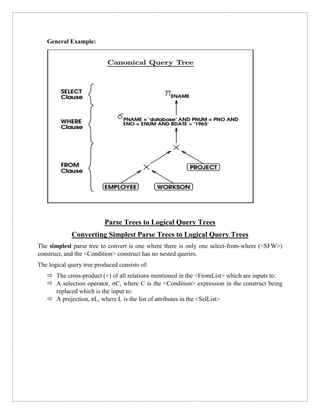
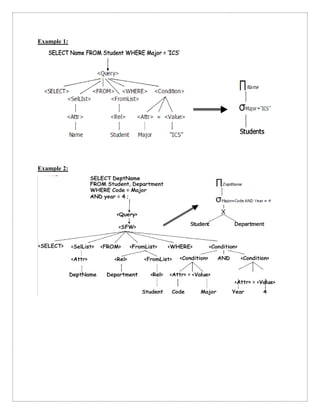
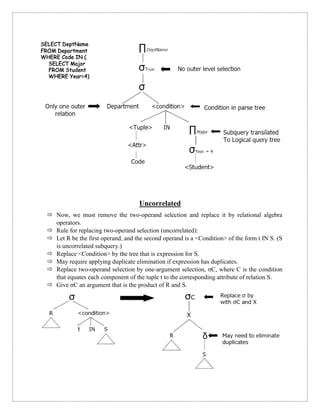
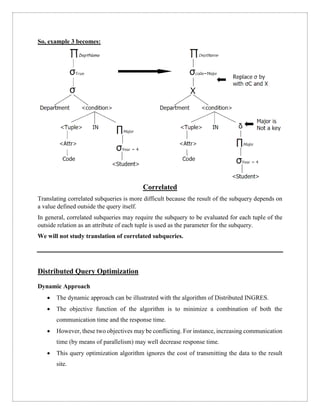
The document discusses query trees in the context of distributed query optimization, explaining their structure and the conversion from parse trees to logical query trees. It outlines various approaches to query optimization, including dynamic, static, semijoin-based, and hybrid methods, emphasizing the trade-offs between communication time and response time. Additionally, it covers the challenges presented by nested queries and the complexities involved in processing correlated subqueries.