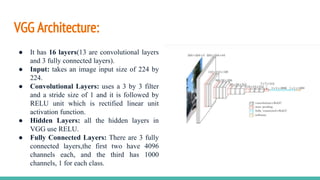
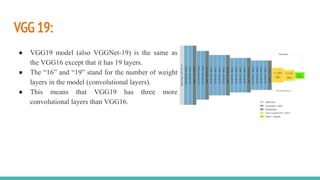
The document discusses the use of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for brain tumor detection, detailing the VGG architectures (VGG16 and VGG19) and their differences in layer count and accuracy. It explains data augmentation techniques for enhancing training datasets, such as geometric transformations and synthetic data generation, and outlines the steps involved in image preprocessing and model training. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and limitations of data augmentation, particularly in the medical field, and provides an overview of the implementation of the model using libraries like TensorFlow and Keras.