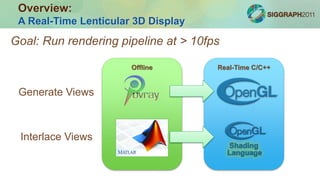
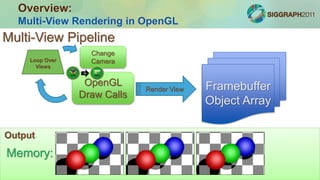
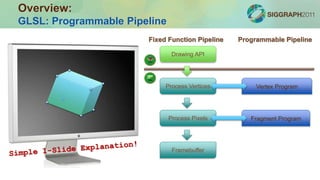
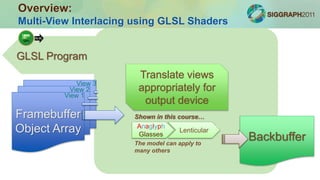
The document outlines a course on constructing glasses-free 3D displays, emphasizing multi-view rendering and interlacing techniques using OpenGL and GLSL. It details real-time rendering pipelines, the setup for multi-view projections, and examples of stereoscopic viewing methods, including anaglyphs and stereoscopic color rendering. Additionally, it discusses applications, potential enhancements like eye-tracking, and demonstrations included in the course.

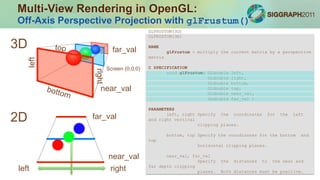
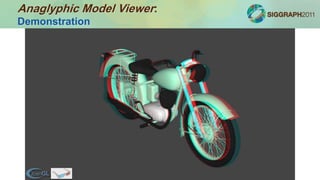



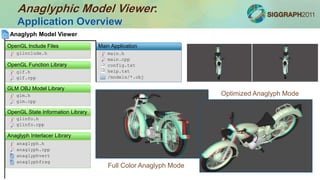
![Anaglyphic Model Viewer:
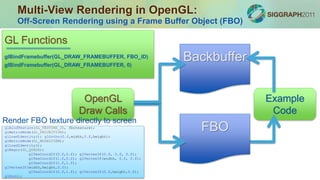
Examining the GLUT Display Callback
main.h
main.cpp
config.txt
help.txt
/models/*.obj
Anaglyph Model Viewer
Main Application
// Define the display function.
void display(void){
. . .
// Render each view.
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
// Enable FBO rendering mode.
glBindFramebuffer(GL_DRAW_FRAMEBUFFER, anaglyph.FBO[i]);
// Enable depth testing and lighting.
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
// Clear the color and depth buffers.
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// Set the projection and modelview transformations.
setViewStereoscopicAnaglyph(&anaglyph, window_width,
window_height, i);
// Display the model.
displayModel();
}
// Display the stereoscopic image using the anaglyph compositor.
displayAnaglyph(&anaglyph, window_width, window_height);
. . .
glutSwapBuffers();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-renderinghirsch15minutes-110811212947-phpapp01/85/BYO3D-2011-Rendering-16-320.jpg)
![anaglyph.h
Anaglyph.frag
anaglyph.cpp
Anaglyph.vert
Anaglyph Interlacer Library
Anaglyph Model Viewer
glinfo.h
glinfo.cpp
OpenGL State Information Library
glm.h
glm.cpp
GLM OBJ Model Library
glf.h
glf.cpp
OpenGL Function Library
glinclude.h
OpenGL Include Files
Anaglyphic Model Viewer:
Examining displayAnaglyph()
// Define the display function for the anaglyph compositor.
void displayAnaglyph(AnaglyphCompositor* anaglyph, int window_width, int window_height){
. . .
// Disable FBO rendering mode.
glBindFramebuffer(GL_DRAW_FRAMEBUFFER, 0);
. . .
// Clear the color buffer.
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Enable the anaglyph compositor shader program.
glUseProgram(anaglyph->anaglyphShader.program);
// Bind FBO textures to anaglyph shader program samplers.
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(anaglyph->anaglyphShader.program, "leftTexture"), 0);
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(anaglyph->anaglyphShader.program, "rightTexture"), 1);
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0+i);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, anaglyph->viewTexture[i]);
}
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
// Set the anaglyph rendering mode.
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(
anaglyph->anaglyphShader.program, "anaglyphMode"),
anaglyph->mode
);
// Display the anaglyph by rendering contents of FBO to screen quad.
. . .
// Disable the shader program.
glUseProgram(0);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-renderinghirsch15minutes-110811212947-phpapp01/85/BYO3D-2011-Rendering-17-320.jpg)
![Anaglyphic Model Viewer:
GLSL Shaders for Anaglyph Compositing
anaglyph.h
anaglyph.frag
anaglyph.cpp
anaglyph.vert
Anaglyph Interlacer Library
Anaglyph Model Viewer
Anaglyph Interlacer Library
glinfo.h
glinfo.cpp
OpenGL State Information Library
glm.h
glm.cpp
GLM OBJ Model Library
glf.h
glf.cpp
OpenGL Function Library
glinclude.h
OpenGL Include Files
/*
* anaglyph.frag
* Anaglyph Compositor Fragment Shader
* Created by Douglas Lanman and Matthew Hirsch.
* Copyright 2011.
*/
// Define samplers corresponding to left and right
images.
uniform sampler2D leftTexture;
uniform sampler2D rightTexture;
// Define anaglyph mode index.
uniform int anaglyphMode;
// Define fragment shader.
void main() {
// Evaluate the left and right
fragment colors.
vec3 leftFragColor = texture2D(
leftTexture,
gl_TexCoord[0].st
).rgb;
vec3 rightFragColor = texture2D(
rightTexture,
gl_TexCoord[0].st
).rgb;
// Assign the output fragment color
using the
// user-selected anaglyph rendering
mode.
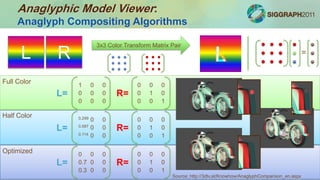
mat3 L, R;
R = mat3( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 1.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
if(anaglyphMode == 2){
// Half-color anaglyph.
L = mat3( 0.299, 0.0,
0.0,
0.587, 0.0,
0.0,
0.114, 0.0,
0.0);
}else if(anaglyphMode == 3){
// Optimized anaglyph.
L = mat3( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.7, 0.0, 0.0,
0.3, 0.0, 0.0);
}else{
// Full-color anaglyph.
L = mat3( 1.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
}
gl_FragColor = vec4(
L*leftFragColor+R*rightFragColor,
1.0
);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-renderinghirsch15minutes-110811212947-phpapp01/85/BYO3D-2011-Rendering-19-320.jpg)
![Anaglyphic Model Viewer:
Possible Extensions: Adding Eye-Tracking
main.h
main.cpp
config.txt
help.txt
/models/*.obj
Anaglyph Model Viewer
Main Application
[screen]
width = 1920
height = 1080
pitch = 0.025800
[camera]
x = 0.000000
y = 0.000000
z = 100.000000
near = 10.000000
far = 300.000000
separation = 6.500000
[viewer]
anaglyph_mode = 1
display_help = 1
display_timer = 1
…
•Camera X and Y control viewer position
•Wiimote and OpenCV headtracking
examples are available online
Johnny Lee](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-renderinghirsch15minutes-110811212947-phpapp01/85/BYO3D-2011-Rendering-20-320.jpg)
