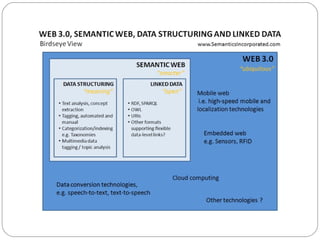
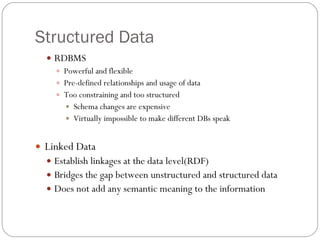
The document discusses the need for a Semantic Web to address information overload on the current web. It explains that the Semantic Web aims to understand the meaning behind web pages by embedding semantics through techniques like RDF and microformats. This will allow computers to better understand and filter information, leading to a smarter online experience for users where they spend less time searching and viewing irrelevant content. Approaches to building the Semantic Web include bottom-up annotation of existing web pages and top-down extraction of entities from pages using natural language processing tools. Linked Data is seen as a key enabler of the Semantic Web by establishing linkages between data.