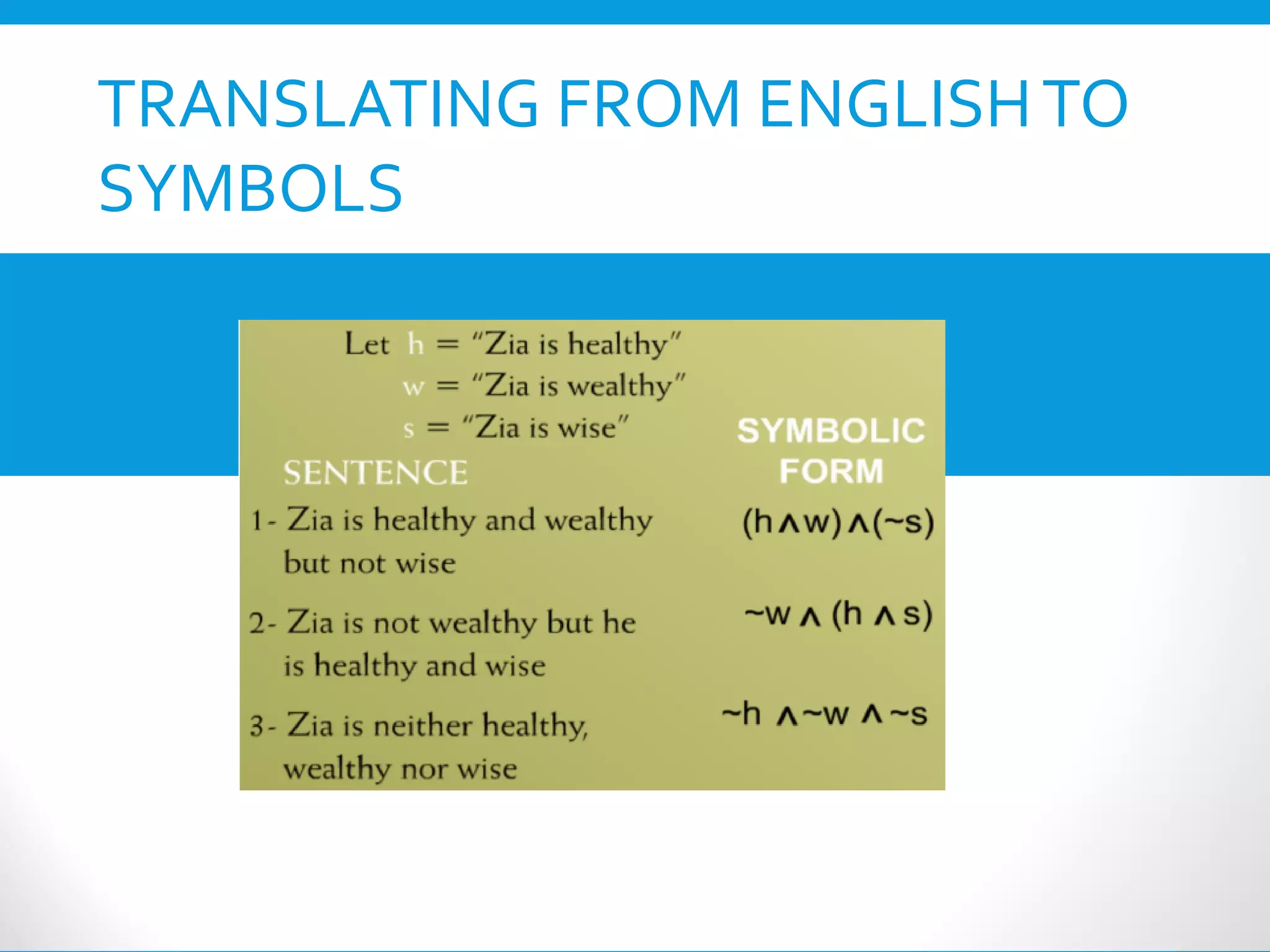
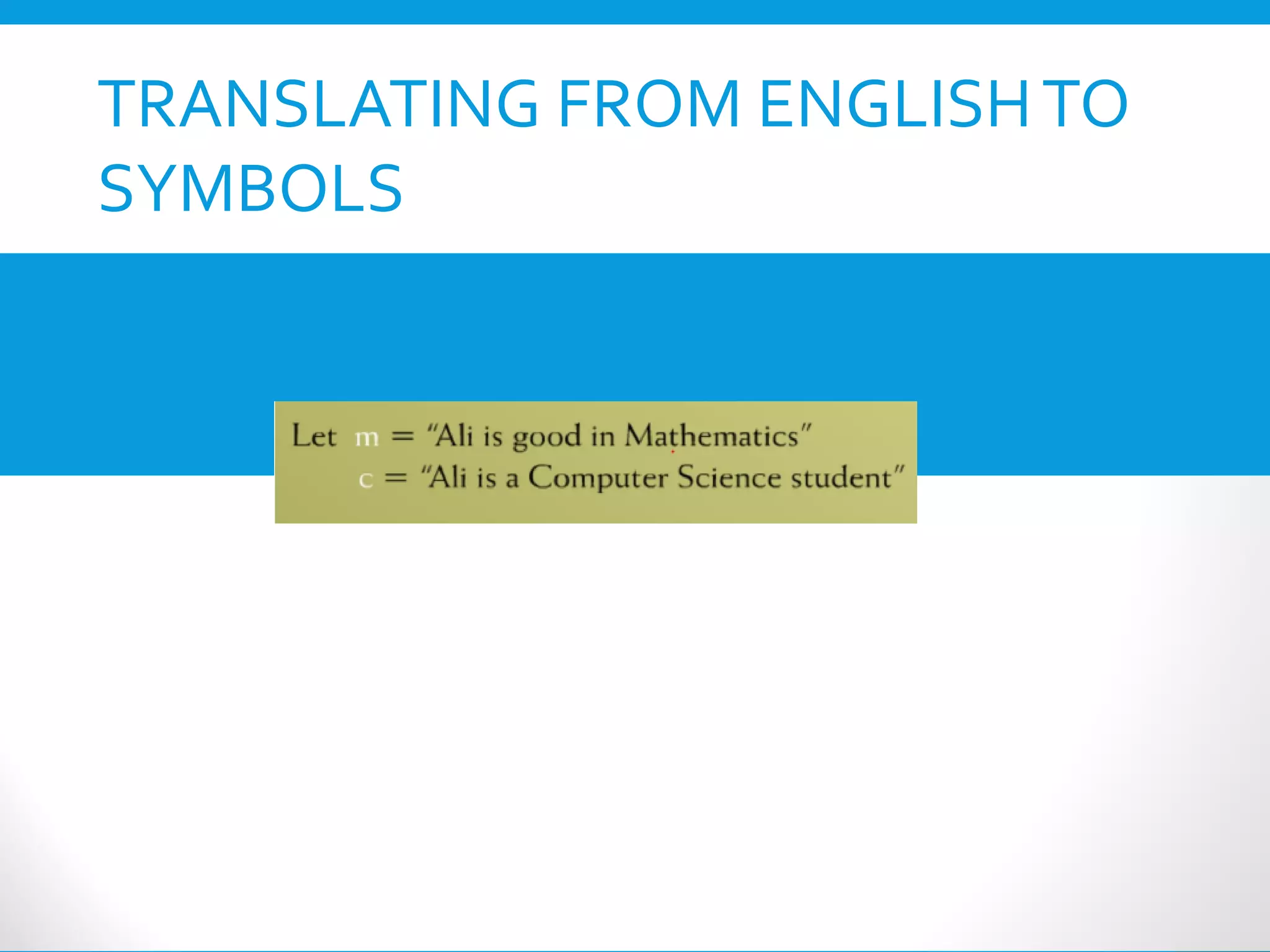
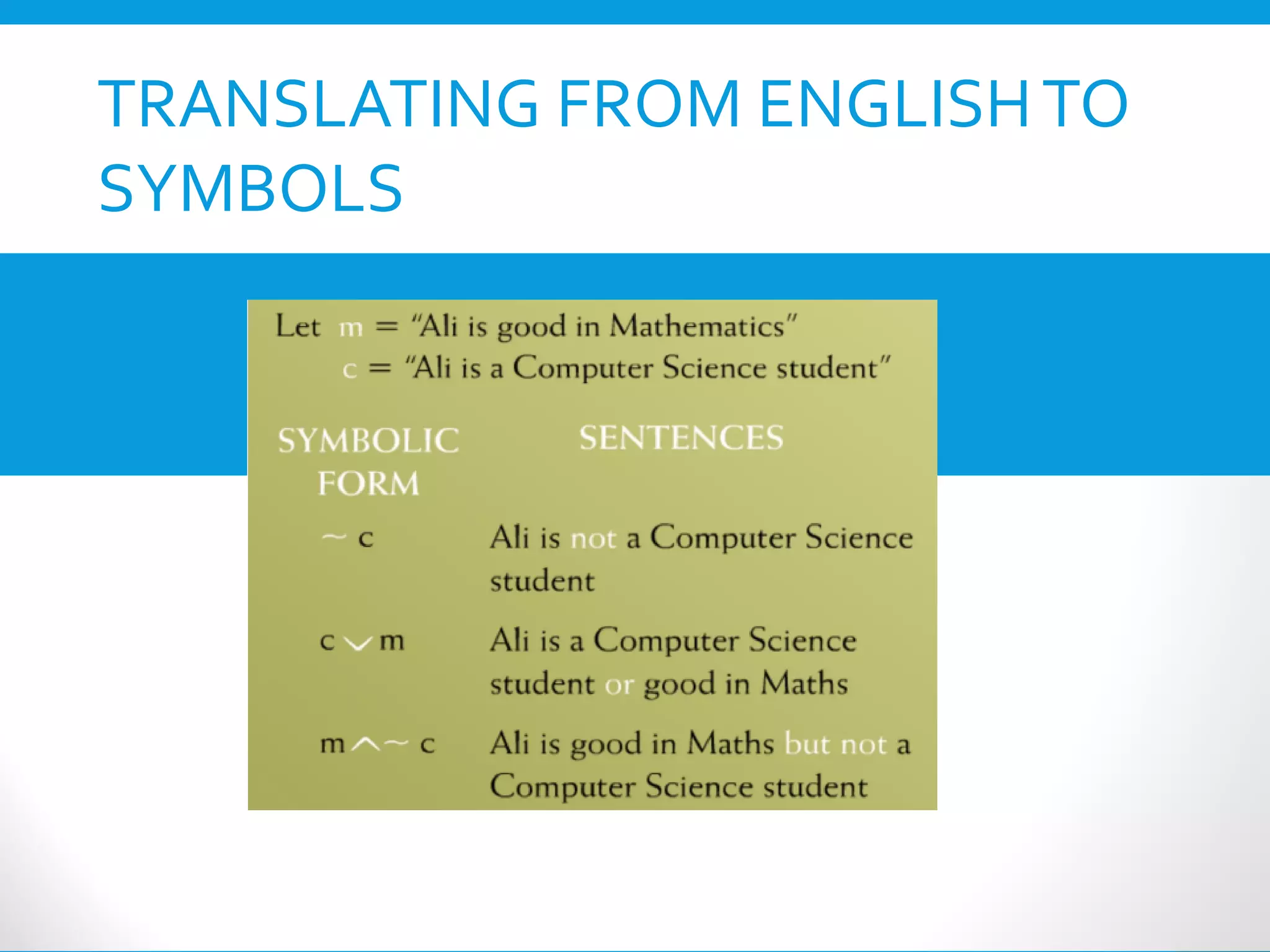
