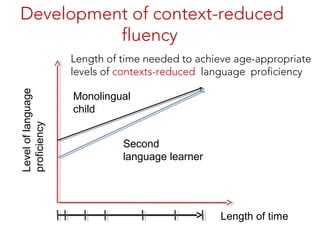
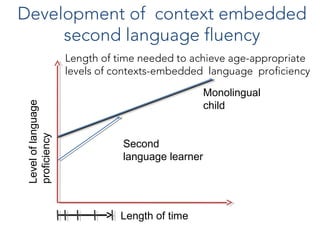
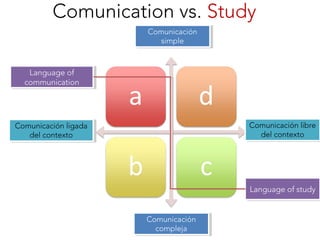
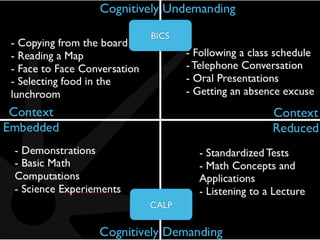
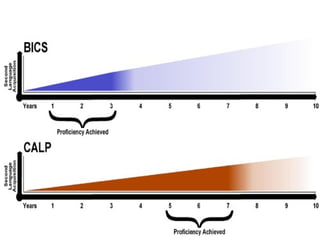
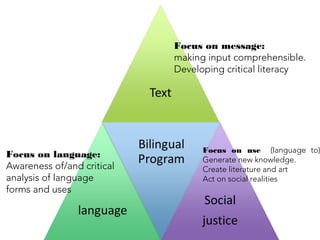
This document discusses Jim Cummins' theory of BICS and CALP. It distinguishes between context-embedded communication, which provides more contextual clues, and context-reduced communication, which provides fewer clues. It notes that acquiring basic interpersonal skills (BICS) in a second language takes less time than cognitive academic language proficiency (CALP). The Common Underlying Proficiency theory holds that proficiency in a first language supports proficiency in a second. Achieving academic proficiency takes longer for second language learners than for monolingual children. The document also discusses different types of language use and various approaches to bilingual education.