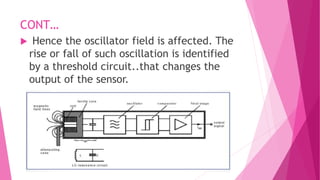
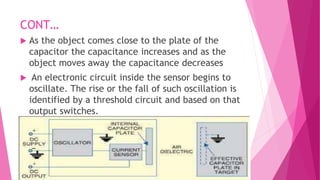
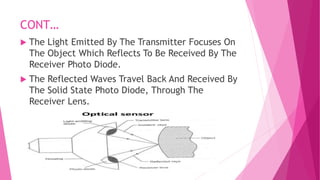
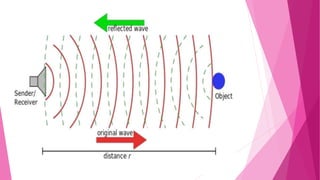
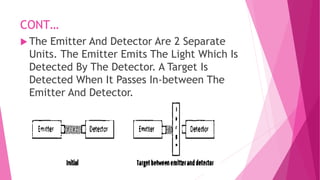
The document provides an overview of proximity sensors, including their definition, types (inductive, capacitive, ultrasonic, and optical), construction, working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It highlights how these sensors detect objects without physical contact and discusses their significance in various industries, including automotive and technology. Additionally, the role of proximity sensors in smartphones to prevent accidental touch events during calls is mentioned.