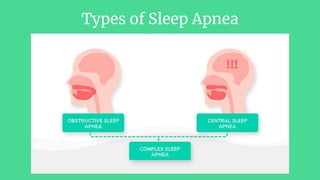
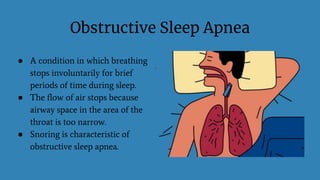
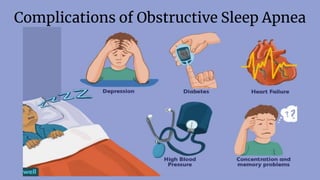
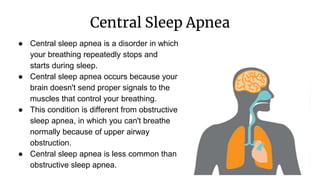
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts. There are two main types: obstructive sleep apnea caused by airway obstruction and central sleep apnea caused by the brain failing to signal breathing muscles. Risk factors include obesity, large tonsils, and certain anatomical features. Symptoms include loud snoring, daytime sleepiness, and headaches. Diagnosis involves a polysomnogram sleep study. Treatments aim to keep the airway open and can include CPAP, surgery, and weight loss.