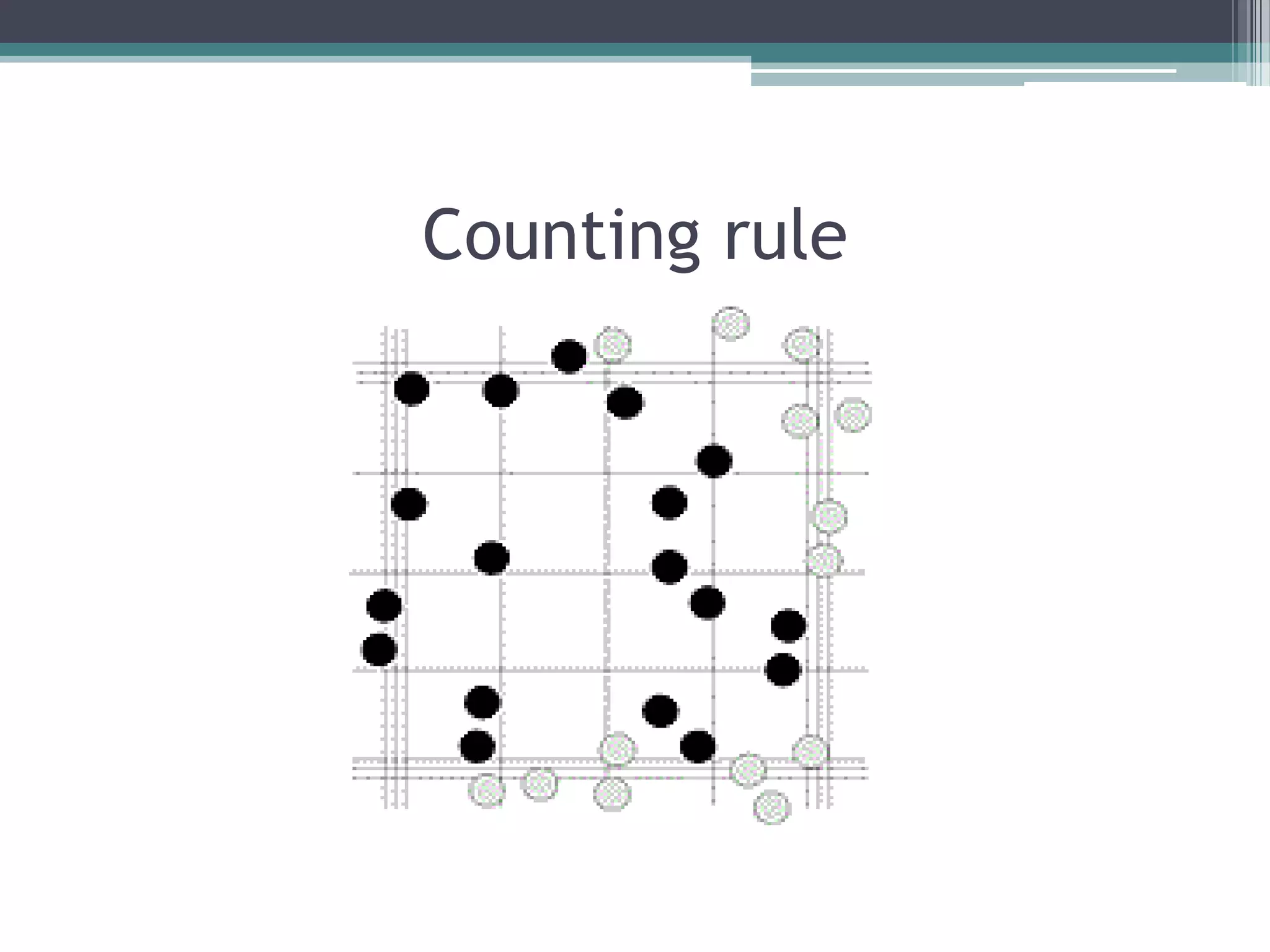
The hemocytometer is an instrument used to count blood cells. It consists of a Neubauer slide with a ruled counting chamber area divided into squares under a cover glass. There are different types of counting chambers including the Neubauer, improved Neubauer, Levy's, and Fuch's Rosenthal. Red blood cell and white blood cell pipettes are used to dilute and introduce the blood sample, and differ in size and graduations. Cells are counted under a microscope using counting rules to avoid double counting, and calculations using dilution and depth factors provide the final cell counts. Sources of error include improper technique, uneven distribution of cells, and contamination.