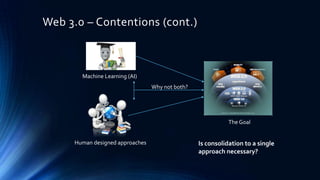
The document discusses Semantic Web (Web 3.0) and defines key concepts such as RDF, SPARQL, triple stores, and OWL. It notes that vendors have created platforms and tools to implement Semantic Web technologies. However, challenges remain such as dealing with vast and vague data, duplication, inconsistencies, and logical contradictions in ontologies. While consolidation to a single approach may not be necessary, machine learning and both human-designed and AI approaches could help address these challenges.