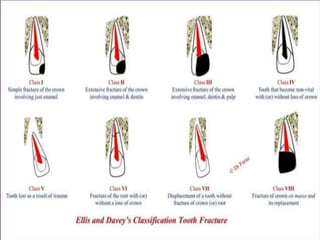
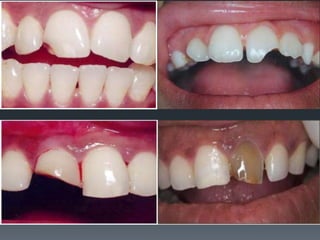
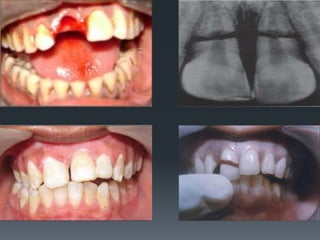
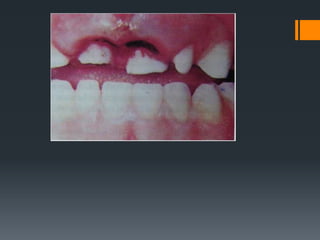
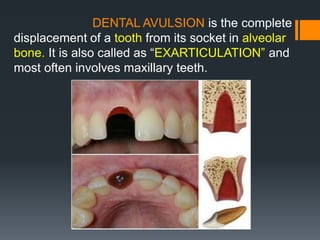
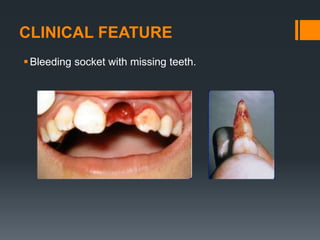
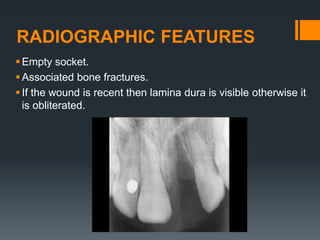
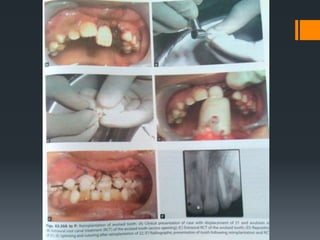
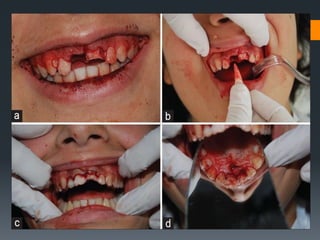
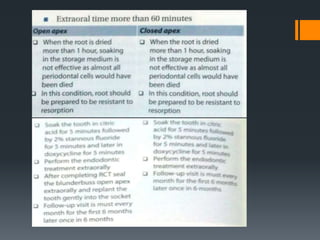
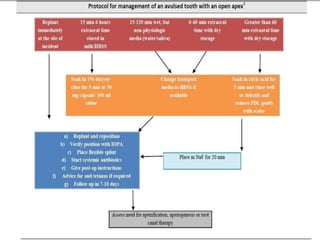
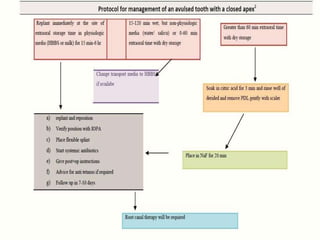
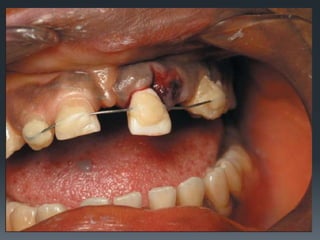
Dental avulsion is the complete displacement of a tooth from its socket. Trauma from sports or accidents can cause avulsion. Clinically, there is bleeding from the empty socket. Radiographically, the socket appears empty with possible bone fractures. Treatment depends on extra-oral dry time - immediate replantation is best if dry time is short, whereas long dry time requires special management. Storage in media like saline or Hanks balanced salt solution best maintains viability of periodontal ligament cells. Complications may include inflammatory or replacement resorption, ankylosis or tooth submergence.