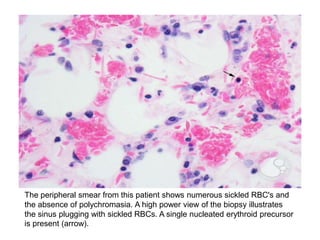
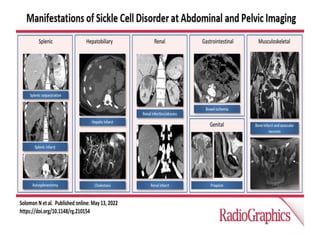
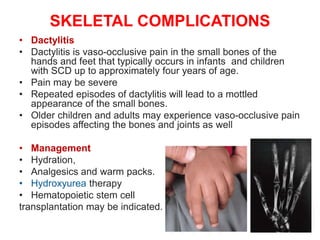
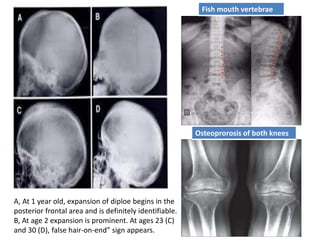
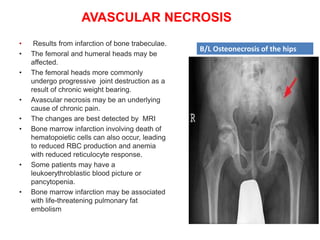
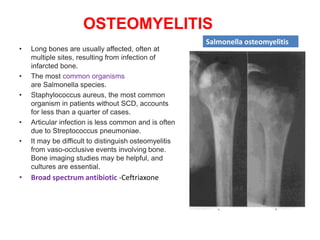
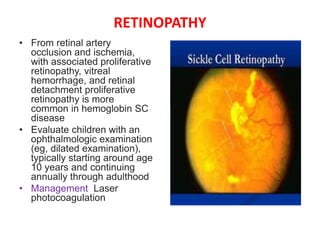
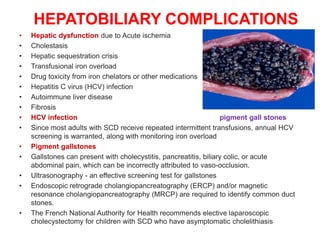
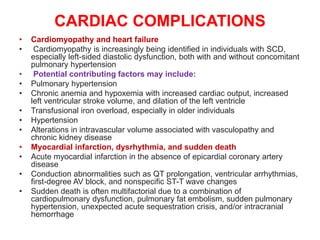
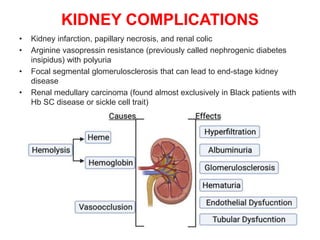
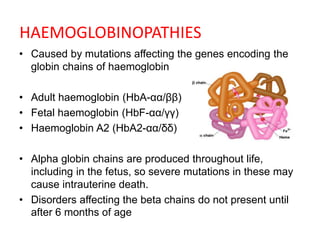
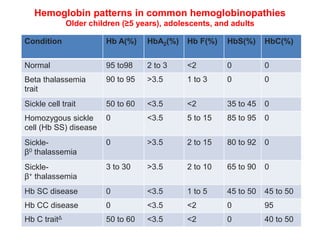
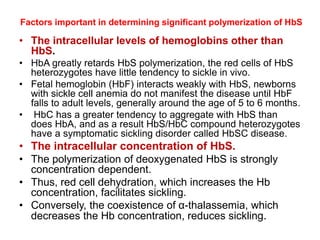
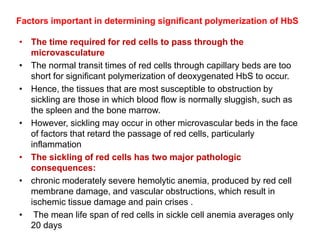
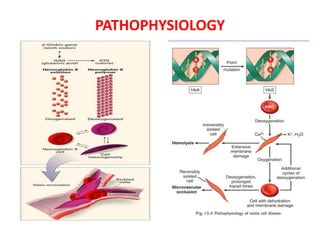
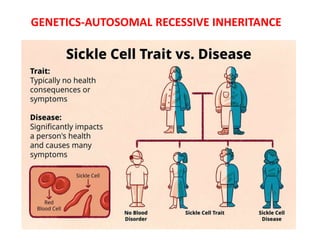
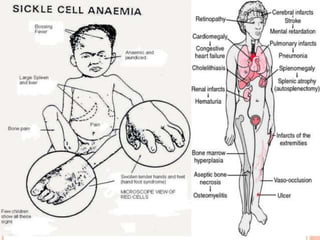
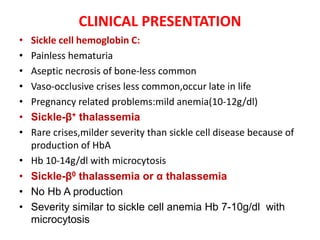
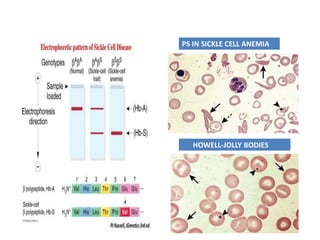
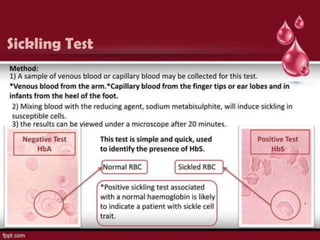
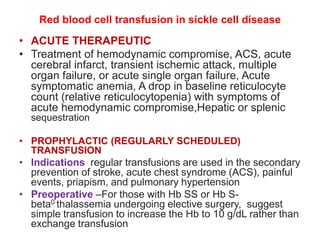
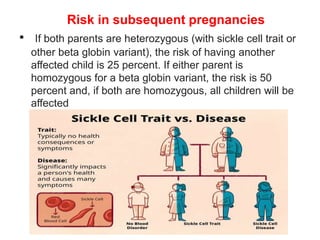
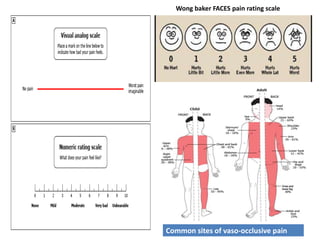
Sickle cell disease is caused by mutations in the beta-globin gene resulting in abnormal hemoglobin S. This leads to polymerization of deoxygenated hemoglobin S and distortion of red blood cells into a sickle shape. Chronic hemolysis and vaso-occlusive crises cause significant morbidity. Diagnosis is made through hemoglobin electrophoresis showing elevated HbS. Treatment involves prophylactic antibiotics, hydration, pain management, hydroxyurea and blood transfusions to reduce complications. Chronic organ damage remains a major cause of mortality in patients with sickle cell disease.








