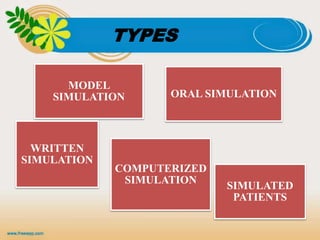
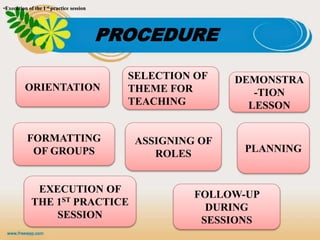
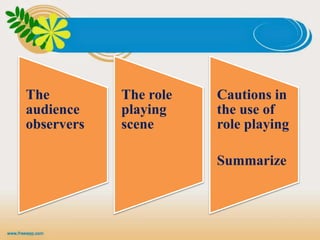
The document presents a presentation on simulation and role play in education, emphasizing their importance in developing decision-making and problem-solving skills among students. It outlines the principles, advantages, and disadvantages of both methods, highlighting how simulation bridges theory and practice while role play enhances communication and group problem-solving abilities. Ultimately, the document concludes that these techniques significantly contribute to the training of competent teachers by building confidence and practical skills.