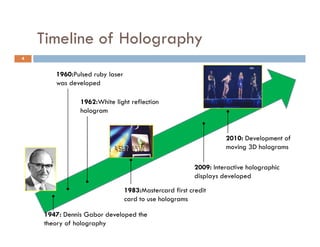
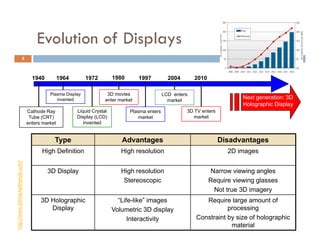
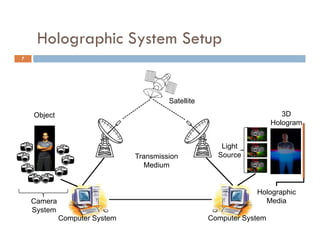
The document outlines the evolution and future potential of holographic technology, detailing its value proposition, system setup, components, and current limitations. It emphasizes advancements in laser systems, microprocessors, and photorefractive materials that drive the effectiveness and cost of holographic displays. Future opportunities for holography span various industries including advertising, education, and medical fields, highlighting a trend towards immersive experiences leveraging 3D and virtual reality.




![Light Source: Evolution
g
12
Mercury Solid-state Semiconductor
arc lamp laser
l laser di d
l diodes
(1948) (1960s) (1980s)
Dr. Theodore [1]
Maiman
studies a ruby
crystal in the
shape of a
cube in a laser.
[1] http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/269607/holography/92904/Pulsed-laser-holography](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mt5009holographyfinal-110424213808-phpapp01/85/3D-Holography-When-Might-it-become-Economically-Feasible-12-320.jpg)
![Laser System: Performance
y
13
1) The lower the laser power the longer the exposure time
power,
A second to few minutes for CW lasers vs. “nanoseconds” for Pulsed lasers
2) Laser power requirement
i) Increases with Size of holograms
Typical
T i l power l l H N l
levels: HeNe lasers: 1 20 W Di d lasers: 5-50mW,
1-20mW, Diode l 5 50 W
DPSS lasers: 20-200mW, Ar lasers with etalon: 100-500mW
For large holograms, on the order of 10-sq m, laser powers on the order
of 1 W i preferred if cost i not an issue [1] solid-state or A i gas
f 1-W is f d t is t i lid t t Ar ion
lasers as candidates
ii) Increases with Distance of hologram set-up
Min. power output for laser light shows: ~400mW
[1] http://www.loreti.it/chaptersPDF/Ch11_Non-Laser_Illum.pdf
[3] h // i ll i /P d /D /CVIMG H l h Whi df](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mt5009holographyfinal-110424213808-phpapp01/85/3D-Holography-When-Might-it-become-Economically-Feasible-13-320.jpg)
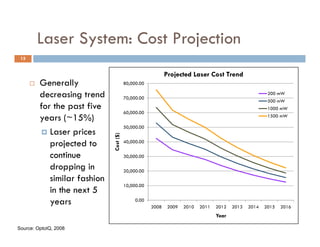
![Laser System: Performance vs. Cost
y
14
3) Higher laser power systems translate to higher costs
(several thousand to tens of thousand dollars) [1]
Laser System Costing
35000 CW
Pulsed
30000
25000
20000
Cost ($)
15000
10000
5000
0
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400
Power (mW) * Modulator & optic system costs not included [1]
[1] Diode pumped SSL Costs: http://www.amazing1.com, 2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mt5009holographyfinal-110424213808-phpapp01/85/3D-Holography-When-Might-it-become-Economically-Feasible-14-320.jpg)
![Holographic Media
g p
16
Comparison in Key Performance Metrics in Holographic Recording
Materials [1,2]
M t i l [1 2]
120% 30,000
Recording medium
100% 25,000 should have
High diffraction
Diffraction Efficiency (%)
)
1)
Resolution Limi (um)
80% 20,000
efficiency
60% 15,000 2) Wide resolution
range
g
it
40% 10,000
Max. Resolution limit [um]
Max. Resolution limit [mm−1]
20% 5,000 Min. Resolution limit [um]
Min. Resolution limit [mm−1]
Max. efficiency Effi i
Max. Diff
M Diffraction Efficiency
i
0% 0
Dichromated gelatin
Photopolymers
Elastomers
Photographic emulsions
Photographic emulsions
Photothermoplastics
Photochromics
otorefractives
Photoresists
(Phase bleached)
mplitude)
P
Pho
e,
P
(Am
[1] Lecture Holography and optical phase conjugation held at ETH Zürich by Prof. G. Montemezzani in 2002
[2] Ablation of nanoparticles for holographic recordings in elastomers: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/la102693m](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mt5009holographyfinal-110424213808-phpapp01/85/3D-Holography-When-Might-it-become-Economically-Feasible-16-320.jpg)
![Holographic Media
g p
17
1) Silver Halide Emulsion
High exposure sensitivity over a wide range of spectral regions
High resolving power
Suitable for transmission/reflection holograms (amplitude and phase type)
/ g ( p p yp )
2)
5) Dichromated Gelatin Material
Photorefractive polymer [1]
Record multicolour reflection holograms the 3D telepresence
Used for 3D dynamic holograms, enables
Suitable f veryi highl efficiency and low noise holograms
No d for
N need for special glasses
l
3) Photorefractive Crystals seconds; quasi real-time
Refreshes images every 2
Good for large-area and holography
Material use for real-time dynamically updatable holographic recording media
Recyclable! Photothermoplastics can also b recycled several h d d times and are
l bl h h l l be l d l hundred d
most suitable for holographic interferometry
4) Photoresist Material
Suitable for producing surface relief holograms
Most sensitive to ultraviolet/blue light only.
