This document provides an overview and summary of a presentation on understanding recent changes to India's service tax law. The presentation covers:
- An economic overview of India and the growing importance of the services sector.
- An explanation of the shift in India's service tax law from a selective positive list approach to a comprehensive negative list approach implemented in July 2012.
- A summary of the key changes introduced by the new negative list approach, including the definition of taxable services, rules for determining the place of provision, and new compliance requirements.







![12
Selective Approach to Service Tax
Taxation by choice
Service not defined but taxable service defined.
> 120 taxable services [section 65(105)]
Resulted in distortions / prejudice
Untapped tax potential
Economically unjustified
Issues – Classification, Illogical definitions,
Constitutional challenges, deemed services etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sessioni-130422051120-phpapp02/85/Mumbai-Presentation-17-4-2013-Session-i-12-320.jpg)




![18
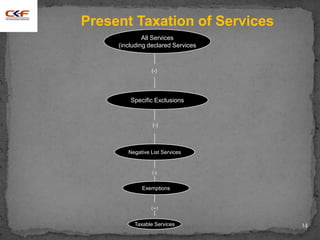
All services Taxable
[section 65B (44)]
Declared services Taxable
(section 66E)
Services covered under Not Taxable
negative list of services
(section 66D)
Services exempt under Mega Exempted
Notification No. 25/2012-ST
dated 20.6.2012
Other specified Exemptions Exempted](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sessioni-130422051120-phpapp02/85/Mumbai-Presentation-17-4-2013-Session-i-18-320.jpg)












