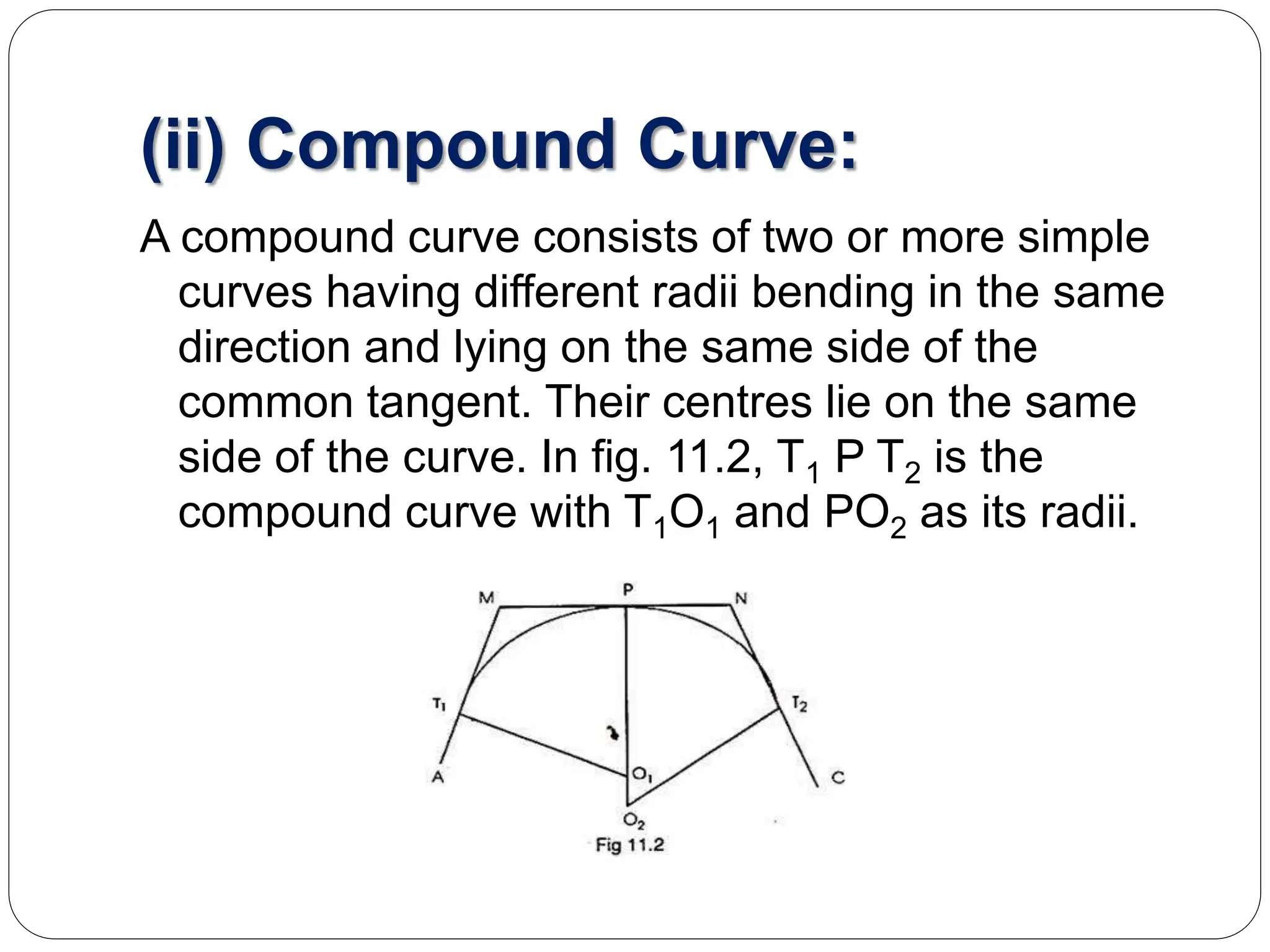
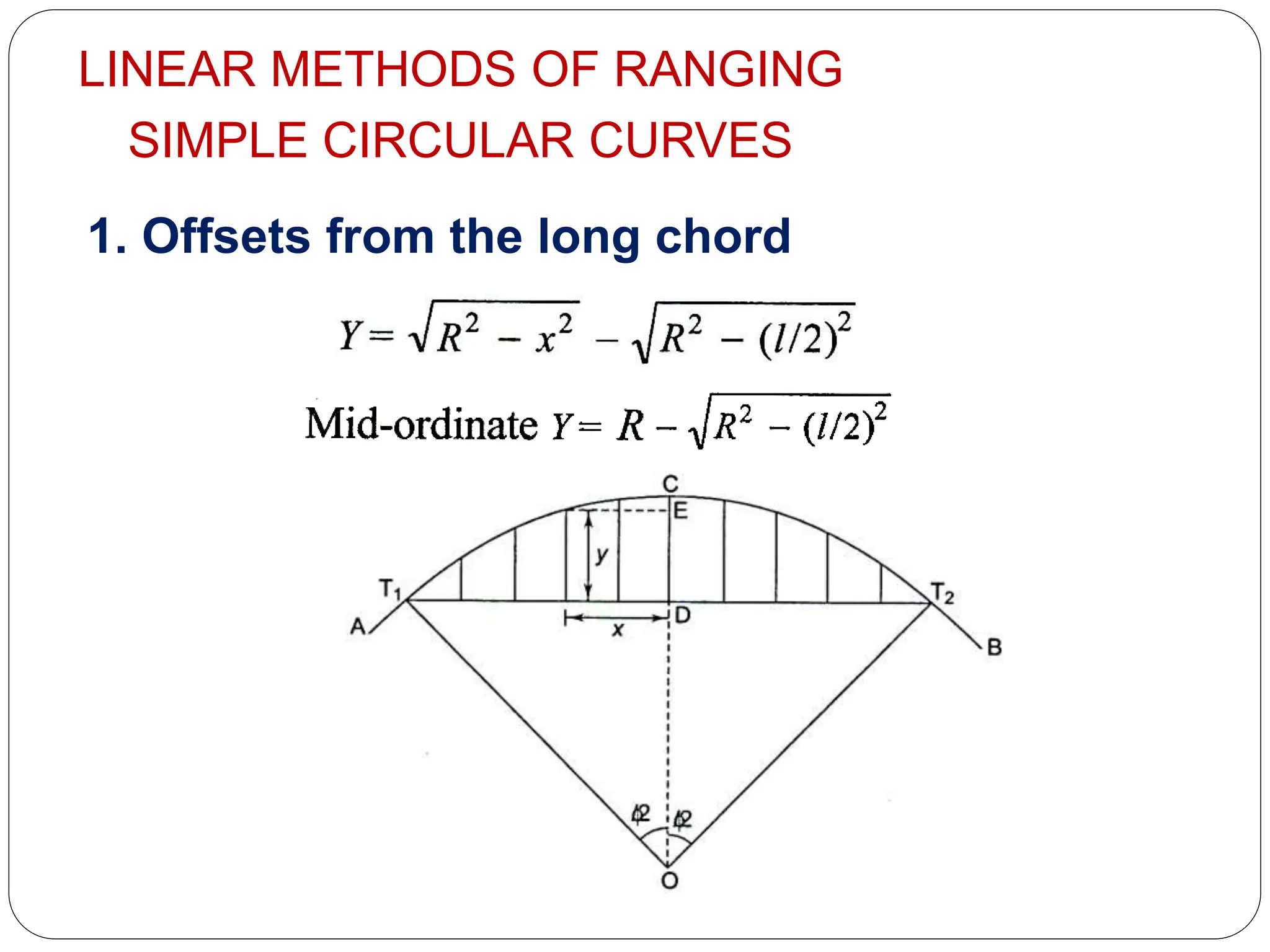
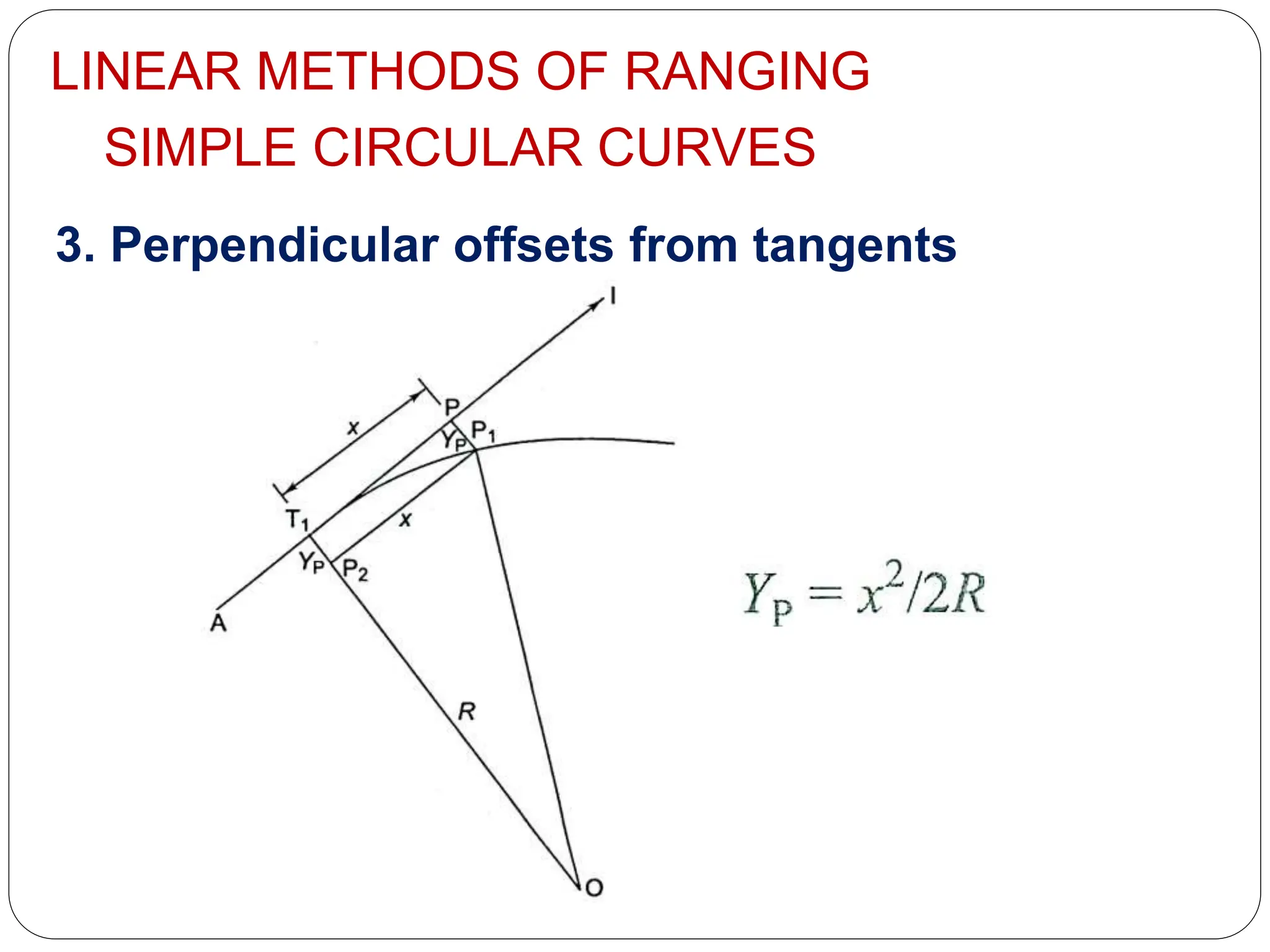
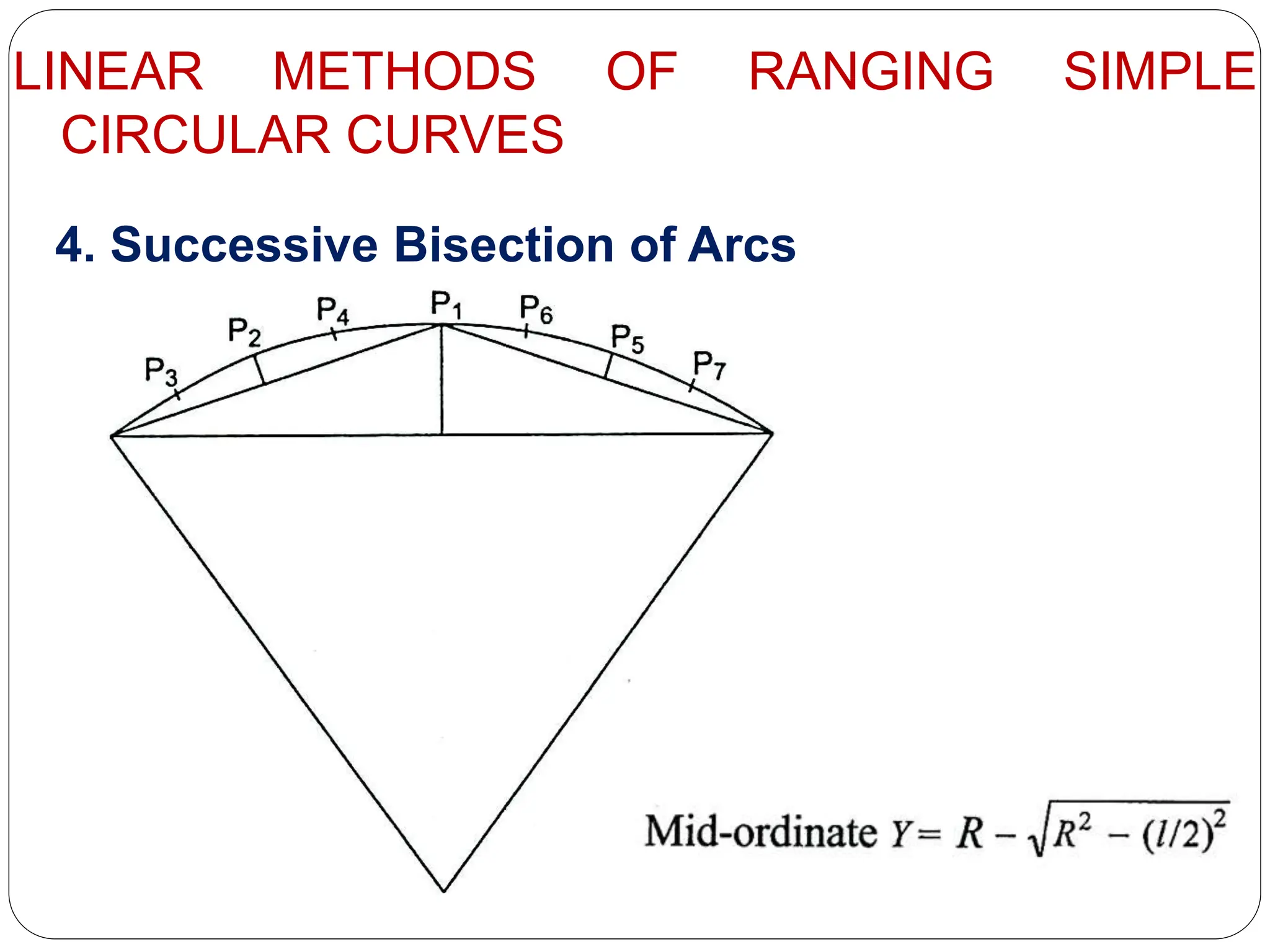
The document discusses different types of curves used in civil engineering projects including roads, railways, and canals. It defines simple, compound, reverse, and deviation curves. Simple curves consist of a single circular arc connecting two straight lines, while compound curves use two or more arcs of different radii bending in the same direction. Reverse curves use two arcs bending in opposite directions. Terminology for curve surveying is also outlined, and linear methods for laying out simple circular curves are described, including offsets from the long chord, radial offsets from tangents, and perpendicular offsets from tangents. The document provides examples to calculate curve parameters and set out a curve given information like the deflection angle, tangent distance, and radius.