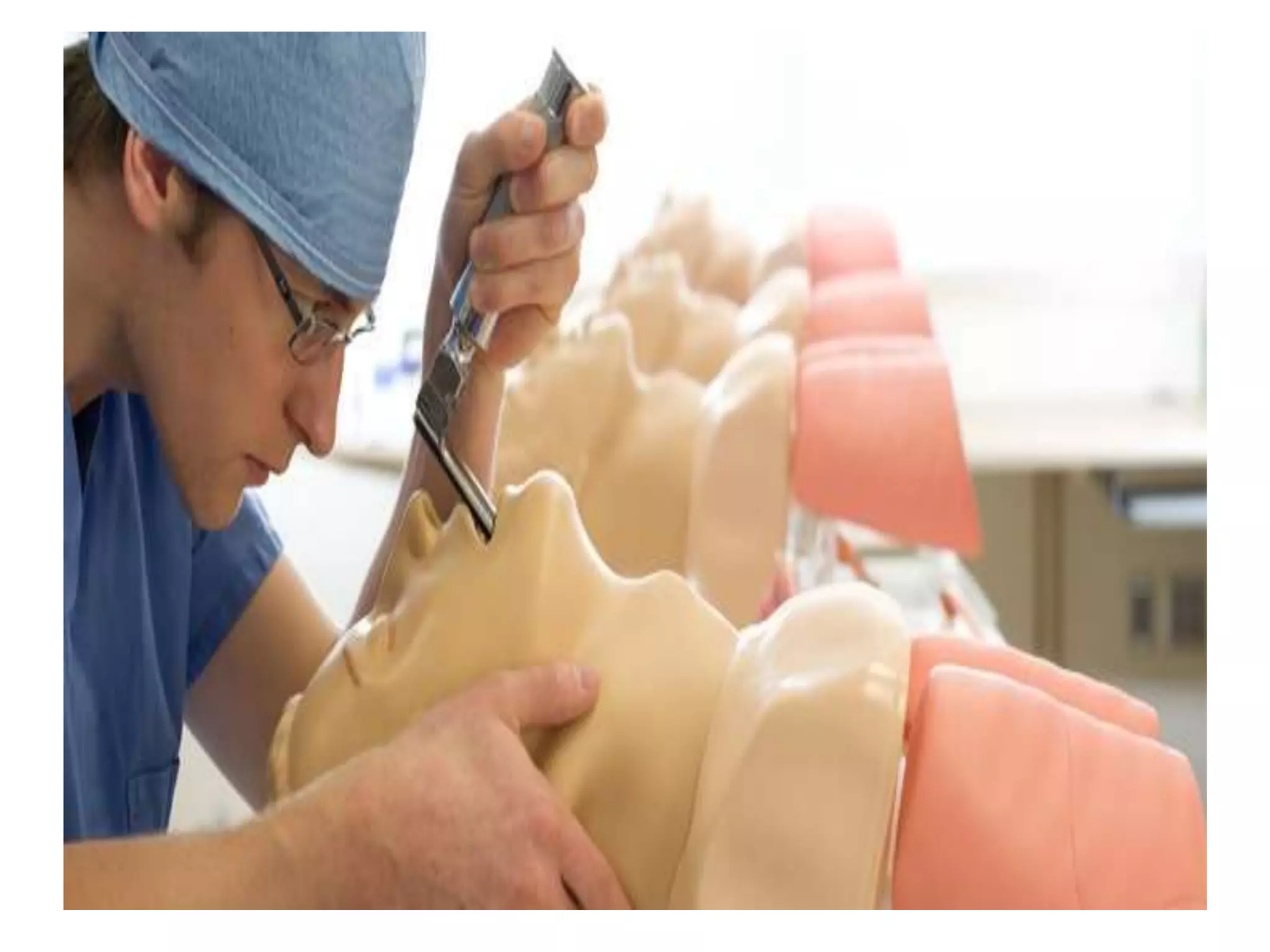
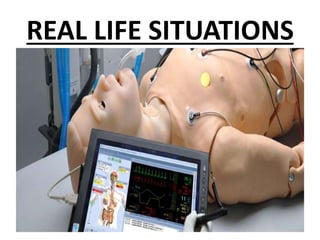
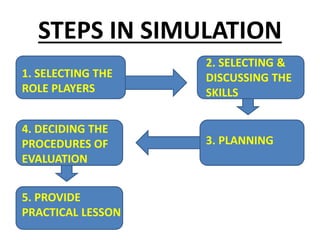
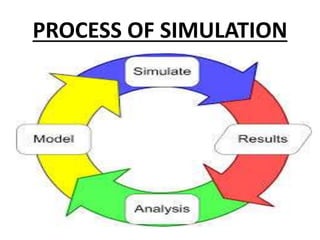
This document discusses simulations and provides definitions, principles, values, and steps involved. A simulation is a visual representation of a process that can require user input. It imitates real-world processes over time by developing a model. Simulations allow players to take on roles and make decisions to experience consequences. They promote critical thinking, help students understand decision-making, and enable empathy. Key steps in simulations include selecting role players, discussing skills, planning, and providing feedback. Common simulation activities are role playing, sociodrama, and gaming.