Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times

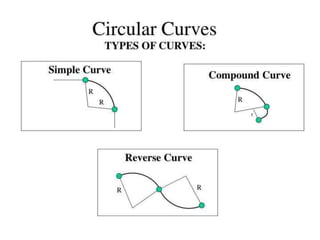
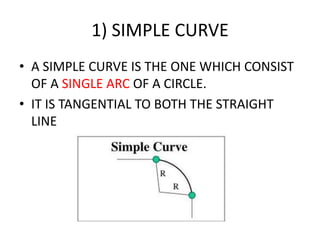
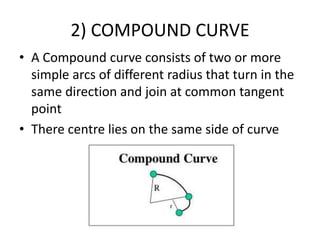
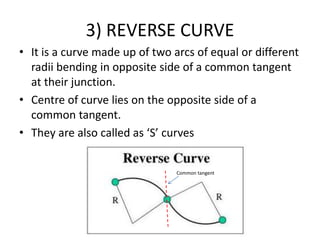
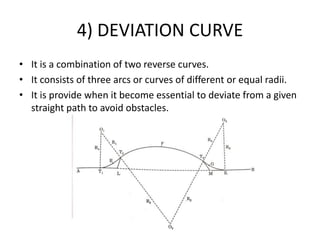
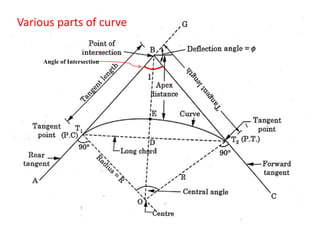
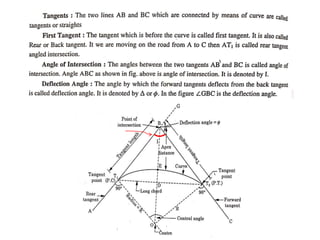
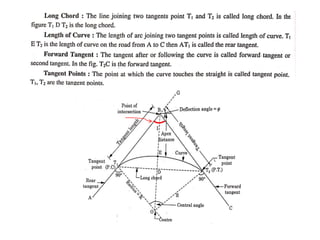
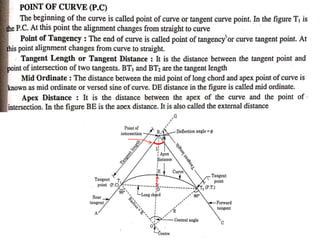

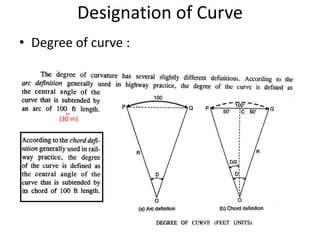
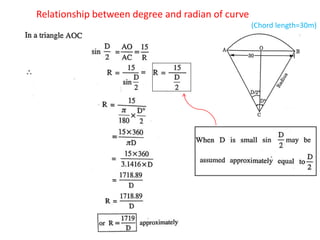
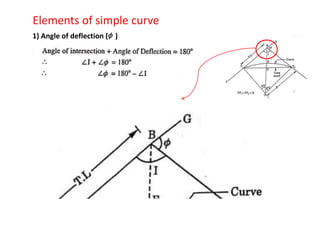
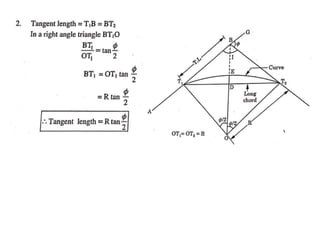
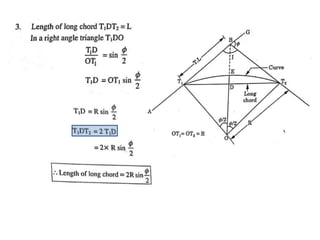
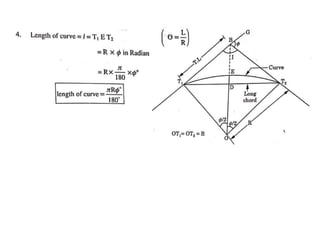
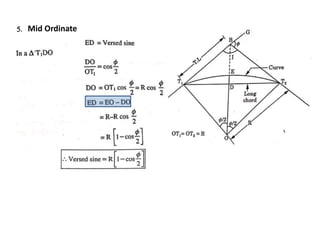
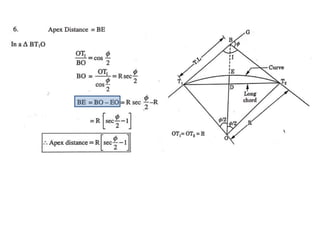

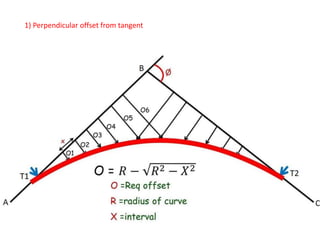

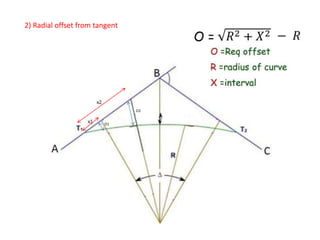


This document discusses different types of curves used on highways and railways to change the direction of motion. A simple curve consists of a single arc of a circle that is tangential to both the straight lines it connects. It is defined by its radius or degree of curvature. The elements of a simple curve include the angle of deflection and mid ordinate offsets that define its shape and position relative to the tangent lines.
























