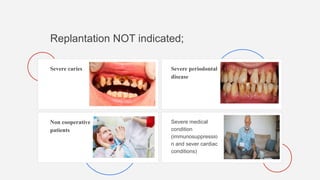
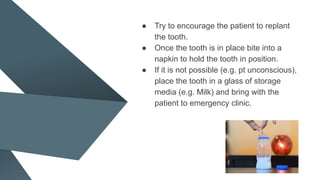
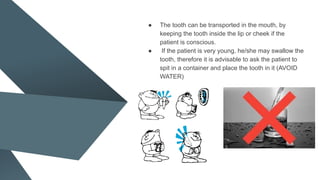
Avulsion of a tooth refers to the complete displacement from its socket and constitutes a dental emergency, occurring in 0.5-3% of dental injuries. Immediate first aid includes keeping the tooth moist in an appropriate medium and attempting replantation, while considering patient conditions that may affect the prognosis. The document emphasizes the importance of proper storage media for avulsed teeth and outlines treatment protocols based on the condition of the avulsed tooth and elapsed time since injury.