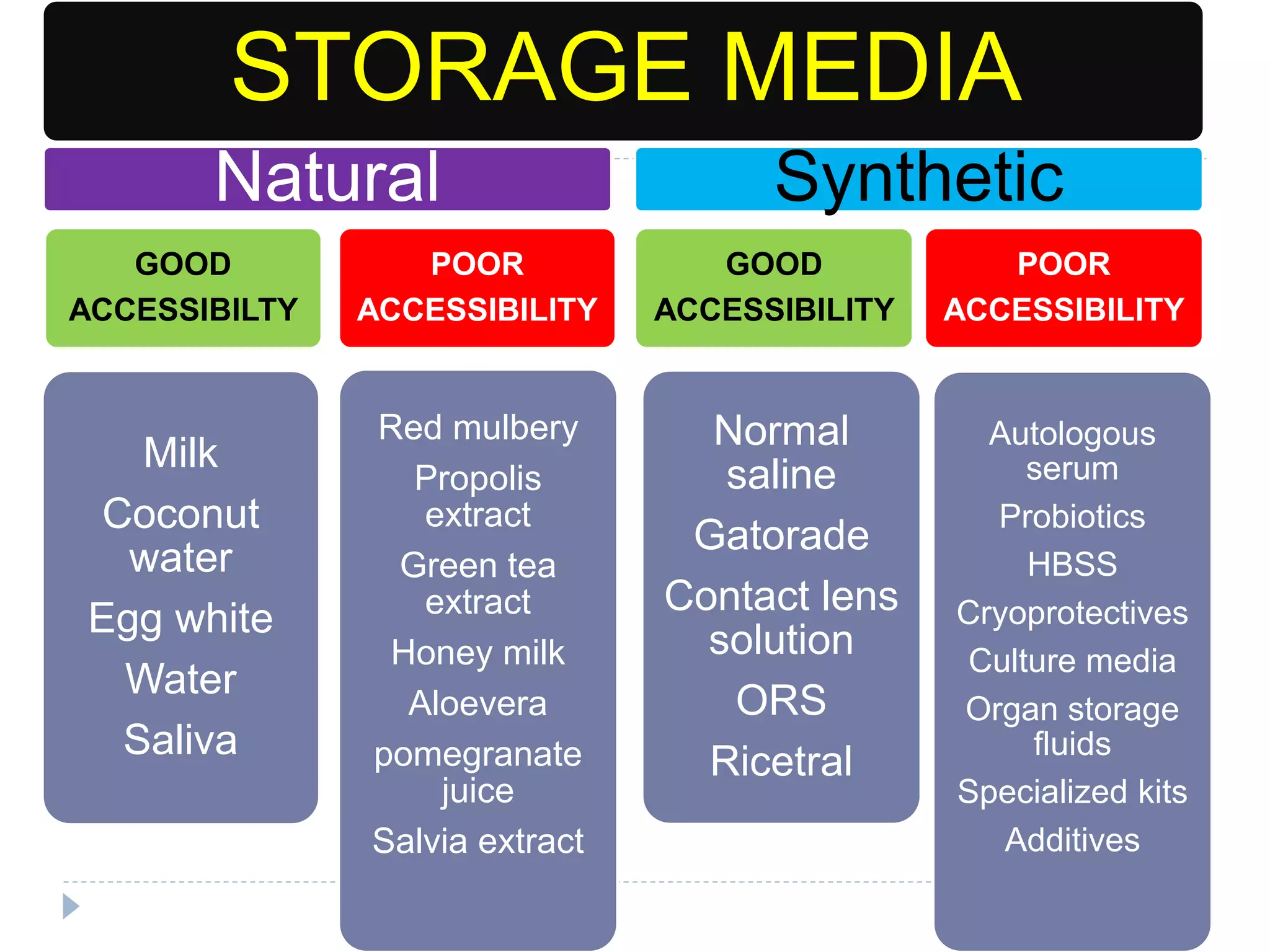
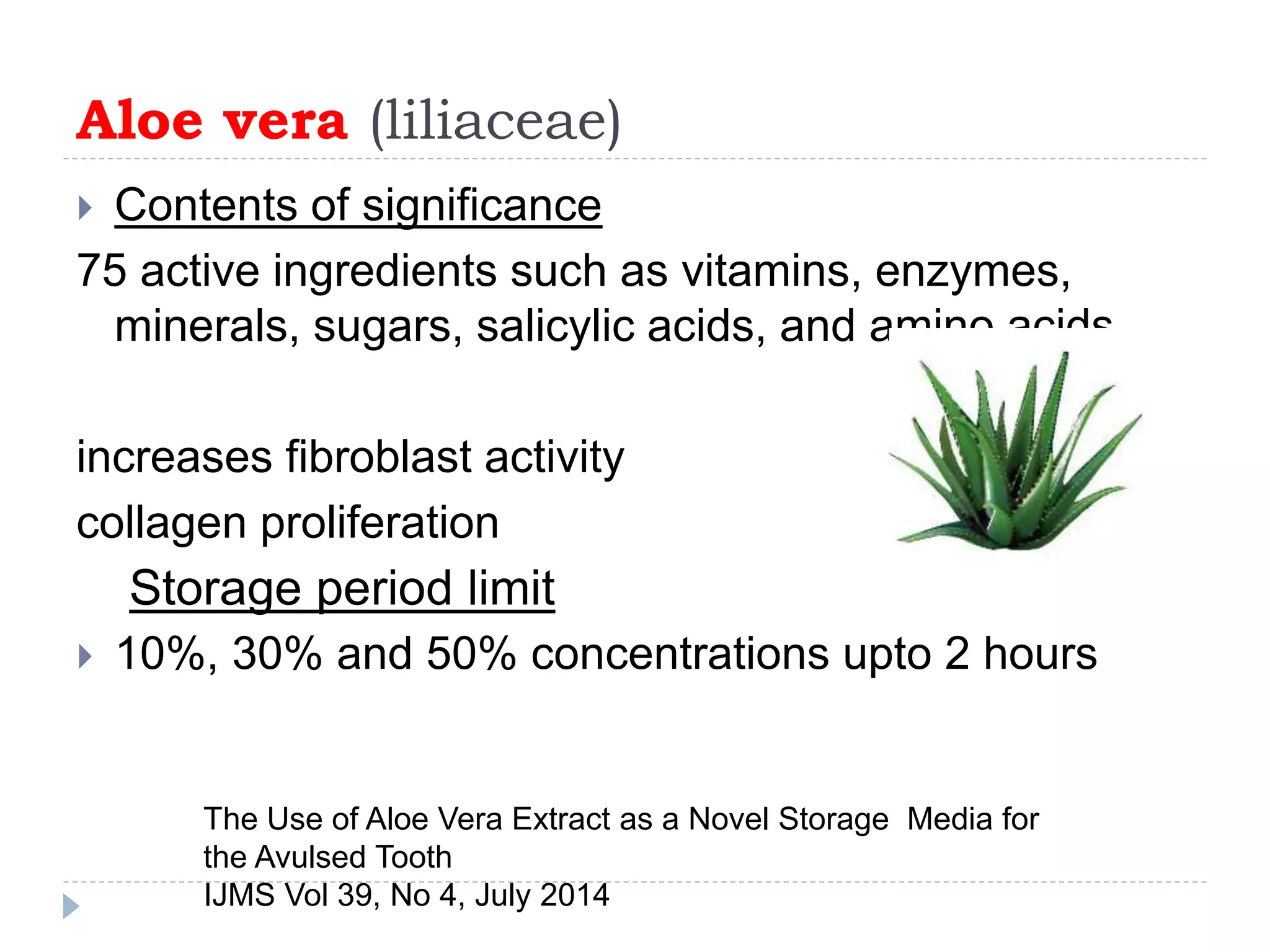
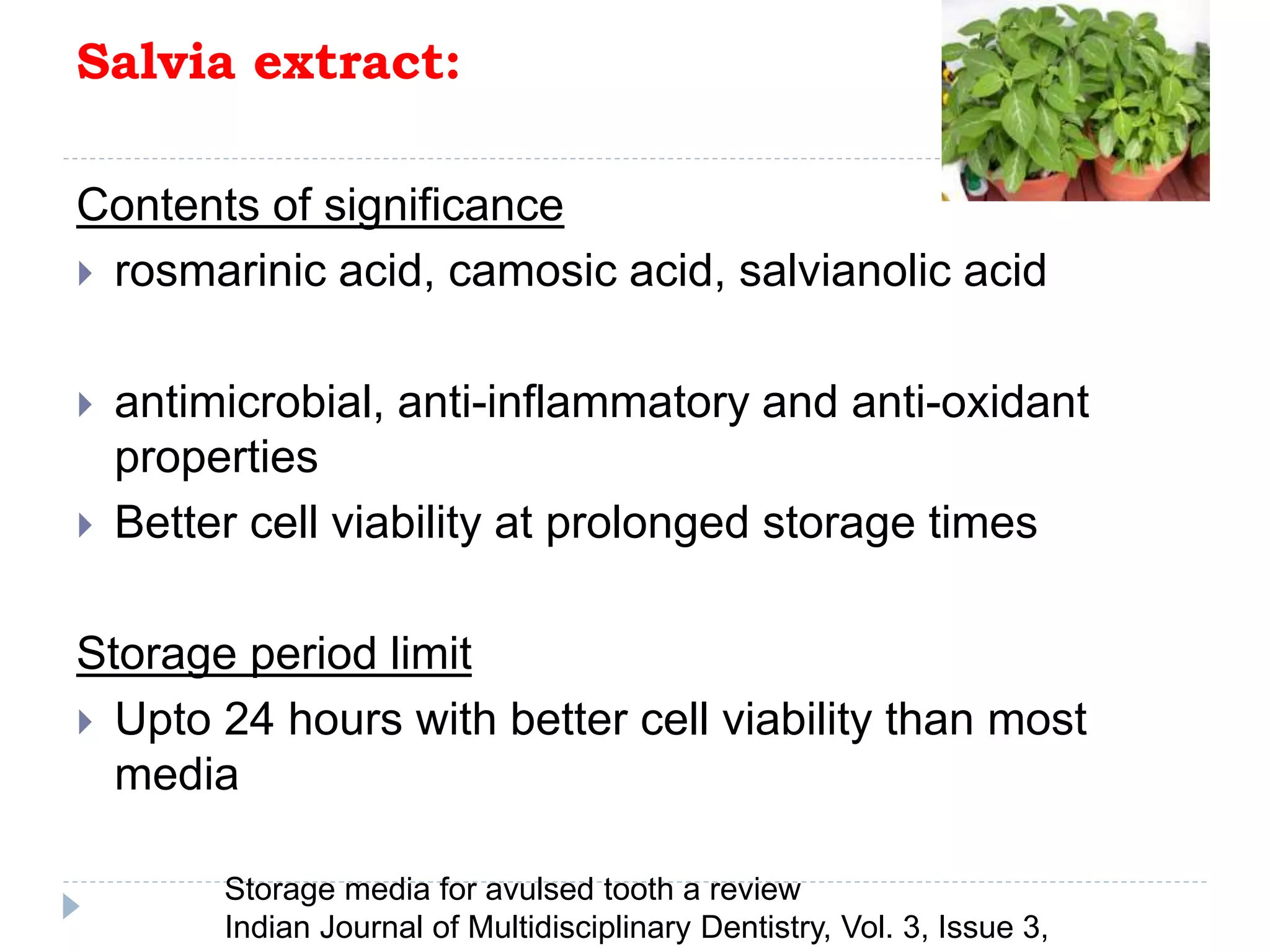
