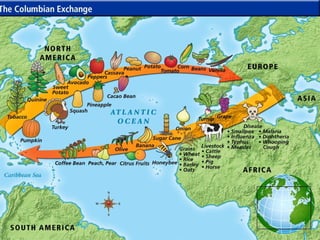
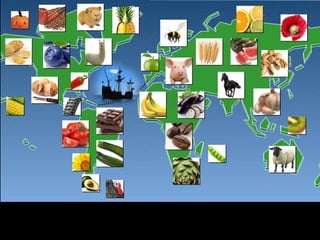
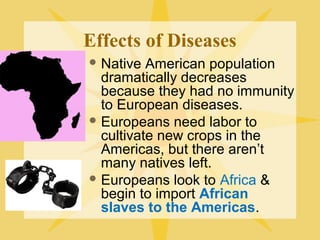
The document discusses the Columbian Exchange that occurred following contact between Europe and the Americas. It led to widespread cultural and biological changes. Animals, plants, and diseases were exchanged between the two regions. Smallpox and other diseases brought by Europeans devastated native populations in the Americas, while crops native to the Americas like potatoes, tomatoes, and maize became staples in European diets and economies. The global impacts of the Columbian Exchange were wide-reaching.