Web 3.0 will be driven by technological changes and include developments like the semantic web, software and data as a service, artificial intelligence, and faster broadband connections. The semantic web aims to add a layer of meaning to web content by structuring data with identifiers, documents, and statements. This will enable computers to better understand the meaning of information and allow for more intelligent searching, personalized experiences, and integration across databases. Web 3.0 technologies like cloud computing and artificial intelligence also have the potential to improve software development and power new applications.
![By: Saurabh S Shendge [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-100420084146-phpapp02/75/Web-3-0-1-2048.jpg)
![What is web 3.0 ? Is a Range of Developments:~ Semantic web [meaning of data]. SaaS [Software as a Service]. DaaS[Data as a Service]. Artificial Intelligence. Faster broadband connection, always, anywhere.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-100420084146-phpapp02/85/Web-3-0-2-320.jpg)







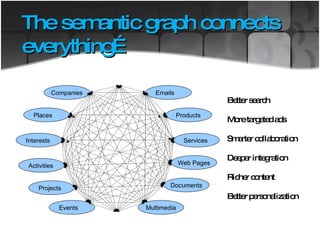





![Components that will make web a semantic web Identifiers: Uniform Resource Identifier [URI] Documents: Extensible Markup Language Statements: Resource Description Framework Provides a formal description of concepts , terms and relationships](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-100420084146-phpapp02/85/Web-3-0-19-320.jpg)



![Statements : Resource Description Framework [RDF] RDF is a markup language to describe information and resource available on web. Putting in RDF makes it possible to get it on web. Simple model based Designed to be read and understood by computers RDF statement is lot like simple sentence , except almost all words are URI. .Subject .Predicate .Object Ex.2. :~ “Aaron really likes Berner-Lee's weaving the web” <http://aaron.com> <http://love.example.org/terms/reallyLikes> <http://w3.org/People/berners-Lee/Weaving the web>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-100420084146-phpapp02/85/Web-3-0-23-320.jpg)
![RDF queries… Why use RDF rather than XML? Directly and unambiguously into Model Decentralized Generic parsers available Part of semantic web Do we use XML schema in conjunction with RDF? Language that restricts XML syntax RDF has its own Normalization Forms No [partially] possibly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-100420084146-phpapp02/85/Web-3-0-24-320.jpg)





