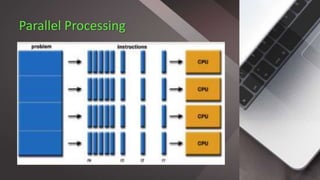
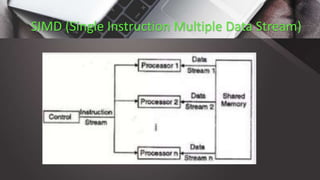
Parallel processing involves using multiple processors simultaneously to solve computational problems. It breaks problems into discrete parts that can be solved concurrently. Examples include multicore processors and hyper-threading CPUs. Benefits include reduced time, ability to solve larger problems, cost savings, and concurrency. Vector processors operate on arrays of data called vectors to improve performance of numerical simulations. SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) architecture executes the same instruction on multiple data elements at once using multiple processing units with a single control unit. Intel introduced MMX as an early SIMD instruction set, allowing single instructions to process multiple data simultaneously. The main advantage of SIMD is improved performance from processing multiple data elements concurrently, while disadvantages include larger register sizes, higher power consumption