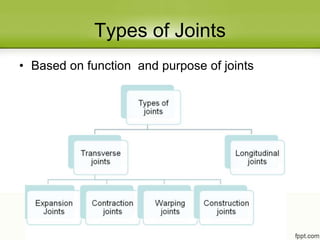
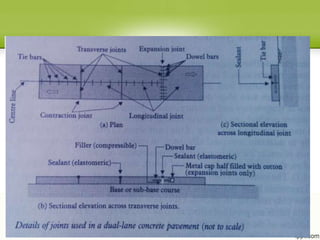
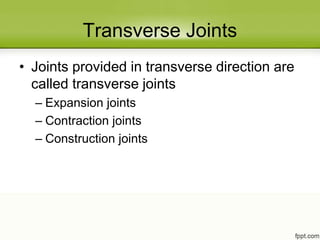
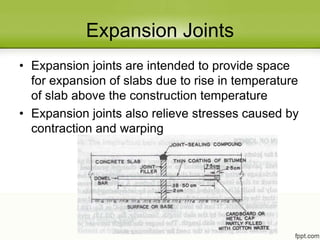
Concrete slabs in pavements are susceptible to cracking due to volumetric changes from temperature variations, shrinkage, and moisture changes. To prevent cracking, joints are provided at regular intervals to allow for expansion, contraction, and warping. The main types of joints are transverse joints (expansion joints with space for expansion, contraction joints with grooves) and longitudinal joints between traffic lanes. Proper spacing of joints depends on factors like temperature range, slab thickness, and reinforcement. Contraction joint spacing is calculated based on coefficients of friction and concrete tensile strength, while expansion joint spacing considers the temperature rise.