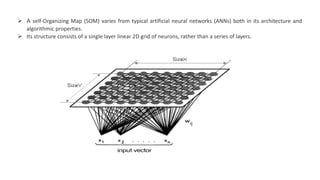
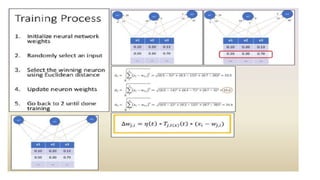
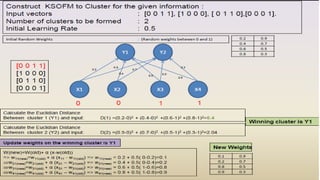
The Kohonen Self-Organizing Map (KSOM) is a type of neural network that uses a single-layer 2D grid of neurons organized through competitive learning instead of traditional error-correction learning. Each node in the grid is directly linked to the input vector and updates its weights based on the input without knowledge of neighboring nodes. The process involves initializing weights, selecting training examples, calculating winning vectors, and updating them to facilitate clustering of new examples.