[1] P.-A. Blanche et al, Holographic three-dimensional telepresence using large-area photorefractive polymer, Nature Volume:
468, Pages: 80–83, 04 November 2010, DOI 10.1038/nature09521](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mt5009holographyfinal-110424213808-phpapp01/85/3D-Holography-When-Might-it-become-Economically-Feasible-17-320.jpg)
![Photorefractive Polymer: Performance
y
18
1) Refresh Rate
University of Arizona (UA) took 2 s to write & erase a full-colour dynamic holographic
image in 2010 vs. 4 mins in 2008 [1,2]
marked improvement of ~100x in 2 years!
Quoting UA lead author of the study Blanche,
“In two years we improved the speed by a factor of 100. If we can improve the speed by
the same factor, we will be over video rate. It will be done.” [2]
Next step: 6 fps (~0.2s); to progress towards a refresh rate of 24-30 fps
2)
) Display Size
p y
17” (current largest)
Have to scale up the display size to 85” for outdoor billboard advertising & 6–8 ft
(
(life-size) for telepresencing to be truly p
) p g y possible
[1] http://news.inventhelp.com/Articles/Electronics/Inventions/three-dimensional-dynamic-holography-12521.aspx
[2] http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2010/11/holographic-video/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mt5009holographyfinal-110424213808-phpapp01/85/3D-Holography-When-Might-it-become-Economically-Feasible-18-320.jpg)
![Photorefractive Polymer: Cost Projection
y j
19
Sony's Display Cost based o j eDisplay C o s& o f P h o t o rSony's t i v e P o l y mper Inch based on
P r on c t e d Size t e f r a c Display Cost e r
[1-3] [1-3]
Technology (as of Dec 2010) b a s e d o n S260r e e n S iTechnology (as of Dec 2010)
c Display z e
5000 D y n a m ic p h o t o r e f r a c t i v e p o l y m e r ( P r o je c t e d )
XEL-1 OLED TV 0 0
350 D y n a m ic p h o t o p o l y m e r ( E x t r a p o 240 f r o m Z e b r a I m a g in g )
la te
XEL-1 OLED TV
Bravia XBR10 Series LED 3D TV S t a t ic p h o t o p o ly m e r ( Z e b r a I m a g i n g ) Bravia XBR10 Series LED 3D TV
4500 Bravia XBR9 Series LCD TV 220 Bravia XBR9 Series LCD TV
30000
200
4000
nch)
25000 180
Cost/inch ($/in
3500 160
Cost ($)
20000
Cost ($)
140
3000
120
15000
2500 100
10000 80
2000
60
1500 5000
40
10 20 030 40 50 60 10 20 30 40 50 60
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Display Size (inches) Display Size (inches)
S c r e e n S iz e ( in c h e s )
Photorefractive polymer is projected to cost ~4x more than
4x
static photopolymer
$1500 for 12”x18” & $3500 & 2 ft by 3 ft static 3D holograms by Zebra
Imaging [4]
I i
[1] Sony XEL-1 OLED TV pricing: http://reviews.cnet.com/oled/sony-xel-1-oled/4505-13948_7-32815284.html
[2] Sony Bravia XBR10 Series LED 3D TV pricing: http://www.best-led-tv.net/46%E2%80%B3-sony-bravia-xbr10.html
[3] Sony Bravia XBR9 Series LCD TV pricing: http://www.practical-home-theater-guide.com/sony-lcd-tv-1.html
[4] Zebra Imaging Print Cost: http://www.3d-display-info.com/zebra-imaging-prints-large-3d-holograms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mt5009holographyfinal-110424213808-phpapp01/85/3D-Holography-When-Might-it-become-Economically-Feasible-19-320.jpg)