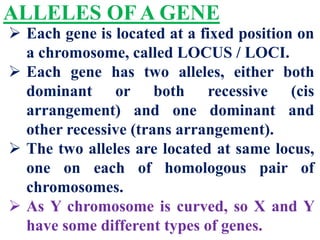
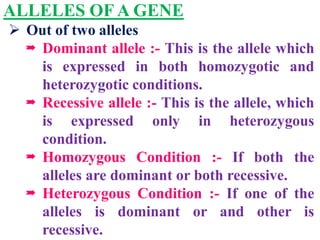
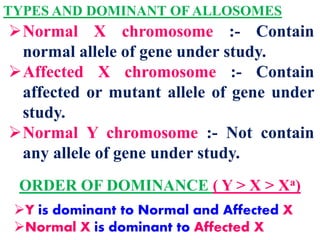
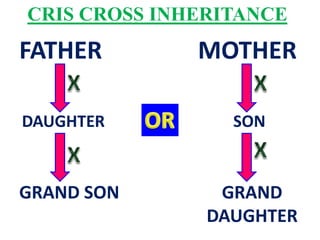
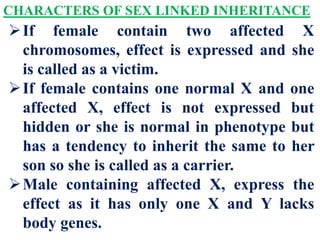
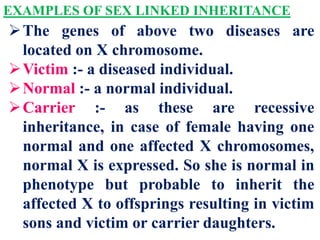
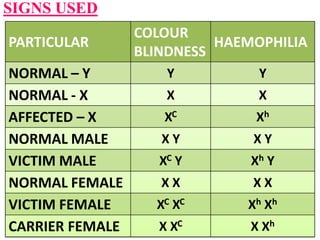
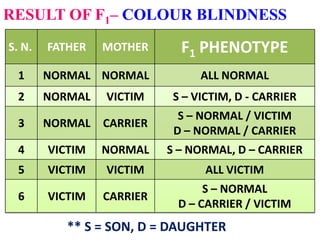
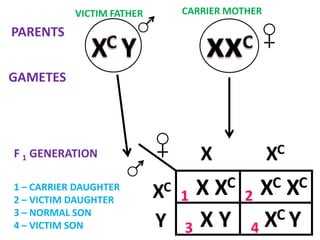
This document discusses sex-linked inheritance in humans. It begins by introducing sexual reproduction and chromosomes. Males have XY sex chromosomes and are heterogametic, while females have XX and are homogametic. Autosomes carry genes for somatic traits, while sex chromosomes determine sex and carry some somatic genes. These sex-linked genes show patterns of inheritance different from autosomal genes. Examples given are color blindness and hemophilia, which are recessive traits linked to the X chromosome. Diagrams show possible genotypes and phenotypes that can result when parents with normal, affected, or carrier genotypes reproduce. The conclusion emphasizes that case studies show possible outcomes, not fixed probabilities, for offspring.