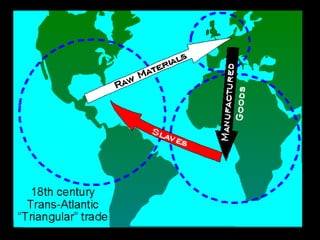
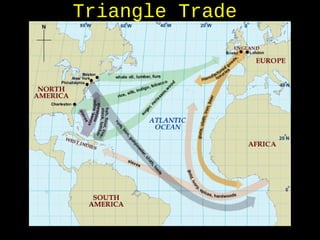
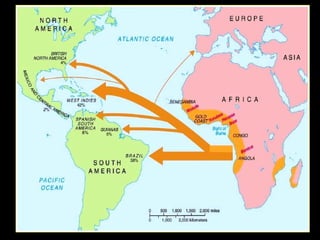
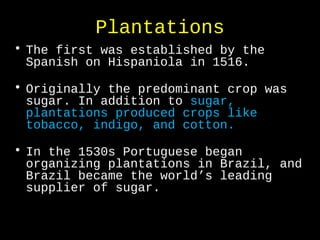
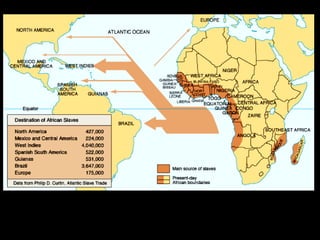
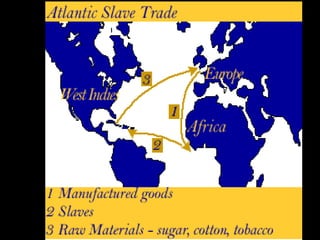
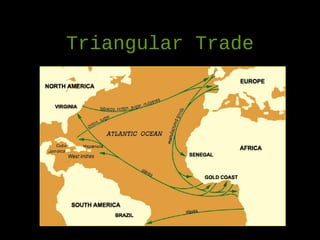
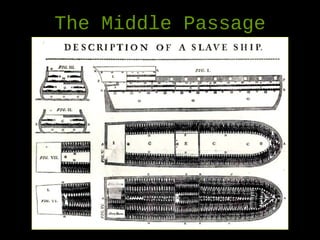
African slavery had significant economic and cultural impacts on the development of the Americas. Economically, slavery made plantation agriculture like sugar cane and tobacco profitable by providing a large, forced labor supply. This led to wealth in colonies, especially Brazil which became a leading sugar producer. Culturally, the slave trade resulted in the diffusion of African traditions and languages to the Americas, increasing diversity. The triangular trade route connected Europe, West Africa, and the Americas financially and facilitated the inhumane export and forced labor of millions of Africans across the Atlantic.