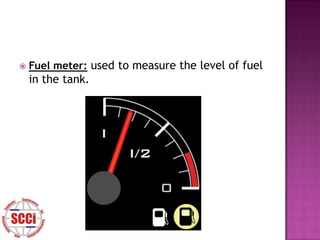
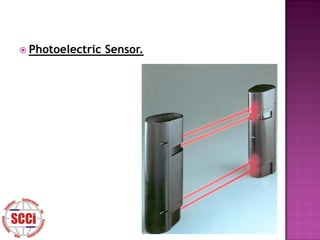
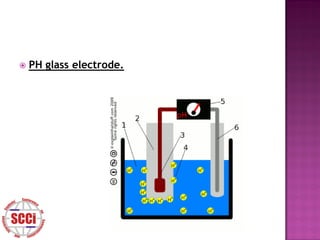
The document discusses sensors, defining them as devices that measure physical quantities and convert them into signals. It describes qualities of good sensors such as sensitivity and lack of influence on the measured property. Additionally, it covers common sensor types, errors, and measurement definitions like sensitivity, deviation, and resolution.