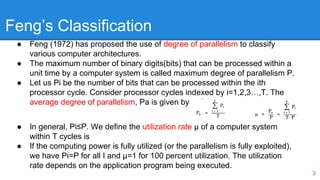
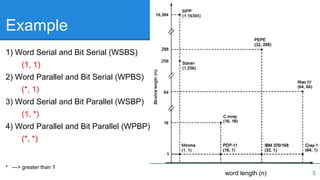
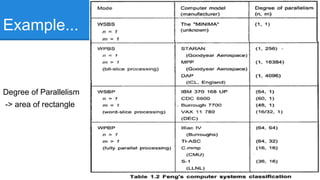
Feng's Classification from 1972 classified computer architectures based on their degree of parallelism. It defined the maximum degree of parallelism P as the maximum number of bits that can be processed within a unit of time. Architectures were classified into four categories based on whether processing occurred at the word and bit level serially or in parallel: word serial/bit serial, word parallel/bit serial, word serial/bit parallel, and word parallel/bit parallel. The degree of parallelism P is calculated as the product of the number of bits in a word and the number of words processed in parallel.