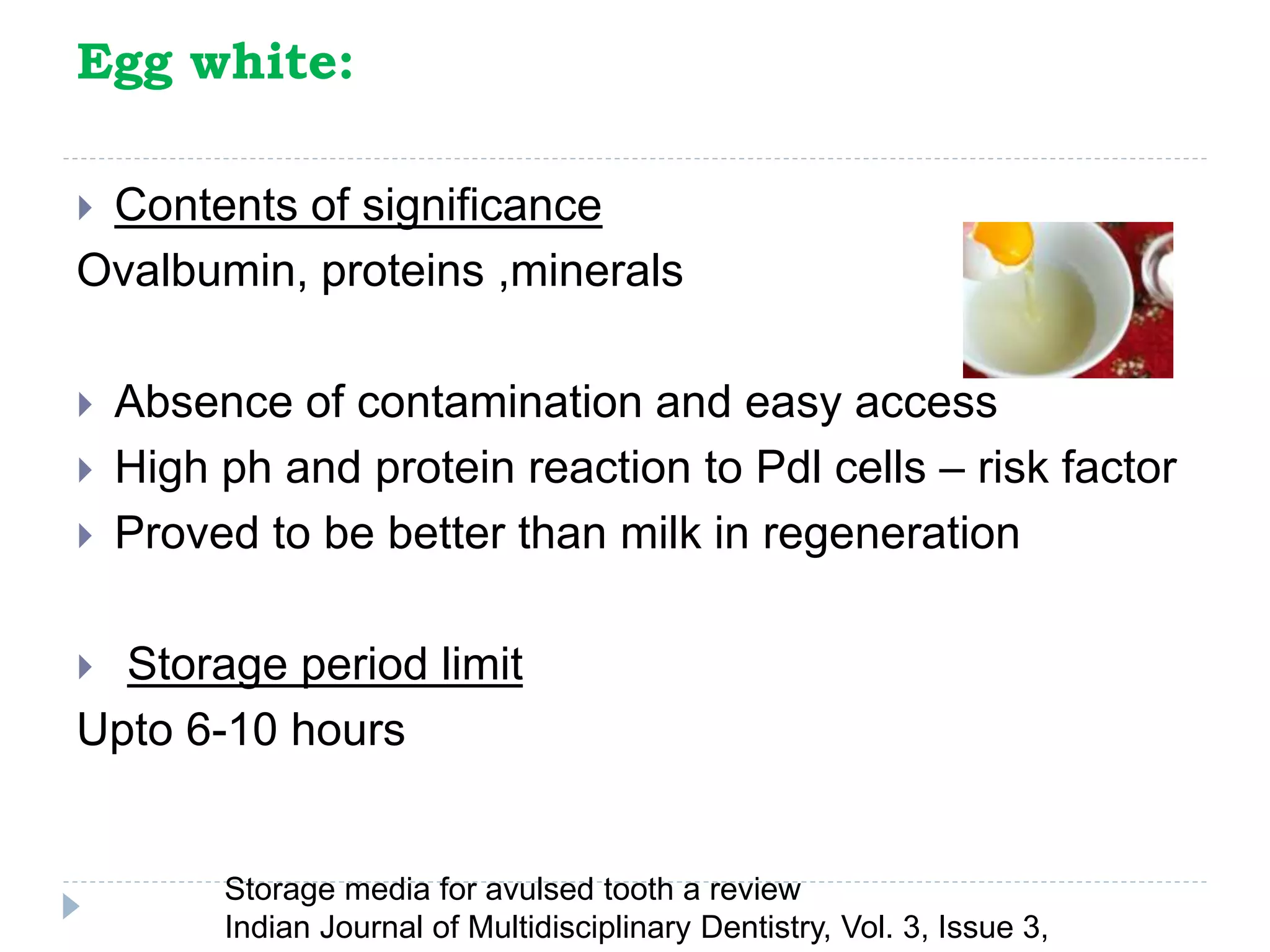
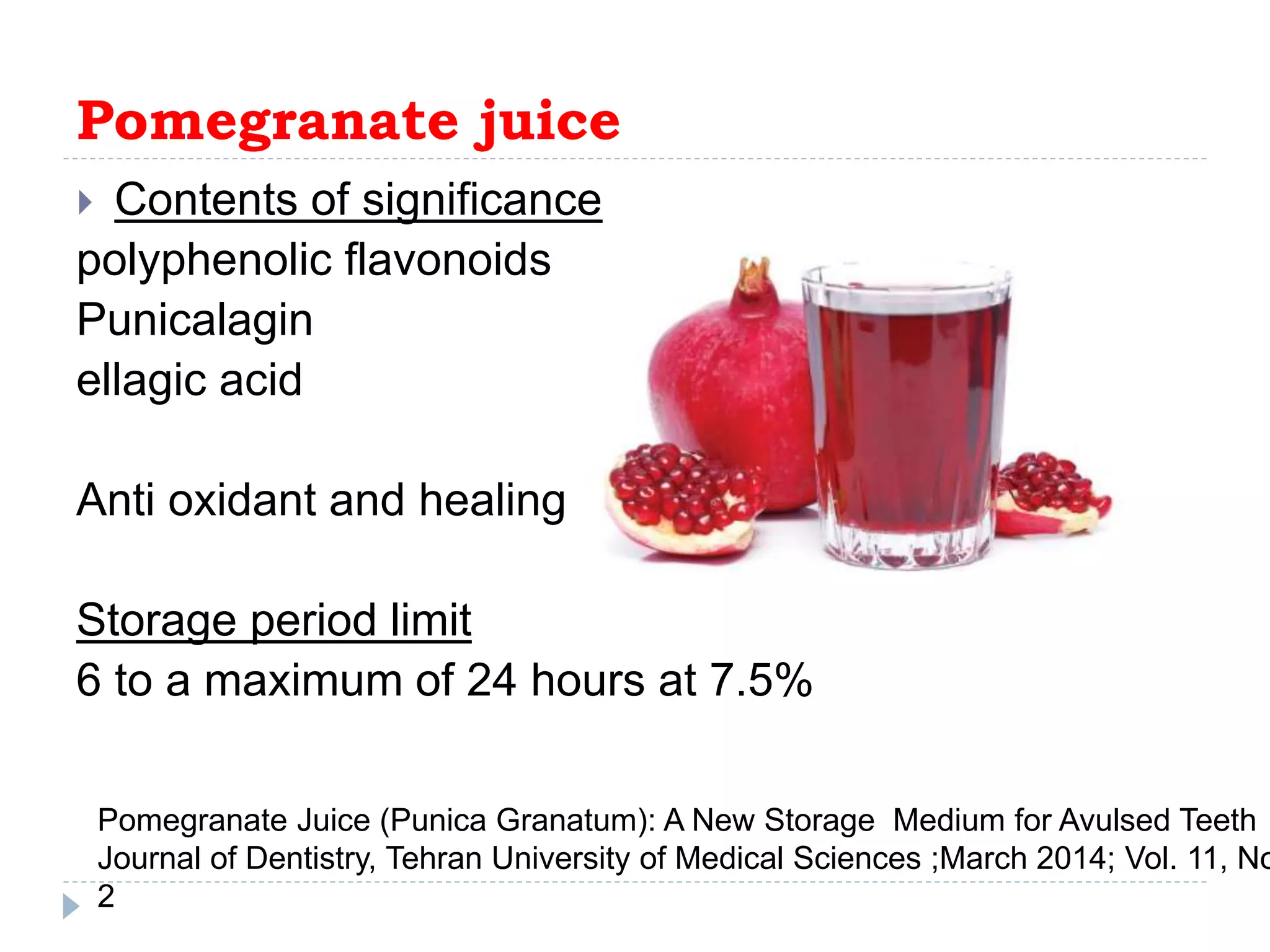
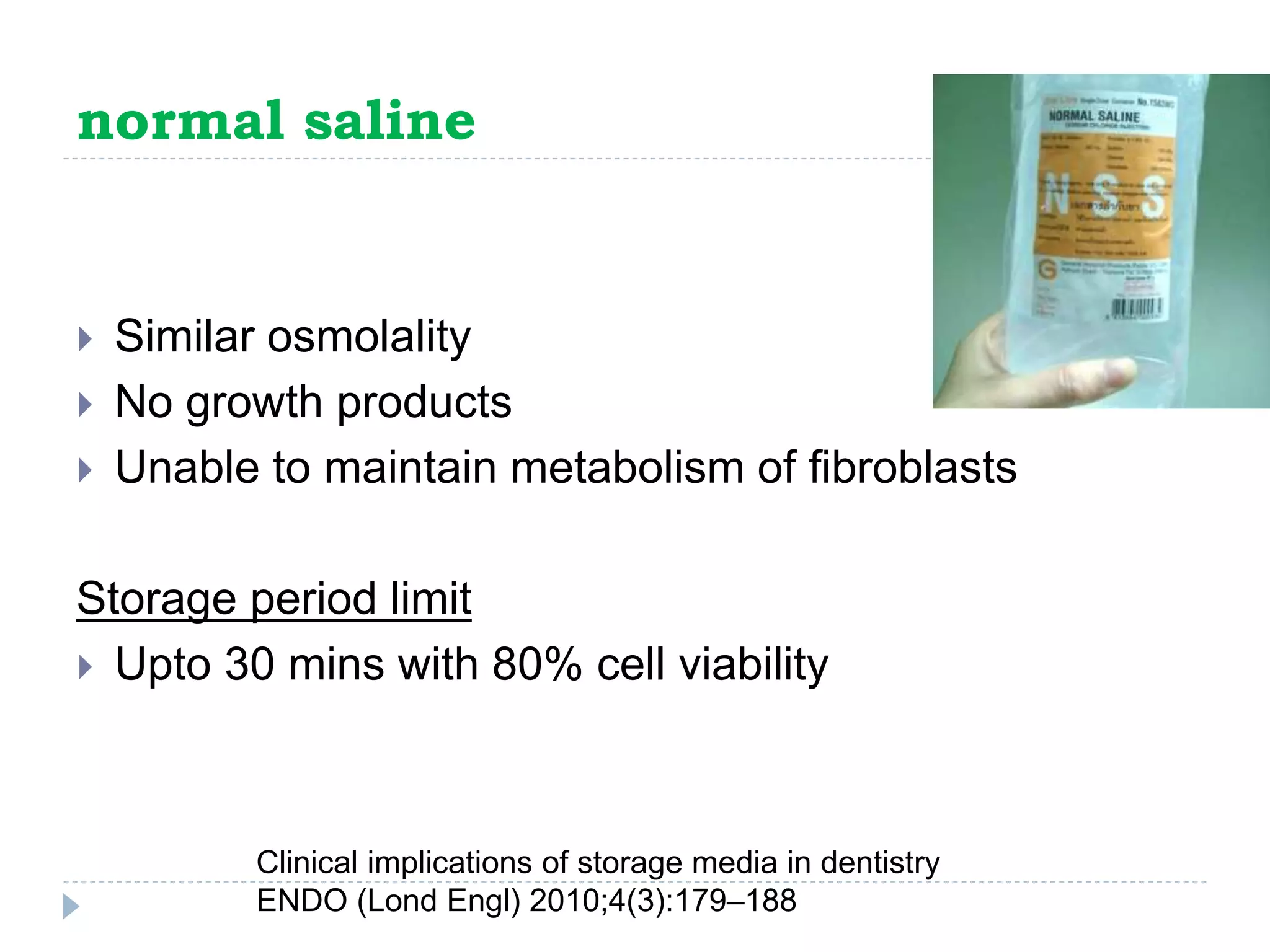
