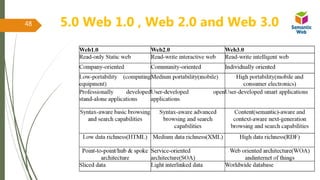
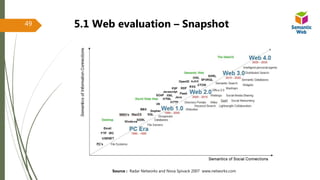
The document discusses the evolution of the web from Web 1.0, characterized by static pages and information sharing, to Web 2.0, which emphasizes user-generated content and collaboration, leading to Web 3.0, known as the semantic web that allows machines to understand and categorize data. It outlines the technologies and concepts that underpin each web generation, highlighting vulnerabilities and the importance of structured data for enhancing interaction. Furthermore, it introduces semantic frameworks and standards that facilitate data sharing and enable intelligent data processing.




















![HOW DO MACHINES KNOW WHAT DATA ?
Identity + Definition + Structure
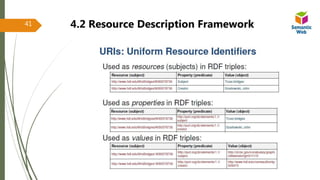
4.2 Resource Description Framework
Data – Is the set of information
Metadata – is "data [information] that provides
information about other data"
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticweb-santhoshnbasavarajappa-170607185659/85/Semantic-web-Santhosh-N-Basavarajappa-31-320.jpg)