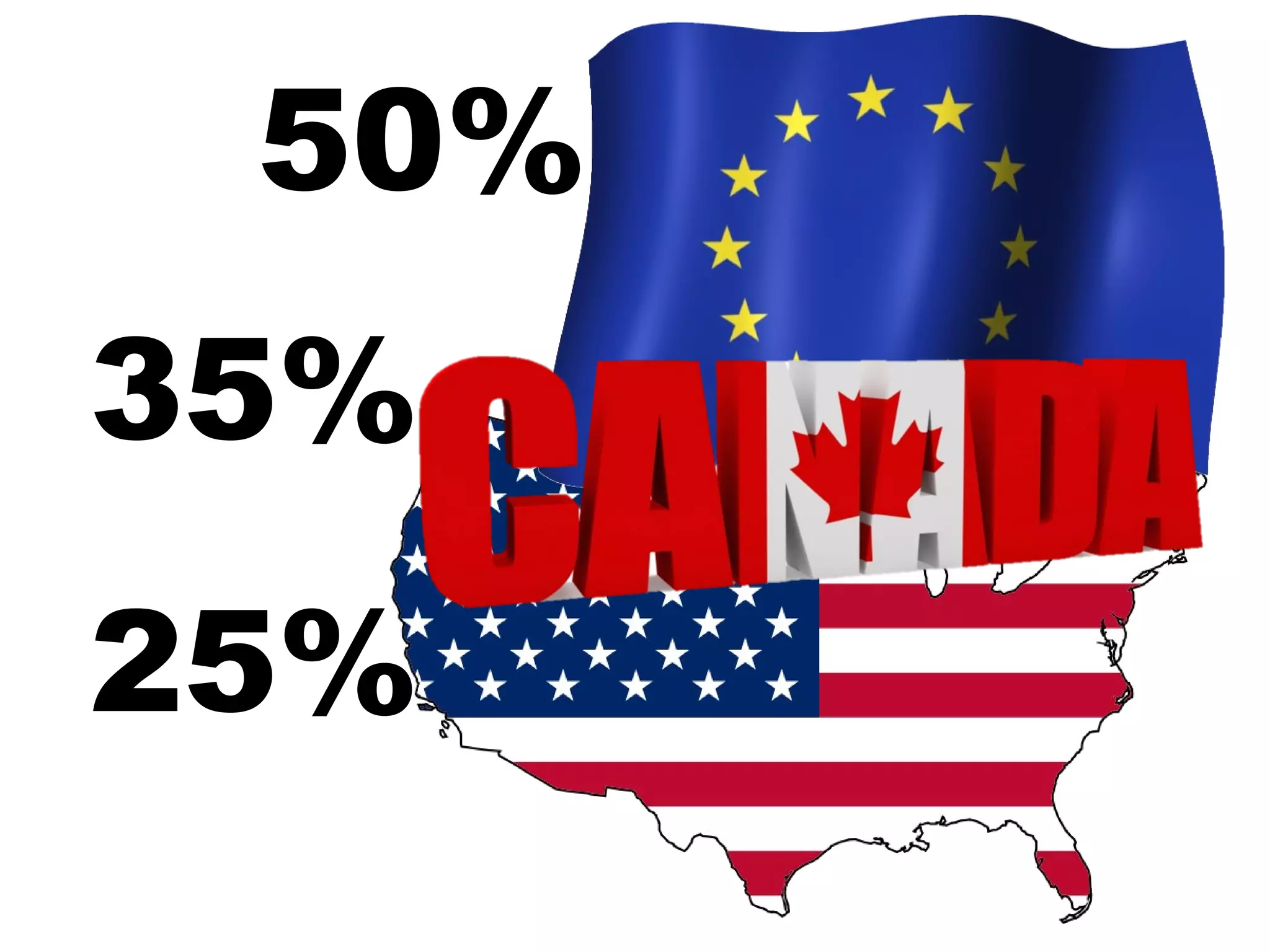
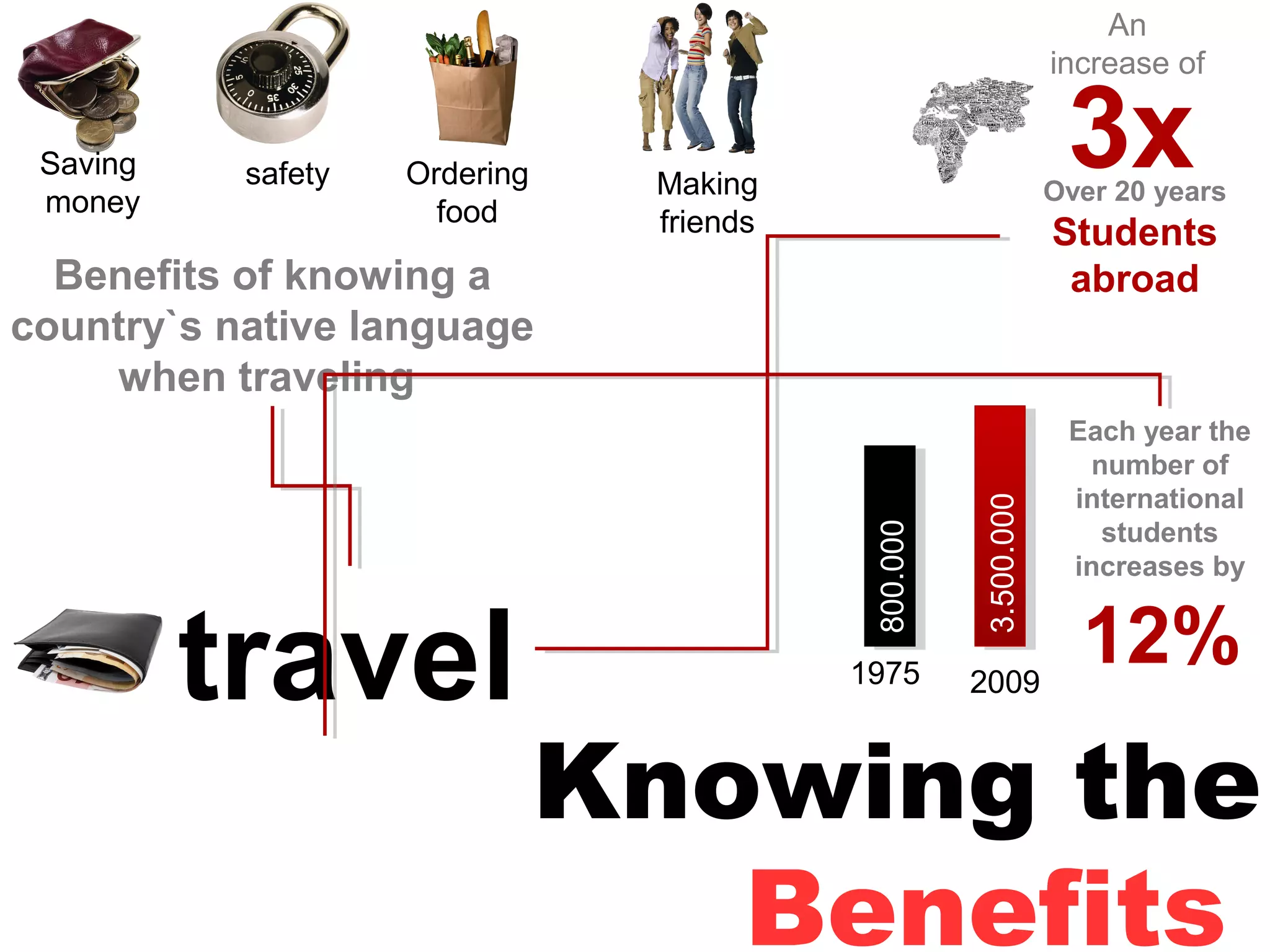
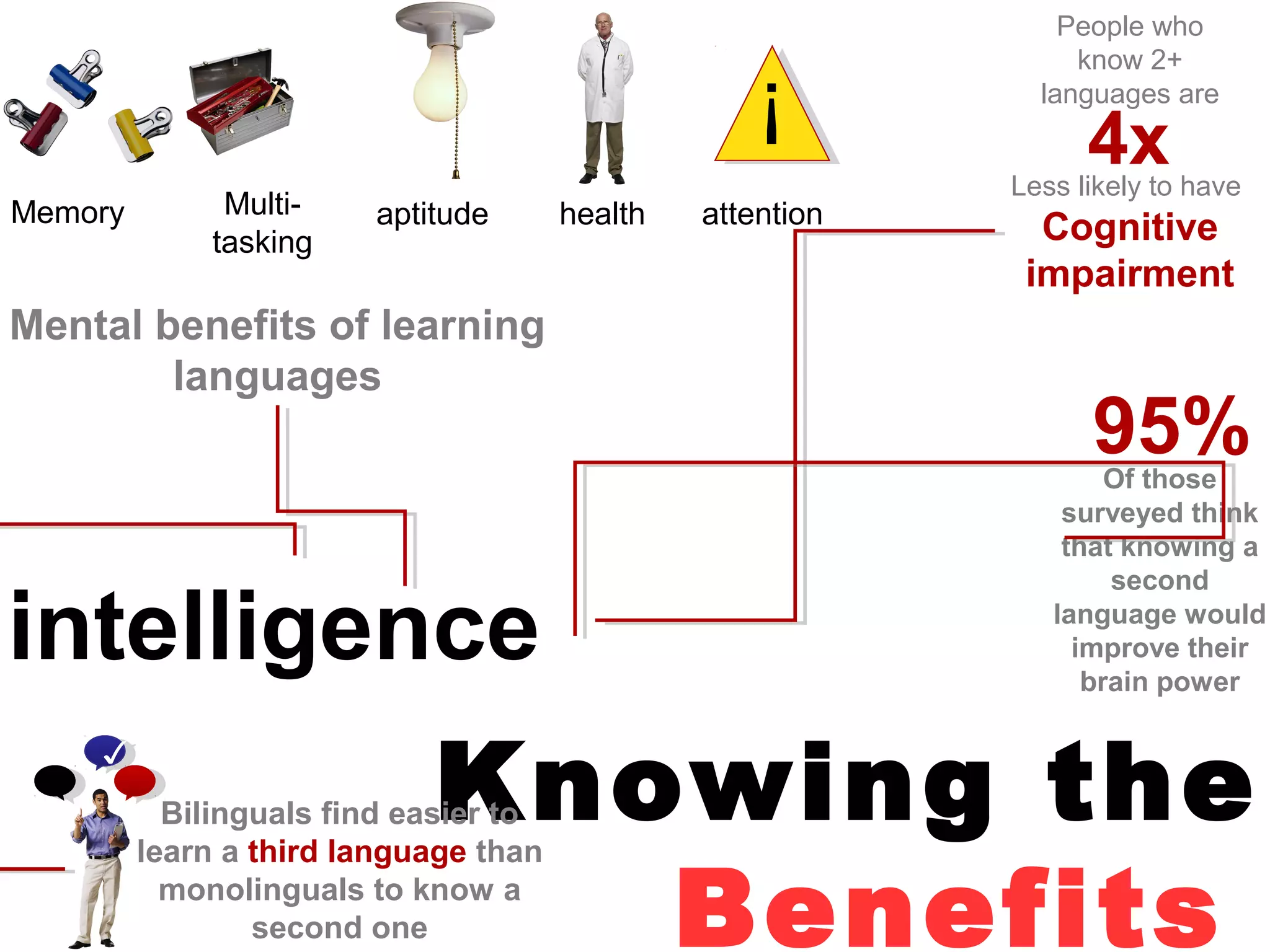
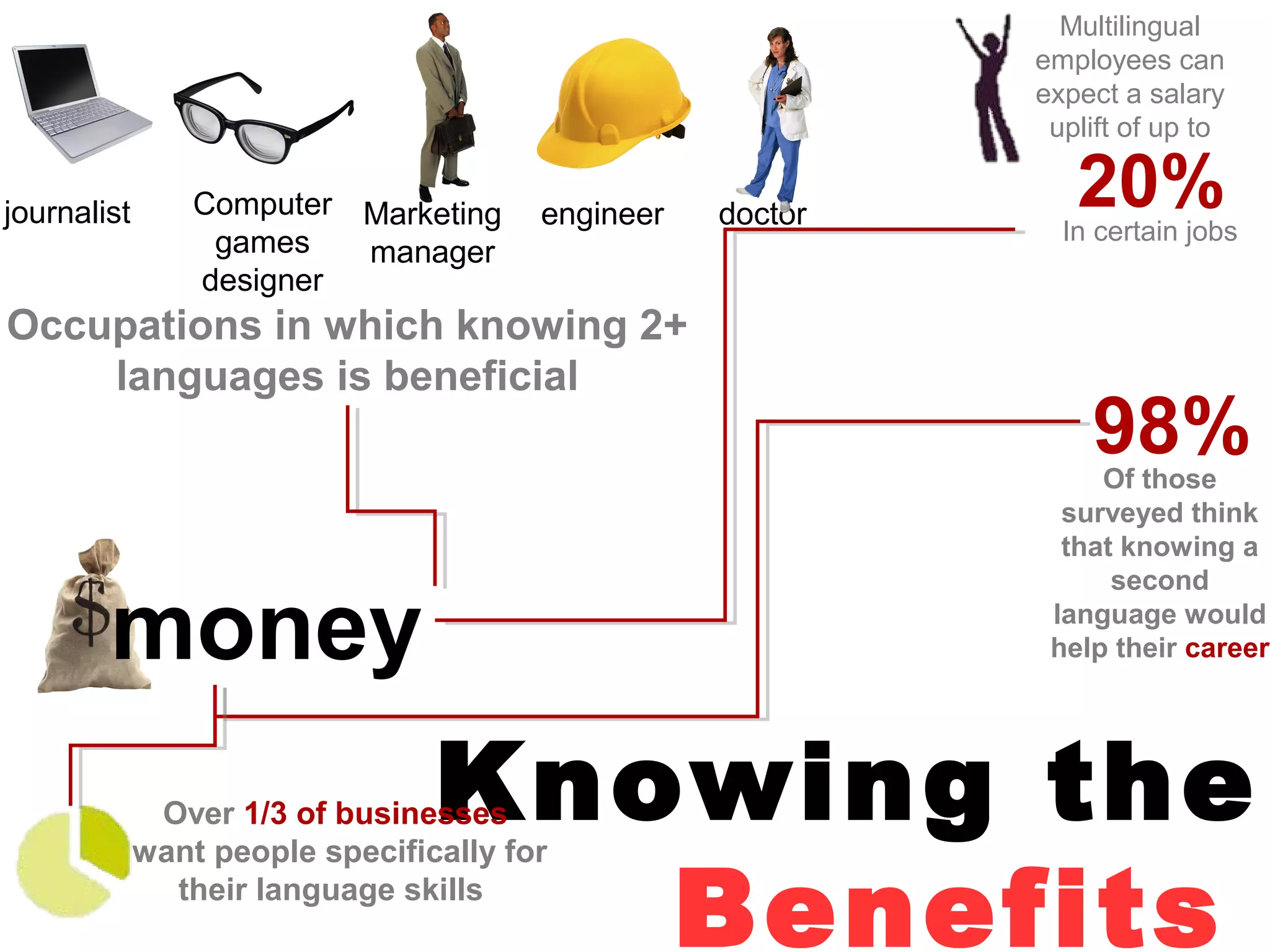
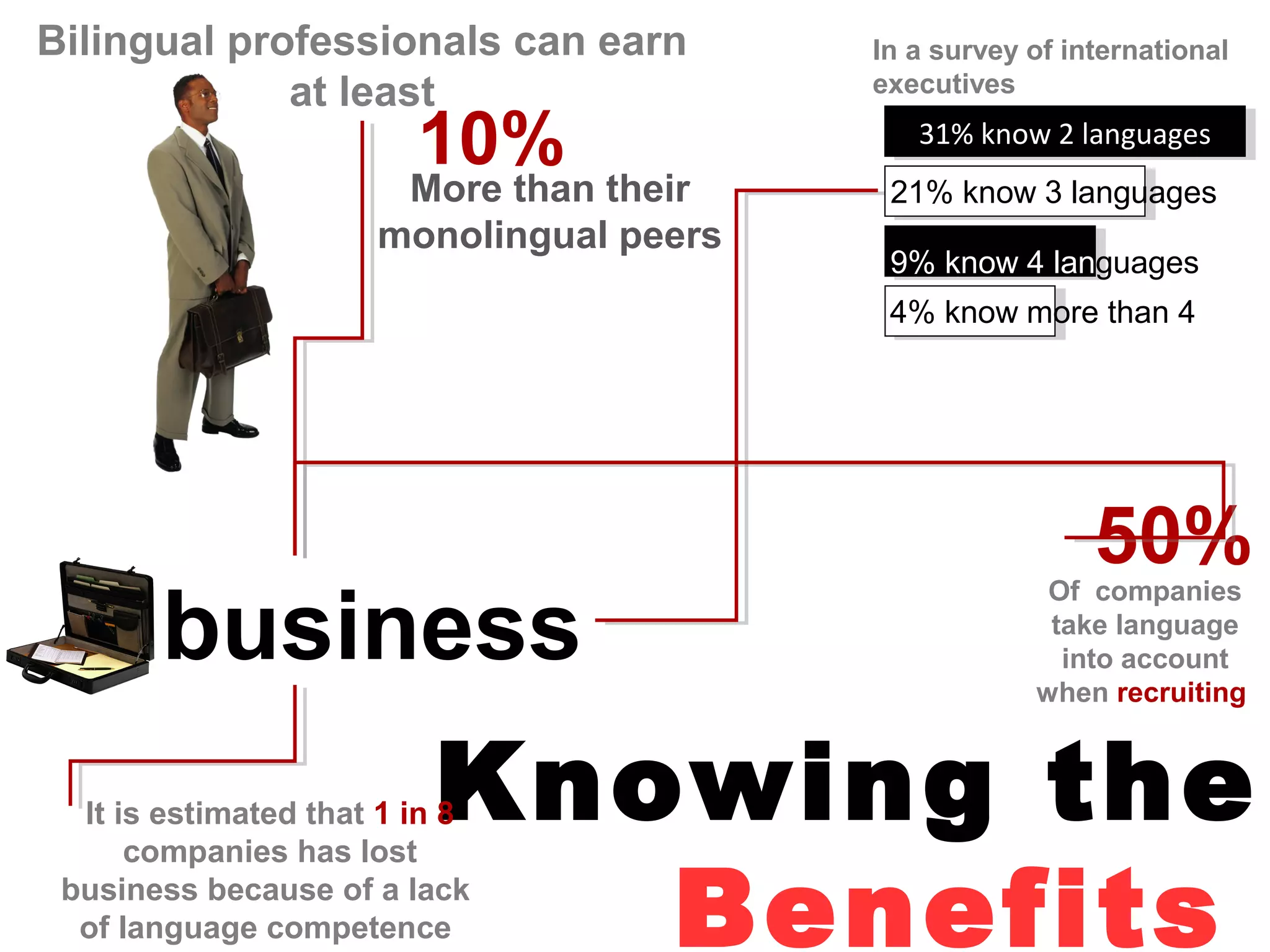
