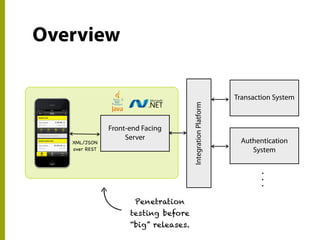
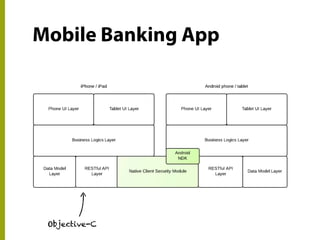
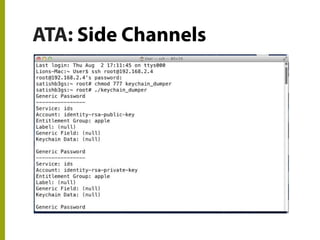
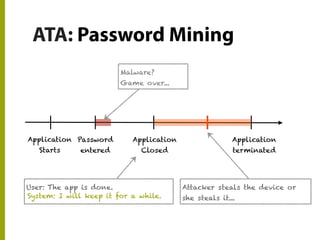
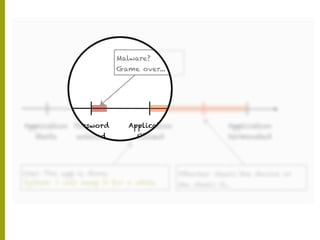
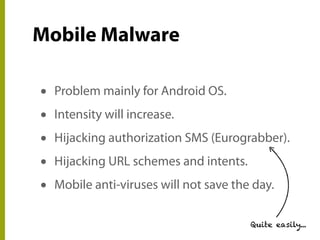
The document discusses the state of mobile banking security, highlighting features of mobile devices, banking architecture, and various security concerns, including attacks such as man-in-the-middle and fake applications. It emphasizes the need for better security measures, including multi-factor authentication and secure coding practices, due to the increasing threat of mobile malware. The presentation also covers the challenges in balancing user experience with security and calls for heightened awareness among users and developers regarding mobile security issues.