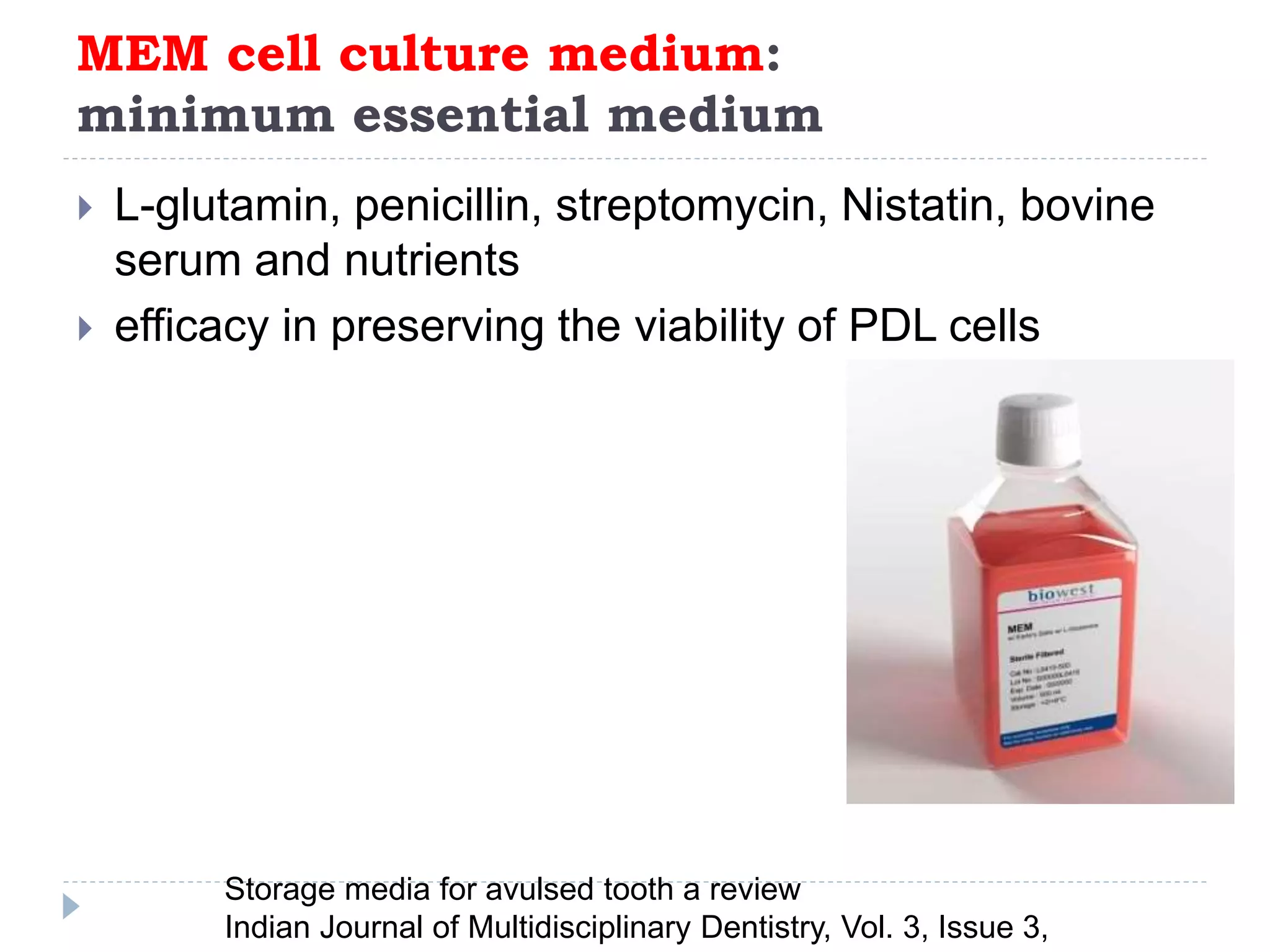
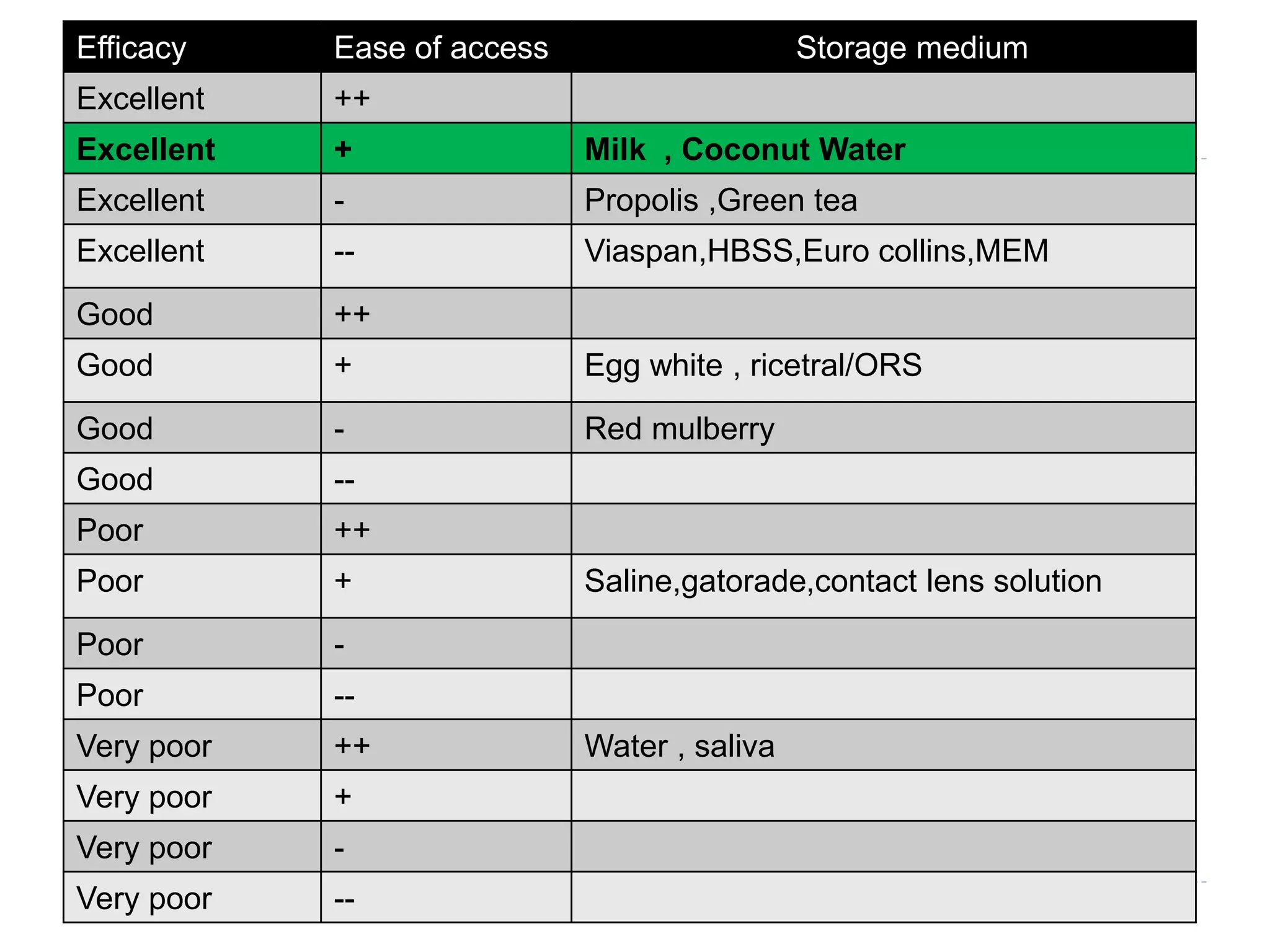
This document discusses various storage media options for avulsed teeth. It begins by explaining the need for storage media when immediate replantation is not possible after tooth avulsion. An ideal storage medium should preserve periodontal ligament cell viability, promote mitogenicity, be non-toxic, and maintain functional cell capabilities. The document then classifies and describes the characteristics and effectiveness of numerous natural and synthetic storage media options, including milk, coconut water, green tea extract, and Hank's Balanced Salt Solution. It provides time limits for how long each medium can effectively store an avulsed tooth.