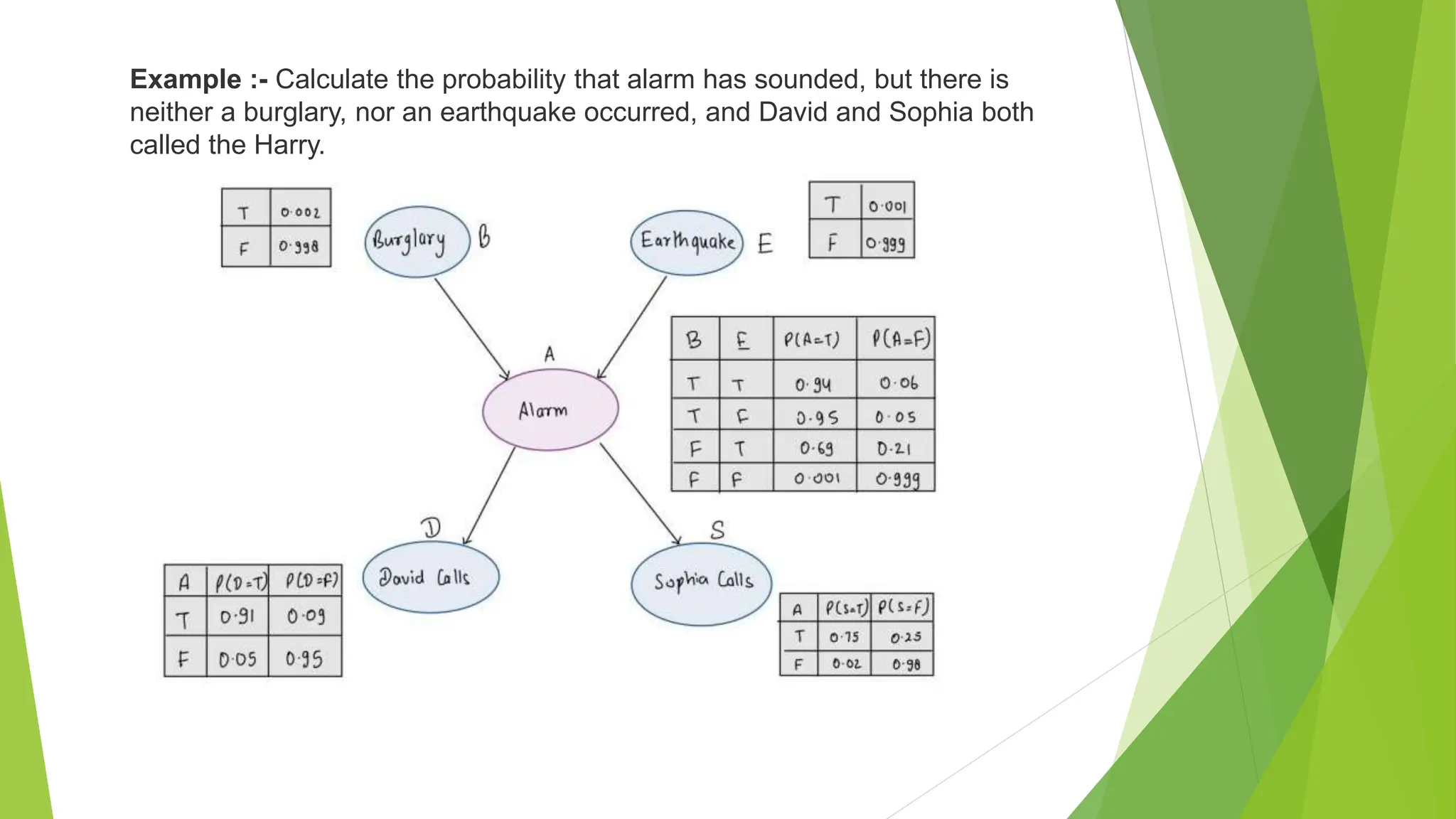
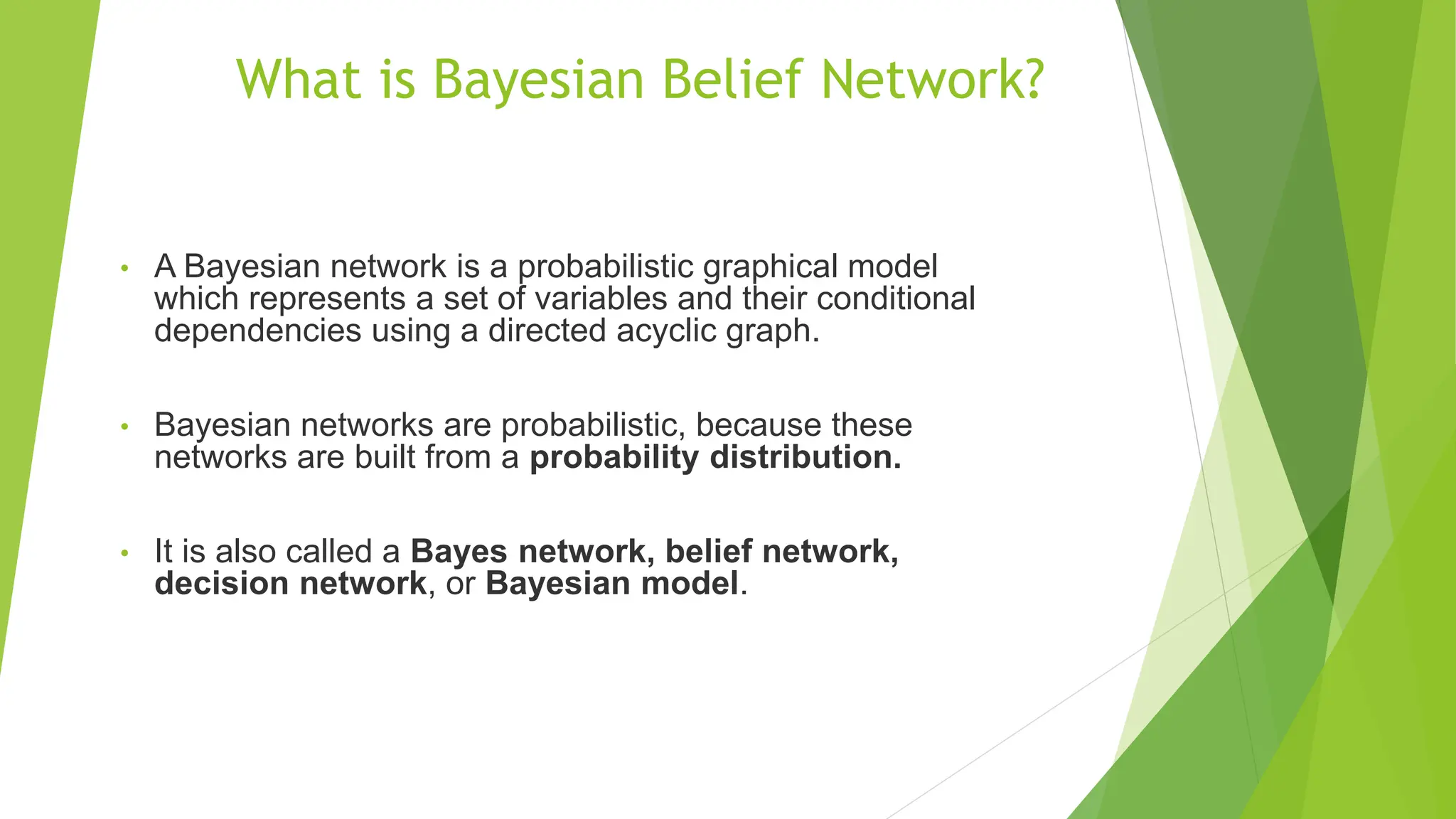
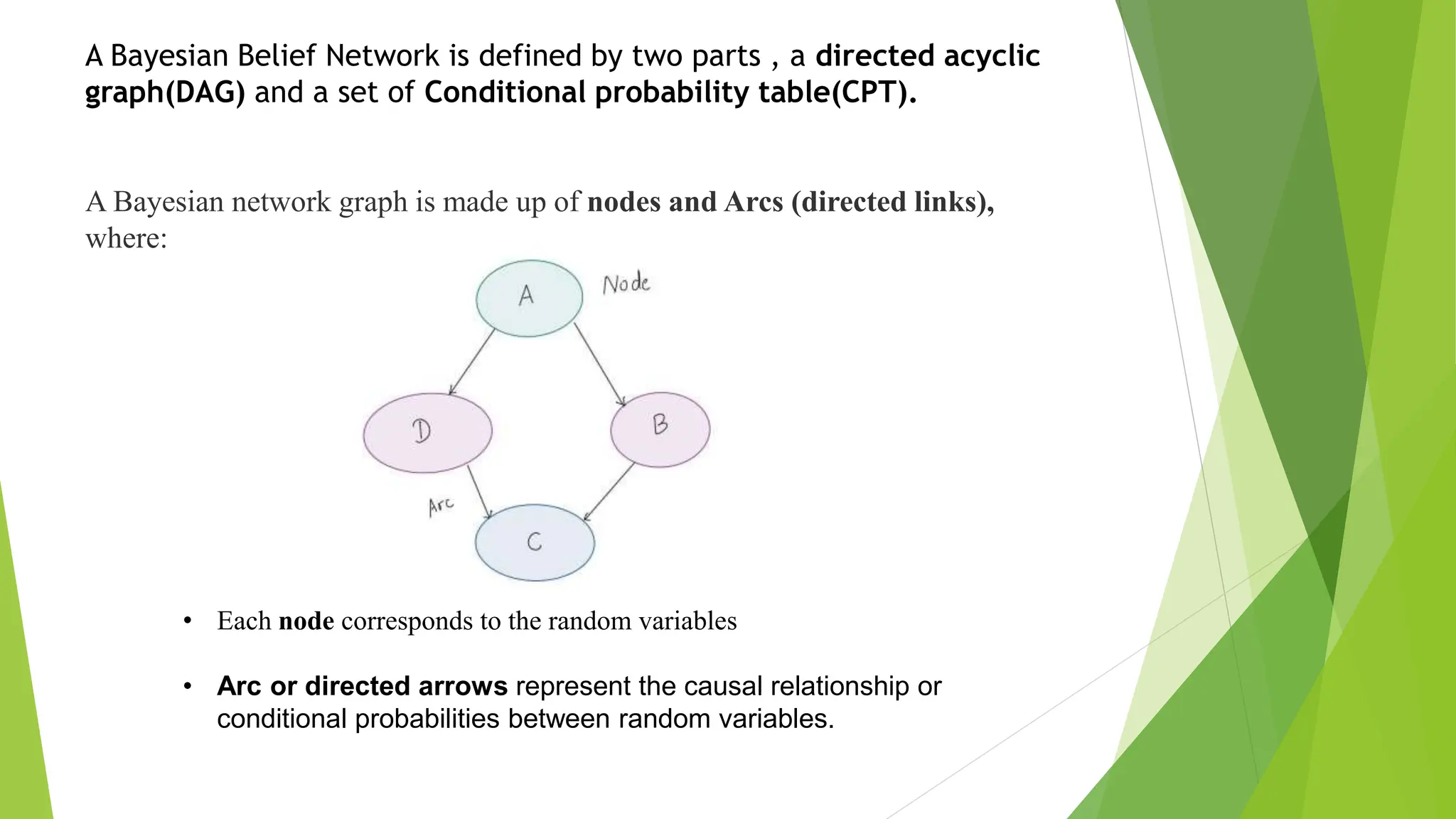
A Bayesian belief network is a probabilistic graphical model that represents variables and their conditional dependencies using a directed acyclic graph. It consists of nodes that represent random variables and directed arrows that represent causal relationships or conditional probabilities between the variables. The joint probability distribution of variables in a Bayesian belief network can be written as the product of conditional probabilities along a path in the graph. Bayesian belief networks have applications in spam filtering, image processing, biomonitoring, and modeling gene regulatory networks.

![Joint probability distribution:
If we have variables x1, x2, x3,....., xn, then the probabilities of a different
combination of x1, x2, x3.. xn, are known as Joint probability distribution.
P[x1, x2, x3,....., xn], it can be written as the following way in terms of the joint
probability distribution.
= P[x1| x2, x3,....., xn]P[x2, x3,....., xn]
= P[x1| x2, x3,....., xn]P[x2|x3,....., xn]....P[xn-1|xn]P[xn].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bayesianbeliefnetworkanditsapplications-231104035854-5e9b190c/75/Bayesian-Belief-Network-and-its-Applications-pptx-4-2048.jpg)