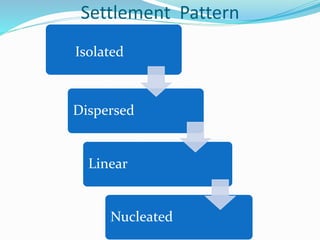
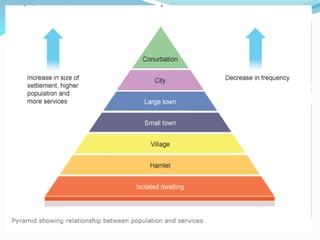
A settlement is defined as a place where people live, ranging from a single house to a large city with over 10 million residents. Settlements can be classified based on their site, type, shape, size, functions, and hierarchy. Rural settlements are typically smaller areas where people engage in farming, fishing, or mining, while urban settlements are larger areas where people work in non-rural industries and services. Characteristics such as population size, social heterogeneity, and economic functions help distinguish rural from urban settlements.