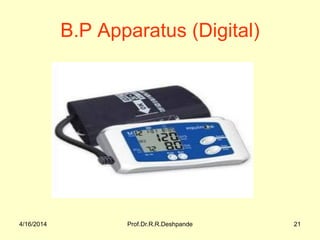
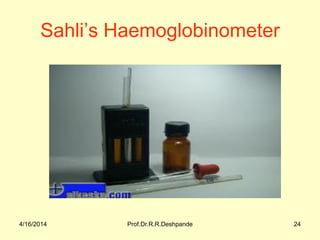
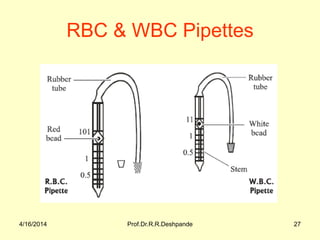
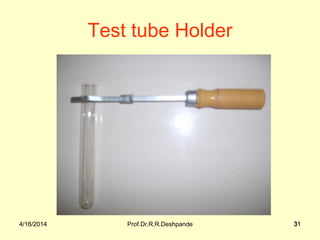
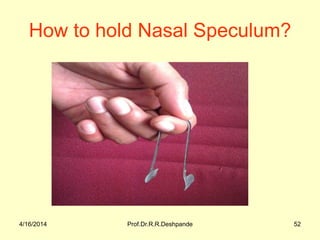
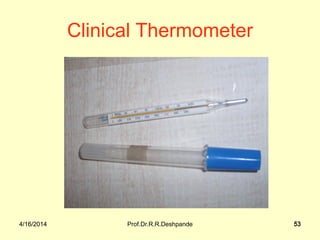
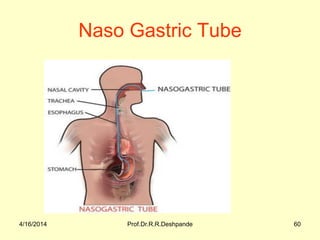
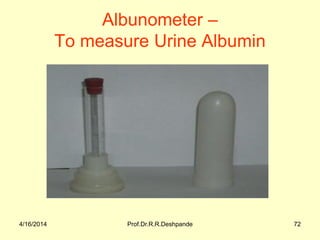
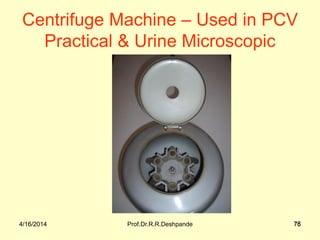
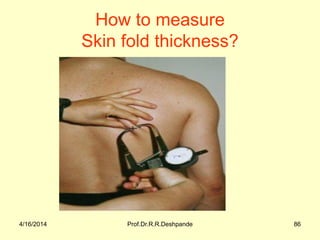
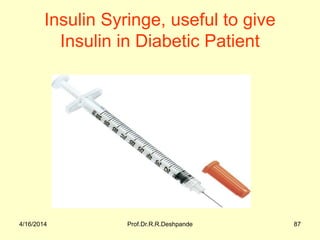
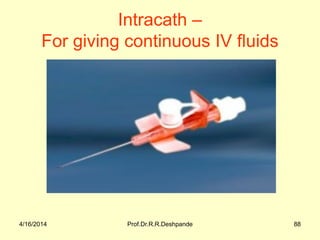
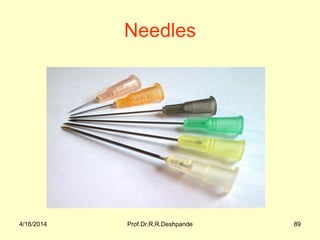
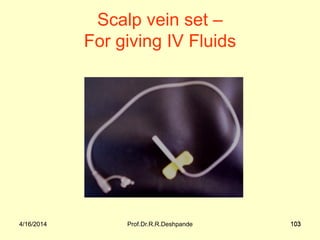
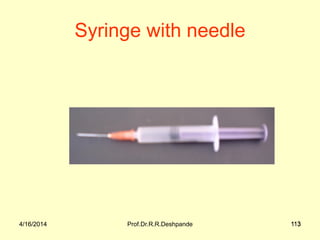
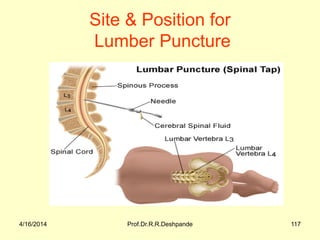
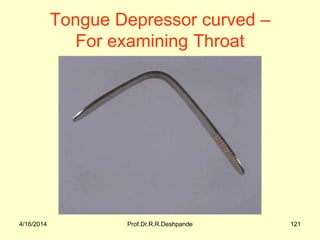
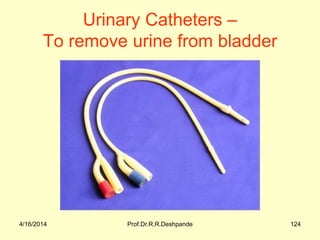
The document presents a detailed overview of instruments used in Ayurvedic physiology and practicals, emphasizing various tools and their uses, including microscopes, stethoscopes, and blood pressure apparatuses. It covers theoretical and practical aspects relevant to the new CCIM syllabus, highlighting the significance of each instrument in medical studies. Additionally, the document provides specifications and operational principles for each tool mentioned.