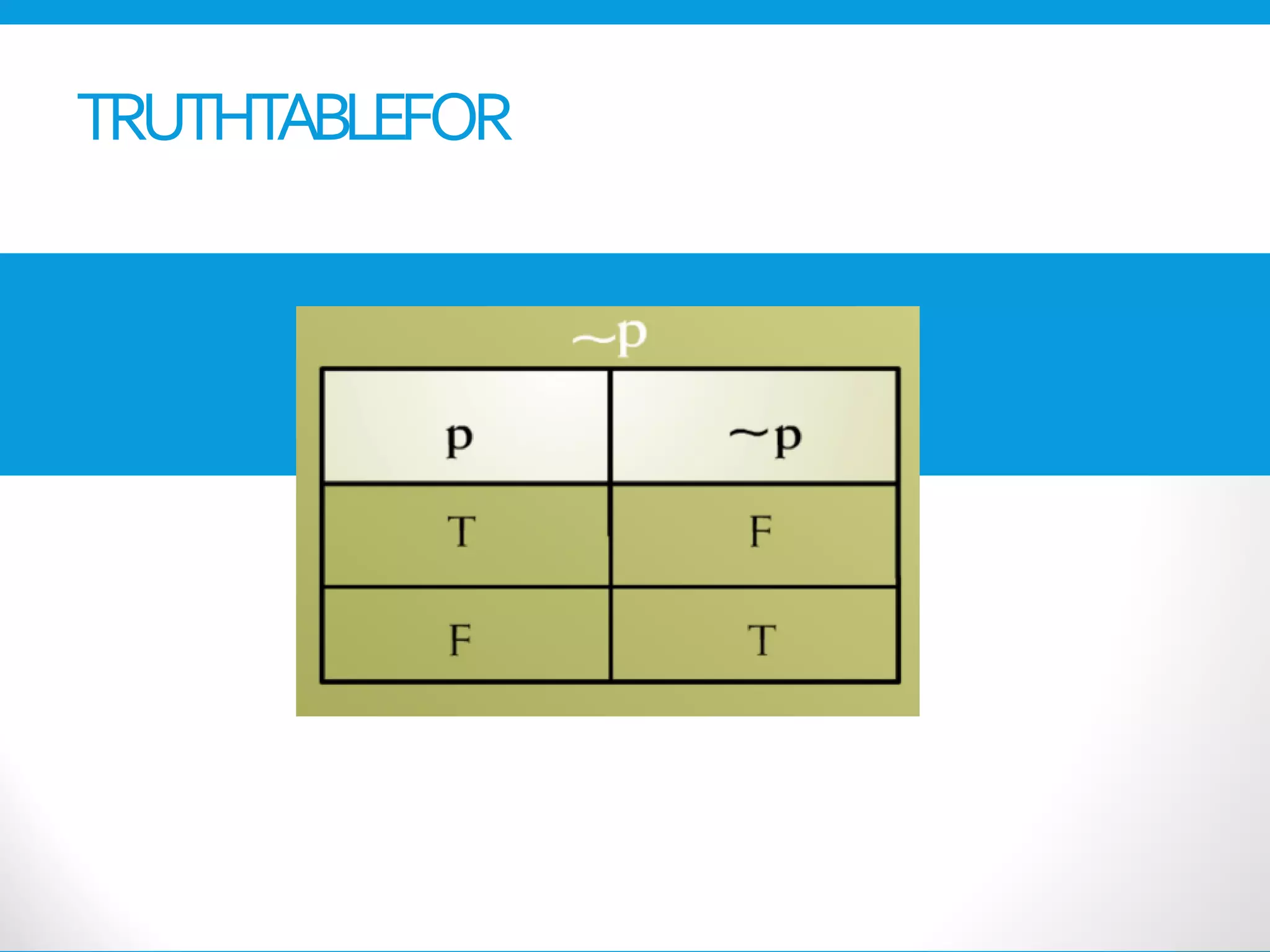
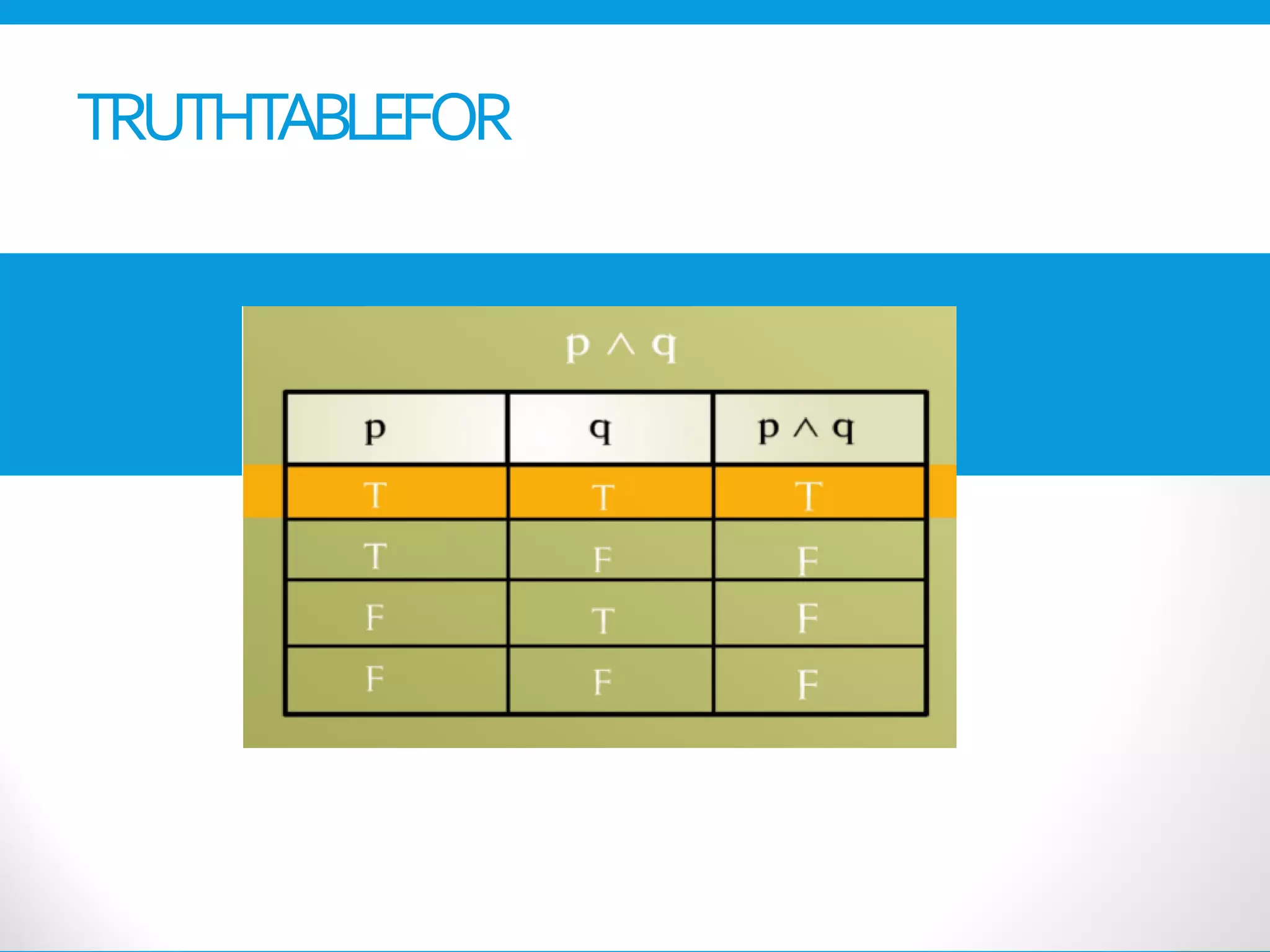
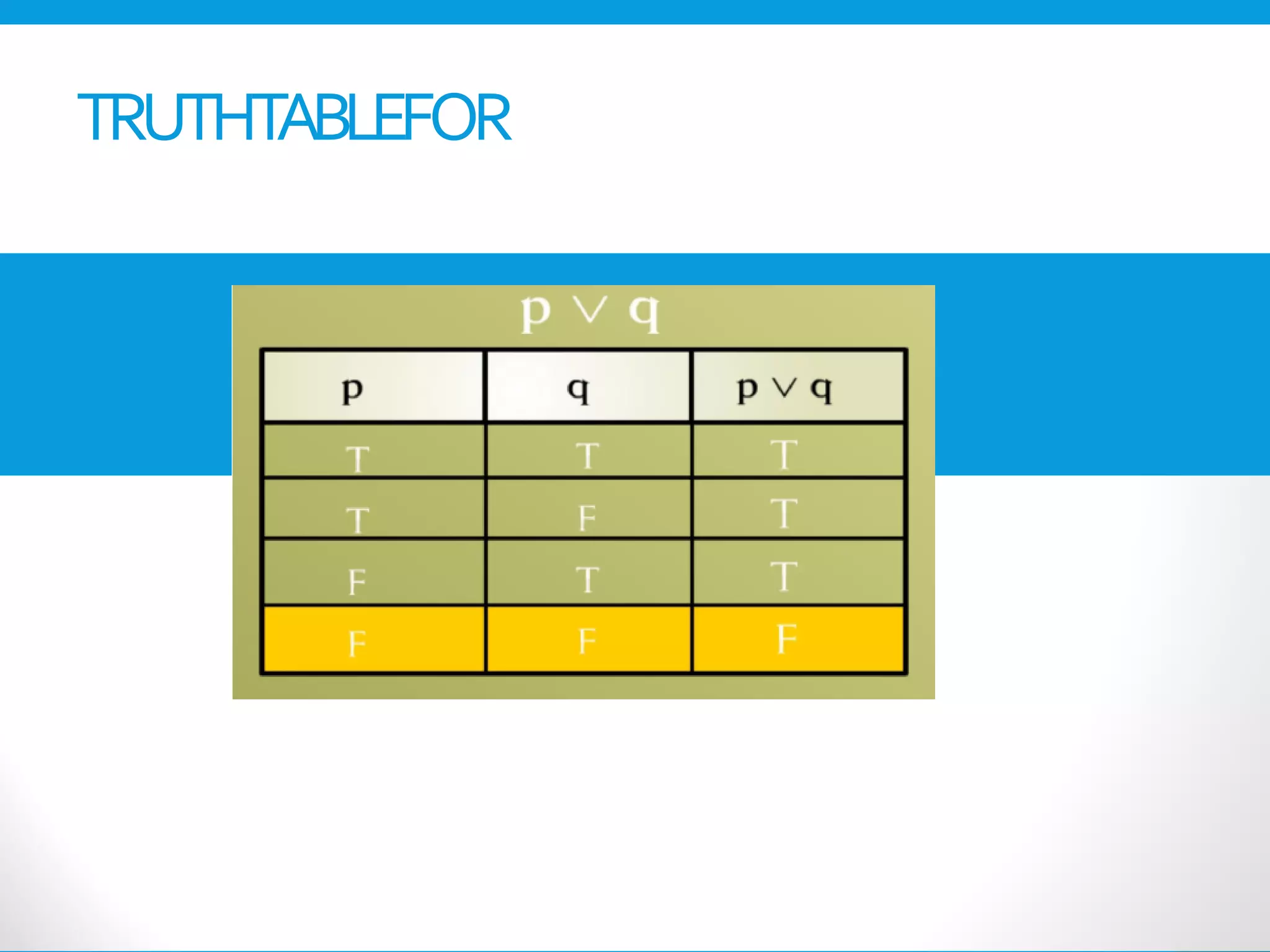
This document provides an introduction to the Discrete Structures course MAT-104. It includes the course objectives, which are to introduce topics like logic, set theory, functions, and graph theory. Active learning strategies like assignments and projects will be used. The course will be evaluated through quizzes, assignments, presentations, and a midterm and final exam. Policies around attendance and plagiarism are also outlined.