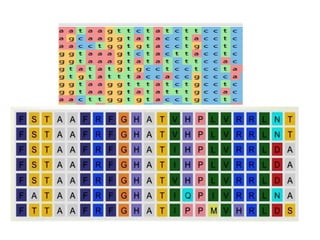
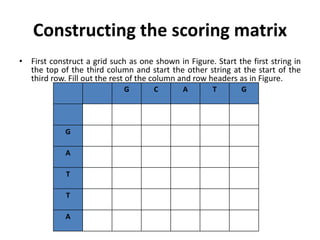
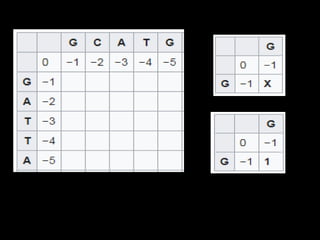
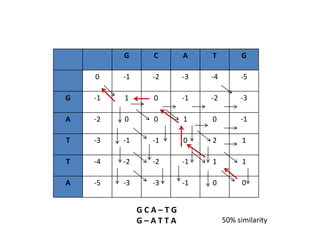
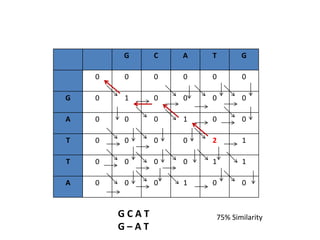
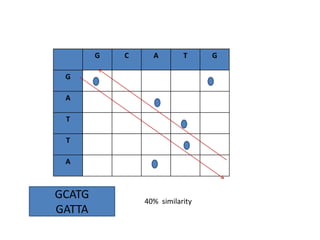
Multiple sequence alignment is a method to arrange DNA, RNA, or protein sequences to identify regions of similarity that may indicate functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships. Computational approaches like dynamic programming are needed to align lengthy or numerous sequences. Global alignment finds the optimal alignment over the full length of sequences using the Needleman-Wunsch algorithm. Local alignment identifies similar regions within divergent sequences using the Smith-Waterman algorithm. Dot plot matrices can also show sequence similarities but have limitations like noise and difficulty extracting information.