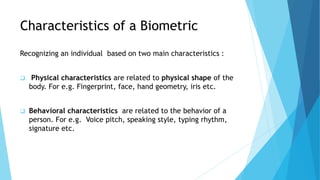
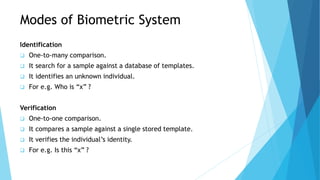
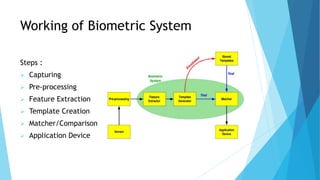
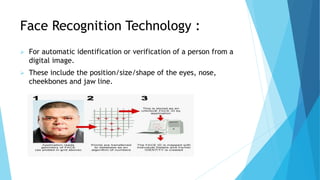
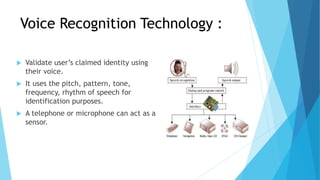
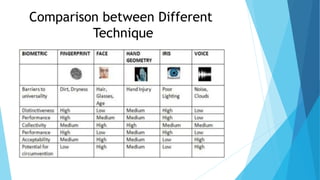
This document outlines a presentation on biometric authentication. It discusses authentication and its types, biometrics and why they are used, the characteristics and modes of biometric systems, different biometric techniques including fingerprint, face, iris, hand geometry and voice recognition, a comparison of techniques, applications and limitations. The working process of a biometric system including enrollment, authentication, capturing, pre-processing, feature extraction and matching is also summarized.