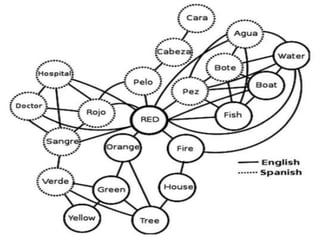
This document discusses different aspects of bilingual memory storage and representation. It describes three main models of bilingual memory organization:
1. Compound bilinguals store information about a concept at a shared conceptual level across languages but represent words independently in each language.
2. Coordinate bilinguals store each language separately, so the meanings of words and their translations are kept distinct.
3. Subordinate bilinguals initially link words in the second language to their first language translations, accessing meaning through the first language.
The models are presented as dynamic, and bilingual representation can change from subordinate to compound as proficiency increases. Concrete words like cognates may be stored compound while abstract words are more coordinate