![• Hydroxyurea and other disease-modifying therapies
• It decreases the frequency and severity of vaso-occlusive
complications (eg, dactylitis, painful episodes, acute chest
syndrome [ACS]) and it may reduce the risk of organ damage
in individuals with Hb SS and Hb S-β0 thalassemia.
•
• Options for patients who cannot take hydroxyurea or who
have continued symptoms despite optimally dosed
hydroxyurea include L-glutamine, crizanlizumab,
and voxelotor.
• Education — The child's parents or caregivers should be
educated about acute and chronic complications of SCD
• Routine immunizations plus influenza, pneumococcal and
meningococcal vaccinations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sicklecelldisease-230706042649-1340deb5/85/SICKLE-CELL-DISEASE-pptx-19-320.jpg)







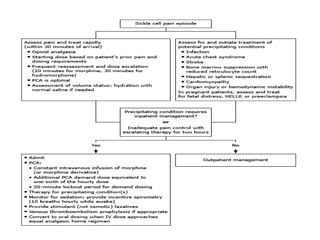


![MULTIORGAN FAILURE
• Acute multiorgan failure is a life-threatening
complication of SCD in which multiple organ
systems are affected by ischemia and/or infarction.
• It is typically seen in the setting of an acute painful
episode
• Complement and other factors have been
implicated.
• Some patients may present with a thrombotic
microangiopathy (TMA, such as thrombotic
thrombocytopenic purpura [TTP] or complement-
mediated hemolytic uremic syndrome [CM-HUS]
picture), which has led to anecdotal use of
plasmapheresis and complement therapy
• Management of multiorgan failure prompt and
aggressive exchange transfusion therapy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sicklecelldisease-230706042649-1340deb5/85/SICKLE-CELL-DISEASE-pptx-36-320.jpg)