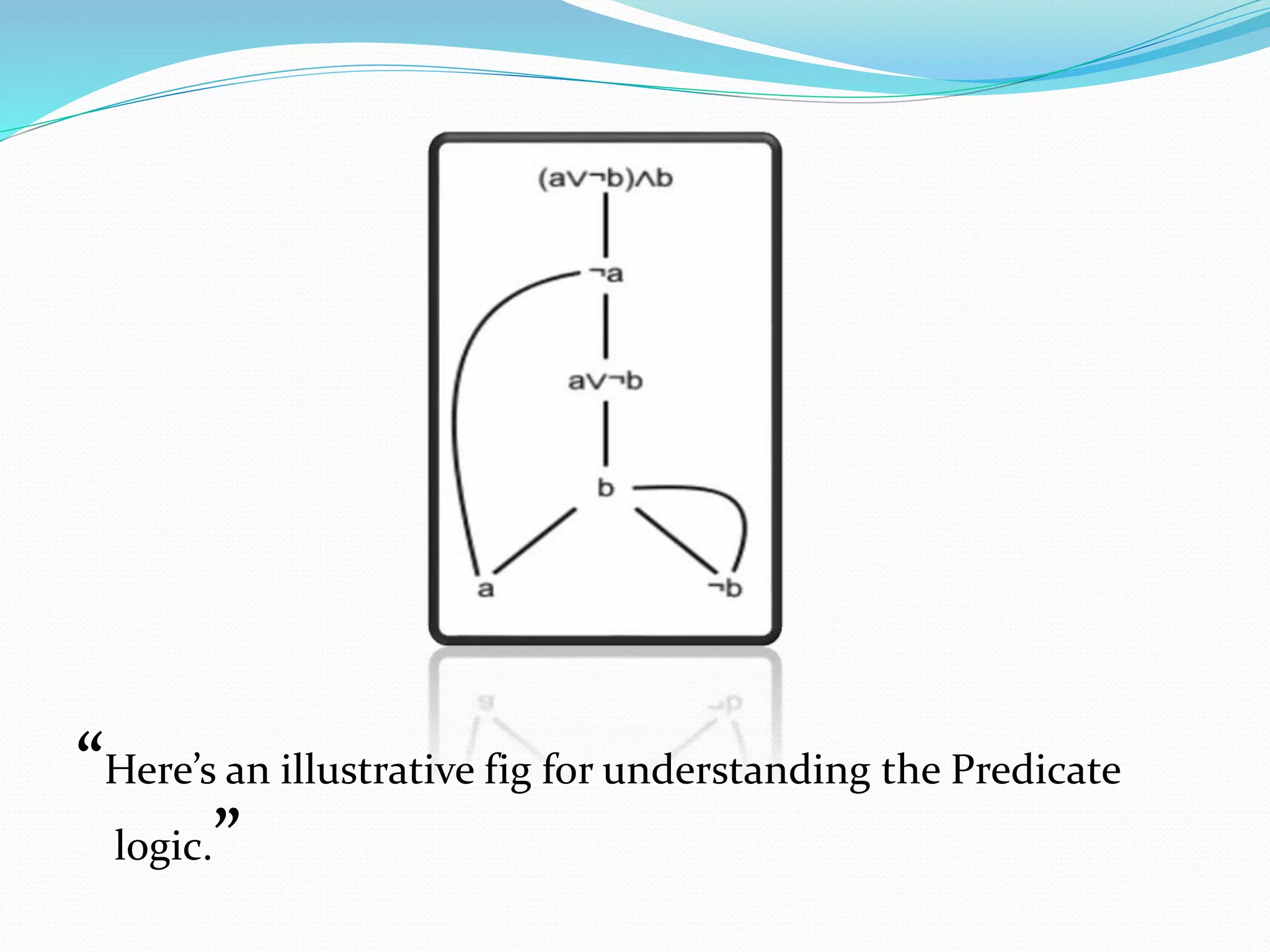
This document provides an introduction to First Order Predicate Logic (FOPL). It defines FOPL as symbolized reasoning where sentences are broken down into subjects and predicates. FOPL is more expressive than propositional logic and allows representing almost any English sentence. It discusses features of FOPL such as generalization of propositional logic and more powerful representation. Applications of FOPL include presenting arguments, determining validity, and formulating theories. The document also defines key terms in FOPL such as constants, variables, functions, and predicates.