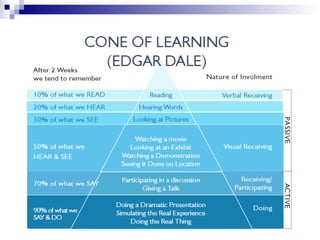
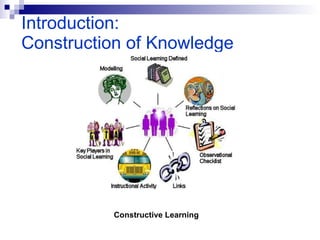
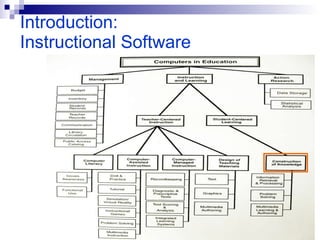
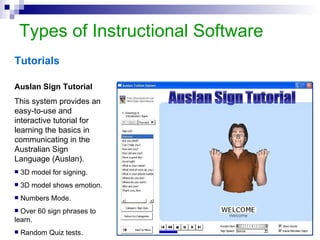
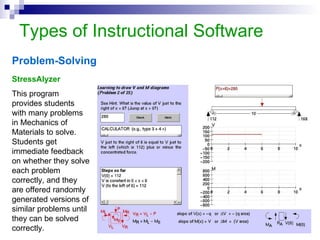
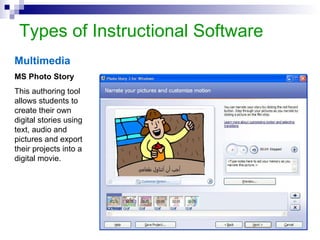
This document discusses instructional simulation and its use in education. It defines simulation as the imitation of a real process or system. Simulations allow students to be actively involved in learning, compress time, save resources, and repeat experiments safely. The document outlines different types of simulations including physical, interactive, constructive, and computer simulations. It provides examples of simulation software used in different subject areas and discusses the benefits simulations provide for student learning.
![Instructional Simulation Alaa Sadik, Ph.D. Department of Instructional & Learning Technologies College of Education, Sultan Qaboos University www.alaasadik.net [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simulationppt1479/75/Instructional-Simulation-1-2048.jpg)