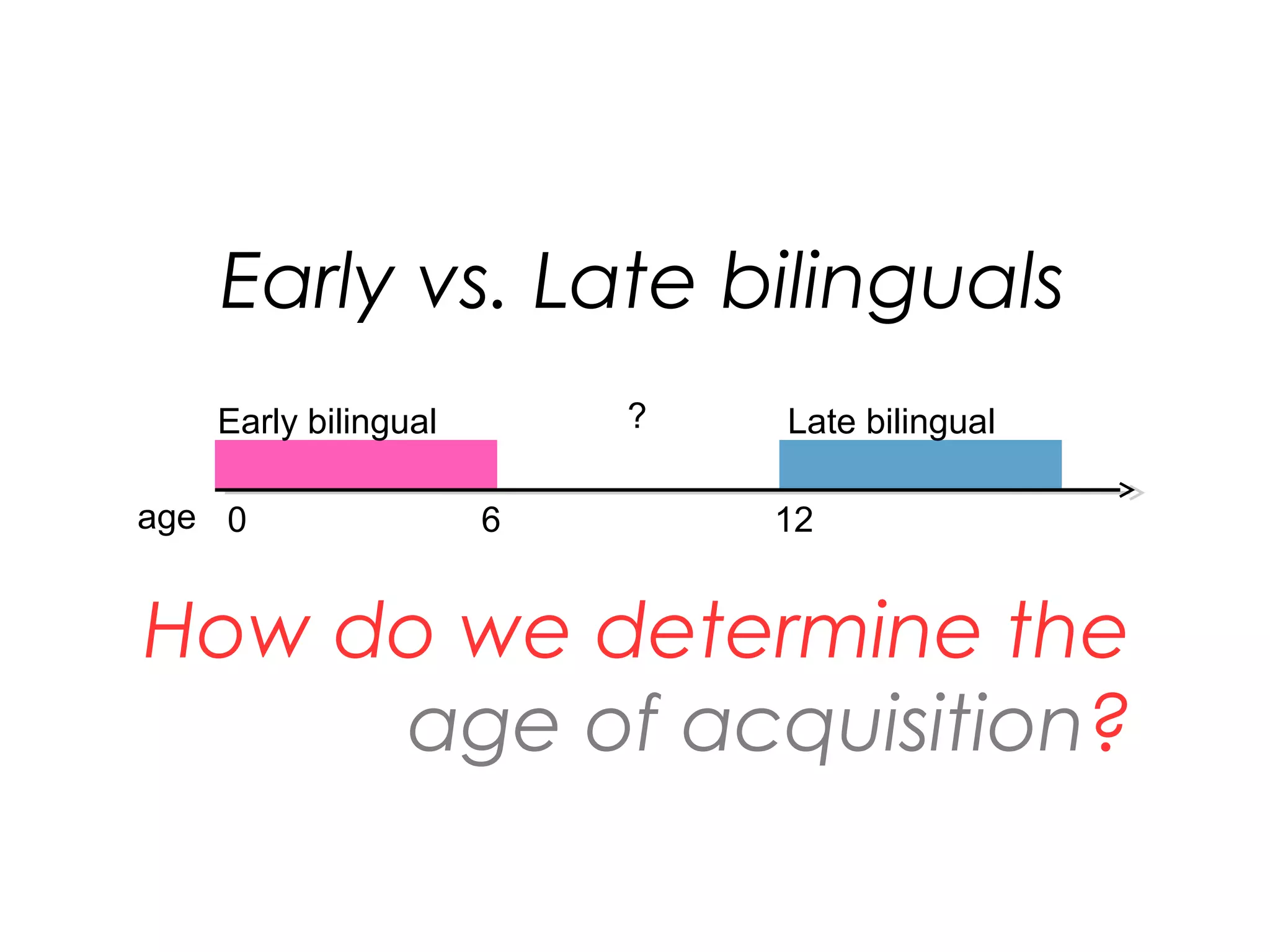
The document explores the advantages and nuances of bilingualism, highlighting its benefits in cognitive abilities, career opportunities, and social attractiveness. It categorizes types of bilingualism, including productive, receptive, compound, coordinate, and subordinate bilingualism, and discusses the differences between early and late bilinguals. Furthermore, it includes insights from studies on how bilingualism can enhance brain function and reduce the risks of cognitive impairments like Alzheimer's disease.


























![Language Mixing
Using this definition, and presuming that
English is the dominant language in the
following utterances:
“Is this what we are having for dinner
today? Sira naba tuktok mo? [Are you
crazy?] It’s not Saturday and I don’t eat
tuyo [smoked/dried fish] except on
Saturdays. It just doesn’t seem right!”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sesin1bilingualism-150826165923-lva1-app6892/75/Sesion-1-bilingualism-33-2048.jpg)







