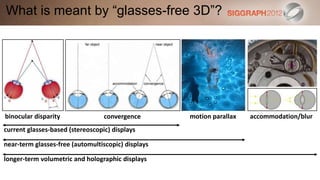
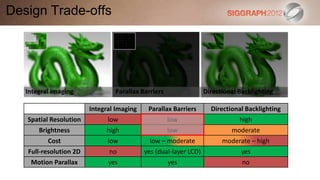
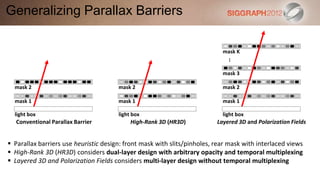
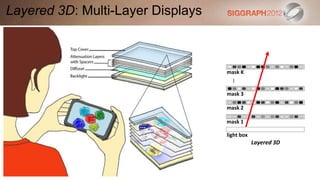
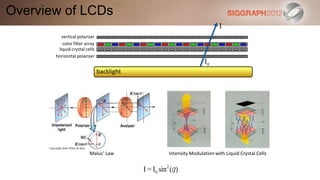
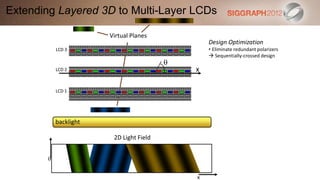
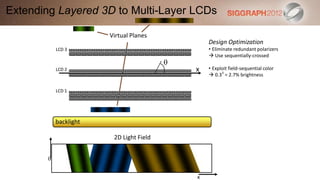
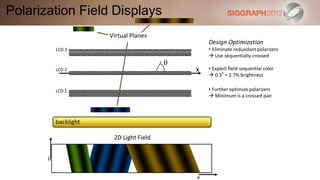
This document discusses various technologies for glasses-free 3D displays. It begins with a taxonomy that categorizes direct 3D display technologies as either glasses-bound or unencumbered. It then focuses on unencumbered automultiscopic displays, discussing multi-layer displays like layered 3D and polarization fields, as well as dual-layer displays using a technique called High-Rank 3D. Specific technologies like parallax barriers, integral imaging, and directional backlighting are also covered.


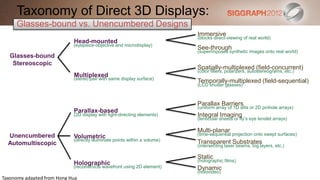


![Taxonomy of Direct 3D Displays:
Dynamic Holograms (Holovideo)
Tay et al. MIT Media Lab Spatial Imaging Group
[Nature, 2008] [Holovideo, 1989 – present]
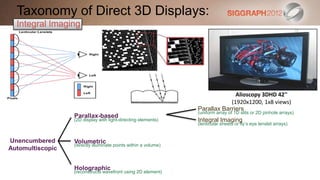
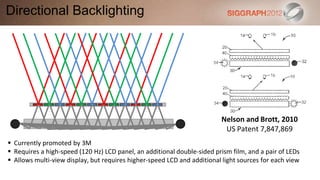
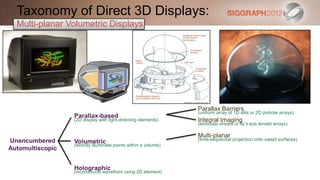
Parallax Barriers
(uniform array of 1D slits or 2D pinhole arrays)
Parallax-based
(2D display with light-directing elements) Integral Imaging
(lenticular sheets or fly’s eye lenslet arrays)
Multi-planar
Unencumbered (time-sequential projection onto swept surfaces)
Volumetric
(directly illuminate points within a volume) Transparent Substrates
Automultiscopic (intersecting laser beams, fog layers, etc.)
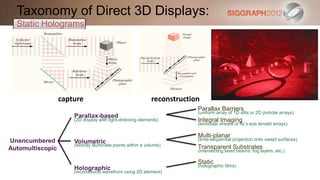
Static
(holographic films)
Holographic
(reconstructs wavefront using 2D element) Dynamic
(holovideo)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3computationallightfielddisplays-120815123039-phpapp01/85/SIGGRAPH-2012-Computational-Display-Course-3-Computational-Light-Field-Displays-10-320.jpg)

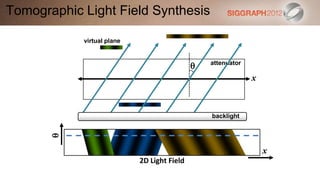
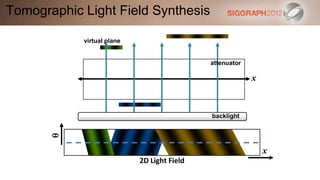

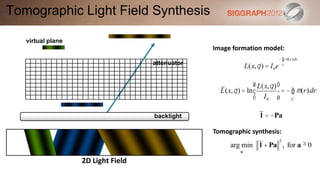
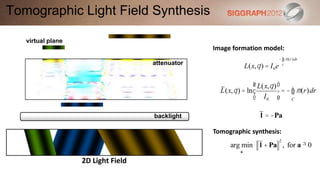






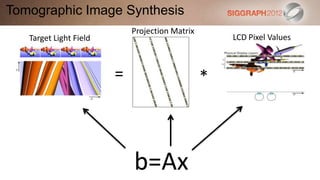
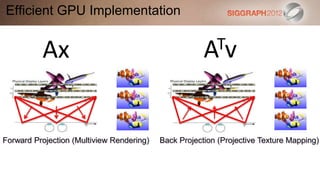
![SART [Simultaneous Algebraic Reconstruction Technique]
b=Ax
pre-compute some weights
initial guess
ATv Ax update
clamp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3computationallightfielddisplays-120815123039-phpapp01/85/SIGGRAPH-2012-Computational-Display-Course-3-Computational-Light-Field-Displays-33-320.jpg)



![Analysis of Parallax Barriers
k
L[i,k]
i
k
g[k]
f[i]
i
L[i,k]
`
light box
L[i, k] = f [i]× g[k] L[i, k ] f [i] g[k ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3computationallightfielddisplays-120815123039-phpapp01/85/SIGGRAPH-2012-Computational-Display-Course-3-Computational-Light-Field-Displays-42-320.jpg)
![Analysis of Parallax Barriers
L[i,k]
k
g[k]
i
f[i] `
light box
T
Ken Perlin et al. An Autosteroscopic Display. 2000. L[i, k] = å ft [i] Ä gt [k]
Yunhee Kim et al. Electrically Movable Pinhole Arrays. 2007.
t=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3computationallightfielddisplays-120815123039-phpapp01/85/SIGGRAPH-2012-Computational-Display-Course-3-Computational-Light-Field-Displays-43-320.jpg)
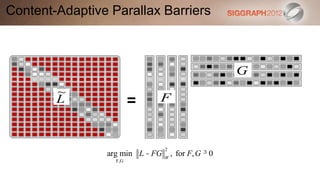
![Content-Adaptive Parallax Barriers
L[i,k]
G
k
g[k]
i ~`
f[i] F L
light box
~
L FG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3computationallightfielddisplays-120815123039-phpapp01/85/SIGGRAPH-2012-Computational-Display-Course-3-Computational-Light-Field-Displays-44-320.jpg)